当前位置:网站首页>[deep learning]: day 1 of pytorch introduction to project practice: data operation and automatic derivation
[deep learning]: day 1 of pytorch introduction to project practice: data operation and automatic derivation
2022-07-28 16:57:00 【JOJO's data analysis Adventure】
【 Deep learning 】:PyTorch: Data manipulation and automatic derivation
- This article is included in 【 Deep learning 】:《PyTorch Introduction to project practice 》 special column , This column mainly records how to use
PyTorchRealize deep learning notes , Try to keep updating every week , You are welcome to subscribe ! - Personal home page :JoJo Data analysis adventure
- Personal introduction : I'm reading statistics in my senior year , At present, Baoyan has reached statistical top3 Colleges and universities continue to study for Postgraduates in Statistics
- If it helps you , welcome
Focus on、give the thumbs-up、Collection、subscribespecial column
Reference material : This column focuses on bathing God 《 Hands-on deep learning 》 For learning materials , Take notes of your study , Limited ability , If there is a mistake , Welcome to correct . At the same time, Musen uploaded teaching videos and teaching materials , You can go to study .
- video : Hands-on deep learning
- The teaching material : Hands-on deep learning
List of articles
1. Data manipulation
# Import torch
import torch
import numpy as np
1.1 Tensor creation
x = torch.arange(12)
y = np.arange(12)
x,y
(tensor([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]),
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]))
tensor( tensor ) Represents an array of numeric values , There can be multiple dimensions , similar numpy Medium n Dimension group , So many n Some methods of dimension group also have tensor , Now let's test what numpy The method in can be used here . To understand numpy You can read this article :
Python Data analysis big killer Numpy Detailed explanation
# Look at shapes
x.shape
torch.Size([12])
# Check the quantity and length
len(x)
12
It can also be used reshape Function to convert an array
x = x.reshape(3,4)
x
tensor([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])
zeros Create all for 0 The elements of
x = torch.zeros(3,4)
x
tensor([[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.]])
ones Create all for 1 The elements of
x = torch.ones(3,4)
x
tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.]])
eye Create diagonal matrix
l = torch.eye(5)
l
tensor([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]])
ones_like Create all shapes that are consistent 1 Element matrix of
x = torch.ones_like(l)
x
tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]])
randn Create a random matrix
x = torch.randn((2,4))
x
tensor([[-0.2102, -1.5580, -1.0650, -0.2689],
[-0.5349, 0.6057, 0.7164, 0.4334]])
There can be multiple dimensions , As shown below , Create a two-dimensional tensor, among 0 Represents the outer floor ,1 Represents an internal layer
x = torch.tensor([[1,1,1,1],[1,2,3,4],[4,3,2,1]])
x
tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[4, 3, 2, 1]])
Tensors can also be related to numpy The arrays of are converted to each other , The details are as follows
y = x.numpy()
type(x),type(y)
(torch.Tensor, numpy.ndarray)
1.2 Basic operation
After creating the tensor , We are interested in how to calculate these tensors . Like multidimensional arrays , Tensors can also perform some basic operations , The specific code is as follows
x = torch.tensor([1,2,3,4])
y = torch.tensor([2,3,4,5])
x+y,x-y,x*y,x/y
(tensor([3, 5, 7, 9]),
tensor([-1, -1, -1, -1]),
tensor([ 2, 6, 12, 20]),
tensor([0.5000, 0.6667, 0.7500, 0.8000]))
It can be seen that and numpy Array is the same , It is also an operation on elements . Let's look at the summation operation
x = torch.arange(12).reshape(3,4)
x.sum(dim=0)# Sum up by line
tensor([12, 15, 18, 21])
y = np.arange(12).reshape((3,4))
y.sum(axis=0)# Sum up by line
array([12, 15, 18, 21])
As can be seen from the above ,tensor and array Can be operated by row or case , But in torch in , Appoint dim Parameters ,numpy in , Appoint axis Parameters
1.3 Broadcast mechanism
Our previous numpy Broadcast mechanism has been introduced in , When two arrays have different latitudes , You can copy elements appropriately to expand elements of one or two latitudes , So let's see torch Does China also support broadcast mechanism
x = torch.tensor([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
y = torch.tensor([1,1,1])
z = x + y
print('x:',x)
print('y:',y)
print('z:',z)
x: tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
y: tensor([1, 1, 1])
z: tensor([[2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7]])
Through the above code, we can find ,torch Broadcast mechanism is also supported in , and numpy The use in is basically the same
1.4 Index and slice
Next, let's see how to treat tensor The results were sliced and indexed , Usage and numpy Almost the same
x
tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
