当前位置:网站首页>Redis design and Implementation (IV) | master-slave replication
Redis design and Implementation (IV) | master-slave replication
2022-06-30 08:22:00 【Just look, not like】
List of articles
Master slave copy
- summary
When the server uses SLAVEOF command , This server becomes the slave server of the target server
# 12315 Will become 6379 From the server
127.0.0.1:12315> SLAVEOF 127.0.0.1 6379
1. Old master-slave replication
- summary
There are generally two steps for old master-slave replication :
- Sync : Is to synchronize the slave server to the same state as the master server
- Command propagation : It means to modify the key value pair of the primary server , When the master is out of sync , Let the master-slave rewrite the operation that has been returning
1.1 Sync
- flow chart

1.2 Command propagation
- summary
When a command is executed on the master server, the master and slave data are inconsistent , The master server sends commands to the slave server , Let it carry out
1.3 Defects of old version replication
There are two situations
First reproduction : The slave server has never replicated any master servers , Or copy the current master service from the server, which is different from the previous master server , The replication work will go well
Copy after disconnection : After disconnection, the slave server will synchronize again , But from the main server RDB The file includes the commands from the beginning of the first synchronization to the successful disconnection and reconnection , This RDB The file is very large and repetitive , Synchronization will be very slow . In fact, the analysis shows that we do not need all the commands before disconnection , Only the command corresponding to the command from disconnection to reconnection is required RDB Just file it
sync Command is a very resource consuming operation
- Use BGSAVE Generate RDB Files are very expensive CPU Memory disk IO Resources for
- send out RDB File to slave server is very network consuming IO resources
- Load from server RDB The file will remain blocked until loading is complete
2. New master-slave replication
- summary
The new master-slave replication will sync Replace with psync, This command has two modes : Full resynchronization and partial resynchronization
- Complete resynchronization
Same as the first copy of the previous version
- Partial resynchronization
This is to solve the problem of synchronization RDB The file is too large , This improved direct transmission of commands during disconnection , From the server, it's done
2.1 Implementation of partial resynchronization
- summary
The implementation of this operation depends on the composition of three functions :
- Replication offset of the primary server (replication offset) And the assignment offset from the server
- Replication backlog buffer for primary server (replication backlog)
- Running the server ID(run ID)
- Copy offset
A copy offset is maintained on the master server and the slave server respectively , If the master server retransmits xx Command length of bytes , Then the offset corresponding to the master-slave server +xx; By comparing the offset of the master server and the slave server, we can know whether it is synchronized
When a slave server is disconnected from the master server , Reconnection sends its own offset , At this time, the offset comparison is different , In this case, the contents of the copy backlog buffer will be used to
- Copy backlog buffer
Every time the master server executes a command, it writes the command to the replication backlog buffer , The master server maintains this zone for the synchronization of the slave server after disconnection , The buffer has a fixed size FIFO The formation of the queue , When a fixed size is set, the primary server writes data every time , When the capacity reaches the limit, it will go out of the queue
According to the above figure, we can see that the storage is based on the offset , When the disconnected slave server reconnects , There are two cases when you send your own offset to the master server
- The offset is within the range of this buffer , Then it is good to directly return the command from offset to reconnection
- If the offset is not within this range , The update is too fast , Then perform a full resynchronization
Adjust the size of this buffer as needed
- Server running ID
Both the slave and master servers are assigned a unique run ID, Restart will reassign this value , this ID You can perform master-slave verification , When synchronizing from the server for the first time , The primary server's ID Store in your own server , When reconnecting
- So if you store from the server ID And the primary server ID The unanimous statement is the previous , Try partial resynchronization
- If it's not consistent , It means that it is not the former , Then complete resynchronization
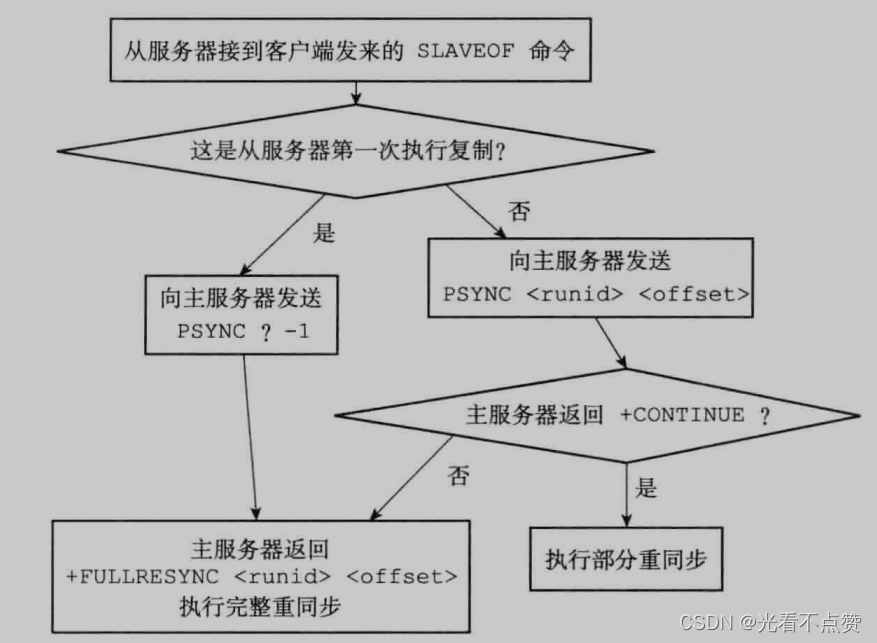
2.2 PSYNC Implementation of commands
Use PSYNC There are generally two situations
- The slave server has never replicated any master servers , Or used
SLAVEOF no onecommand , Then the slave server will send a new service to the master serverPSYNC ? -1command , Please complete the complete resynchronization with the main service - If you have copied from the server , When you start a new copy, you will save your last run ID And the copied offset is sent to the primary server , According to these two values, the master server will have about three strategies
- reply