# Select the data of the first and second columns
x[:,[0,1]]
tensor([[1, 2],
[4, 5]])
2. Automatic differentiation ( Derivation )
Linear algebra, you can see my numpy article , There is a specific introduction , Let's focus on how to find the derivative .
In deep learning , For many layers of neural networks , Artificial derivation is a very complicated thing , Therefore, it is very important to find the derivative automatically work Things about
Here we assume to be right y = x T x y=x^Tx y=xTx To find the derivative . First, we initialize a x value
x = torch.arange(4.0)
x
tensor([0., 1., 2., 3.])
Now, before we calculate the gradient , You need a place to store the gradient , Like when we're doing some cycles , Need an empty list to store content . Let's see how to use requires_grad_ To store
x.requires_grad_(True)
print(x.grad)# The default is None, Equivalent to an empty list at this time
None
Let's calculate y
y = torch.dot(x,x)
y
tensor(14., grad_fn=<DotBackward0>)
# The gradient is calculated by the back propagation function
y.backward(retain_graph=False)
x.grad
tensor([0., 2., 4., 6.])
Here, by default ,pytorch Will save the gradient , So when we need to recalculate the gradient , The first step is to initialize , Use grad.zero_
x.grad.zero_()
# Recalculate y=x Gradient of
y = x.sum()
y.backward()
x.grad
tensor([1., 1., 1., 1.])
Above, we all put y Become a scalar and find the gradient , If y It's not scalar ? You can put y Convert summation to scalar
x.grad.zero_()
y = x*x
y.sum().backward()
x.grad
tensor([0., 2., 4., 6.])
2.3 Separate differential calculation
Here, God Mu gives such a scene ,y It's about x Function of , and z It's about y and x Function of , Before we get to z seek x Partial derivative time , We hope that y As a constant . This method is very effective in some complex neural network models , Concrete adoption detach() Realization , take u by y The constant
The specific code is as follows :
x.grad.zero_()# Initialization gradient
y = x * x#y Yes x Function of
u = y.detach()# take y Separation treatment
z = u * x#z Yes x Function of
z.sum().backward()# Find the gradient through the back propagation function
x.grad
tensor([0., 1., 4., 9.])
What are the above results ? According to the law of derivation :
d z d x = u \frac{dz}{dx} = u dxdz=u
Let's take a look at u How much is the
u
tensor([0., 1., 4., 9.])
2.4 Control flow gradient calculation
One advantage of using automatic differentiation is , When our function is piecewise , It will also automatically calculate the corresponding gradient . Let's look at a case of gradient calculation of linear control flow :
def f(a):
if a.sum() > 0:
b = a
else:
b = 100 * a
return b
First, we define a linear piecewise function , As shown above :
f ( a ) = { a a.sum()>0 100 ∗ a else f(a) = \begin{cases} a& \text{a.sum()>0}\\ 100*a& \text{else} \end{cases} f(a)={ a100∗aa.sum()>0else
Now let's look at how to do automatic derivation
a = torch.randn(12, requires_grad=True)
d = f(a)
d.backward(torch.ones_like(a))
a.grad == d / a
tensor([True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True])
Practice and summary
1. Redesign an example of finding the gradient of control flow , Run and analyze the results .
In the case above , Mu Shen gave an example of a linear piecewise function , Suppose it's not linear , Let's assume that a piecewise function is like this
f ( x ) = { x norm(x)>10 x 2 else f(x) = \begin{cases} x& \text{norm(x)>10}\\ x^2& \text{else} \end{cases} f(x)={ xx2norm(x)>10else
The specific control flow code is as follows :
def f(x):
if x.norm() > 10:
y = x
else:
y = x*x
return y
x = torch.randn(12,requires_grad=True)
y = f(x)
y.backward(torch.ones_like(x))
x.grad
tensor([ 0.3074, -2.0289, 0.5950, 1.2339, -2.2543, 0.5834, -2.3040, -1.9097,
0.9255, 1.6837, -1.4464, -0.3131])
2. Draw differential diagram
send f ( x ) = s i n ( x ) f(x)=sin(x) f(x)=sin(x), draw f ( x ) f(x) f(x) and d f ( x ) d x \frac{df(x)}{dx} dxdf(x) Image , The latter does not use f ′ ( x ) = c o s ( x ) f'(x)=cos(x) f′(x)=cos(x), Here we also need to use matplotlib, If you want to know something, you can read my article :
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
x = torch.linspace(-2*torch.pi, 2*torch.pi, 100)
x.requires_grad_(True)
y = torch.sin(x)
y.sum().backward()
y = torch.detach(y)
plt.plot(y,'r--',label='$sin(x)$')
plt.plot(x.grad,'g',label='$cos(x)$')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.grid()
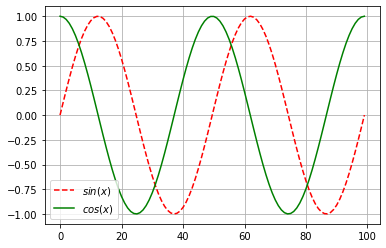
This is the introduction of this chapter , If it helps you , Please do more thumb up 、 Collection 、 Comment on 、 Focus on supporting !!
边栏推荐
- 综合设计一个OPPE主页--页面的售后服务
- Signal shielding and processing
- 在AD中添加差分对及连线
- MD5加密验证
- Re13: read the paper gender and racial stereotype detection in legal opinion word embeddings
- MD5 encryption verification
- [learn slam from scratch] publish the coordinate system transformation relationship to topic TF
- 负整数及浮点数的二进制表示
- Analysis of echo service model in the first six chapters of unp
- ticdc同步数据怎么设置只同步指定的库?
猜你喜欢