+FULLPSYNC <runid><offset>, In other words, a full resynchronization will be performed , This will be saved from the server runid, And send it to me offset To initialize your own offset- reply
+CONTINUE, Represents a partial resynchronization , Just wait to resend the missing data and update your own offset- reply
-ERR, The primary server version is lower than 2.8, I can't recognize this PSYNC command
2.3 Implementation of replication
- Set the address and port of the master server
send out SLAVEOF command , At the same time, the main server's IP And the port number are saved in their own
serverObject Medium materHost and masterPort
- Establish a socket connection
After execution SLAVEOF command , Establish a socket connection .
- send out ping command :
- Check whether the read / write status is normal
- Check if the master server can process command requests
The master server received ping The command will be replied after receiving ping command , Start replying , There are about three responses :
- Return a command reply , But the reply content cannot be read from the server , That means the network is in a bad state , Will disconnect and reconnect
- The master server returned an error to the slave server , Indicates that this connection cannot be processed at this time , Then the server will be disconnected and reconnected
- return pong, Indicates that the synchronization work can be started
- Authentication
If the slave server is set masterAuth, Will authenticate , If there is no setting, you can proceed directly to the next work ; The corresponding primary server has a requirepass Set up , These two settings will cause the following situations
- The master server is not set , Never set , Copy the work directly to the next step
- Both master and slave servers are set , Then compare the password sent from the server with the password set by the master server , If correct, continue , Otherwise return to invalid password
- Master settings , Never set , Returns an error
- Master not set , From settings , Returns an error
- Send port information
After the last step , From the server
REPLCONF listening-port <port-number>, Sends the listening port number of the slave to the master server ; The master server will record the changed port number in the corresponding client state of the slave server after receiving it
- Sync
Sent from the slave server to the master server PSYNC command , Perform synchronous operation ; Before performing a synchronization operation , Only the slave server is the client of the master server , But after the synchronization , The master server also becomes the client of the slave server ; Because of this , The master server can change the state of the slave server by issuing a command , This is also the basis of command propagation from the master server to the slave server
- Command propagation
After the synchronization is completed, it will enter the command propagation state , The master server will always send write commands to the slave server so that synchronization can be maintained
2.4 The heartbeat detection
- summary
By default, the slave server client sends commands to the master server every second
REPLCONF ACK <replication_offset>, among offset Is the current offset , Send this ACK There are three functions
- Detect the network connection status of the master-slave server : If the master server does not receive a message from the slave server within one second ACK, That means there is a problem with the connection , Then the master server will send INFO replication command , Among the list parameters listed are lag One column is the time from last time to this time
- Aided implementation min-slaves Options
- Detection command lost
- Aided implementation min-slaves configuration option
Redis Of
min-slaves-to-writeandmin-slaves-max-lagThese two parameters can prevent the master server from executing write commands without security , For example, the first parameter is 3, The second parameter is 10, Then the slave server is less than 3 individual , Or three slave server delays (lag) Greater than or equal to 10 second , Then the master server will refuse to write the command
- Detection command lost
Due to network fluctuation , The command from the master server to the slave server may be lost halfway , When sending... From the server ACK Command will also send its own offset value , When the master server finds a discrepancy with itself, it will look for the offset sent from the server in the replication backlog buffer as the starting point , End with your own offset , Send this segment to the slave server for synchronization
Note that the steps to detect command loss are very similar to the steps and principles of partial resynchronization , The only difference is that the master and slave are not disconnected when the command is lost , Partial resynchronization is performed after disconnection and reconnection
边栏推荐
- C # listbox how to get the selected content (search many invalid articles)
- Sword finger offer II 076 The kth largest number in the array (use heap to solve TOPK problem)
- 【NVMe2.0b 14-6】Format NVM、Keep Alive、Lockdown command
- Construction of energy conservation supervision system for campus buildings of ankery University
- Experiment 3 remote control
- MIME类型大全
- MySQL cannot connect to the intranet database
- Applet uses QR code plug-in
- Cesium learning notes (II) uploading data using rest API
- Wechat applet reports errors using vant web app
猜你喜欢