Leetcode daily practice - the number of digits in the offer 56 array of the sword finger

Ansa secondary development - two methods of drawing the middle surface

【深度学习】:《PyTorch入门到项目实战》第一天:数据操作和自动求导

Re11:读论文 EPM Legal Judgment Prediction via Event Extraction with Constraints

Alibaba cloud MSE supports go language traffic protection

阿里大哥教你如何正确认识关于标准IO缓冲区的问题

College students participated in six Star Education PHP training and found jobs with salaries far higher than those of their peers

Probability theory and mathematical statistics Chapter 1

RE14: reading paper illsi interpretable low resource legal decision making

关于 CMS 垃圾回收器,你真的懂了吗?
随机推荐
ABAQUS GUI interface solves the problem of Chinese garbled code (plug-in Chinese garbled code is also applicable)
Im im development optimization improves connection success rate, speed, etc
Binary representation of negative integers and floating point numbers
QT designer for QT learning
Ansa secondary development - two methods of drawing the middle surface
Nowcode- learn to delete duplicate elements in the linked list (detailed explanation)
First day of QT study
结构化设计的概要与原理--模块化
【指针内功修炼】字符指针 + 指针数组 + 数组指针 + 指针参数(一)
有趣的 Kotlin 0x07:Composition
获取时间戳的三种方法的效率比较
NoSQL introduction practice notes I
Implementation of transfer business
Some opinions on bug handling
Cluster construction and use of redis5
Interesting kotlin 0x08:what am I
Tcp/ip related
给定正整数N、M,均介于1~10 ^ 9之间,N <= M,找出两者之间(含N、M)的位数为偶数的数有多少个
关于Bug处理的一些看法
ticdc同步数据怎么设置只同步指定的库?