2021-05-06

一次cpu 跌底排查

Redis设计与实现(二)| 数据库(删除策略&过期淘汰策略)

Is it difficult to jump job ByteDance? With these skills, you can easily pass

【NVMe2.0b 14-1】Abort、Asynchronous Event Request、Capacity Management command

Redis设计与实现(七)| 发布 & 订阅
![[nvme2.0b 14-7] set features (Part 1)](/img/0d/c26ae2475ae69291d83b4096ea942b.png)
[nvme2.0b 14-7] set features (Part 1)

Deploy the cow like customer network project on the ECS

微信公众号第三方平台开发,零基础入门。想学我教你啊

【NVMe2.0b 14-5】Firmware Download/Commit command
随机推荐
layer.open 当传值为数组或值太长时处理方法
TP5 set direct download file
Cesium learning notes (II) uploading data using rest API
Qqquickpainteditem implements graffiti program drawing board
[nvme2.0b 14-7] set features (Part 1)
Be careful of this hole in transmittable thread local
Transformer architecture understanding
Oracle expansion table space installed in docker
Wechat applet reports errors using vant web app
Gilbert Strang's course notes on linear algebra - Lesson 1
Using typera+picgo to realize automatic uploading of markdown document pictures
Want to change careers, but don't know what to do? This article is written for you who are confused
【JUC系列】Fork/Join框架之概览
String and underlying character types of go data type
【NVMe2.0b 14-5】Firmware Download/Commit command
Game 280 problem2: minimum operands to turn an array into an alternating array
电流探头电路分析
MIME type Encyclopedia
C # about Net cognition
Unit Test