当前位置:网站首页>JUnit unit test
JUnit unit test
2022-06-26 16:33:00 【&volume】
Catalog
1. Test categories :
(1) Black box testing :
No need to write code , Enter value for , See if the program outputs the expected value
Most of them are using black box testing , Is to test according to the code you write
(2) White box testing :
Need to write code , Pay attention to the specific execution process of the program
2.Junit Use :
Junit It's a white box test
(1)@Test Use
1. Define a class
First define the method in the class
package cn.junit;
/*
* Calculator class
* */
public class Calcuator {
/*
* Add
*/
public int add(int a,int b)
{
return a+b;
}
/*
Subtraction
*/
public int sub(int a,int b)
{
return a-b;
}
}
2. Define another test class

package cn.test;
import cn.junit.Calcuator;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CalculatorTest {
/*
test add Method
*/
@Test
public void testAdd()
{
// Create calculator objects
Calcuator c=new Calcuator();
// Calling method
int ad = c.add(1, 2);
System.out.println(ad);
}
}
Just added @Test Because if there is no guide bag, it will become popular
Click on the small light bulb next to it 
Will automatically guide the package 
3. Assertion operations
We often don't output them during the test process , And will assert
Assert.assertEquals( Assertion value , Output value );
package cn.test;
import cn.junit.Calcuator;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CalculatorTest {
/*
test add Method
*/
@Test
public void testAdd()
{
// Create calculator objects
Calcuator c=new Calcuator();
// Calling method
int ad = c.add(1, 2);
Assert.assertEquals(3,ad);
// System.out.println(ad);
}
}
If the two values are different , Will pop up and make mistakes
Example of assertion failure :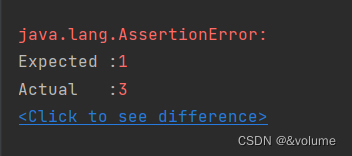
Example of assertion success :
(2)@Before and @After
[email protected]
@Before To keep the code simple , De duplication operation
@Before At every @Test Block the code that must be executed before annotation , Conduct @Before annotation
Comments will be made in @Test Execute before
[email protected]
@After Existence and @Before It's the same , To keep the code simple , To repeat the operation
@After Is at the end of each @Test Block the code that will be executed after annotation , Conduct @After annotation
Comments will be made in @Test Automatically execute after annotation
3. Code testing
package cn.test;
import cn.junit.Calcuator;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CalculatorTest {
@Before
public void testinit()
{
System.out.println("init...");
}
@After
public void close()
{
System.out.println("close.....");
}
/*
test add Method
*/
@Test
public void testAdd()
{
// Create calculator objects
Calcuator c=new Calcuator();
// Calling method
int ad = c.add(1, 2);
//Assert.assertEquals(3,ad);
System.out.println("testadd In progress ");
// System.out.println(ad);
}
/*
* test sub Method
* */
@Test
public void testsub()
{
Calcuator c=new Calcuator();
int sub = c.sub(1, 2);
System.out.println("testsub In progress ");
//System.out.println(sub);
}
}
4. test result
(1) test add Method

(2) test sub Method

3.Junit summary
(1). When defining a test method, the return value should be void type
(2). The parameter list is empty
(3). The verdict If red appears, the test fails
If green appears, the test is successful
(4). Generally, we use assertion operations to process the results
Assert.assertEquals( Assertion value , Output value );
(5)[email protected] Decorating methods are executed before testing methods
(6)[email protected] The decorated method will be executed after the test method is executed ( Whether the test is successful or not, it will be executed );
边栏推荐
- Net based on girdview control to delete and edit row data
- Dialogue with the senior management of Chang'an Mazda, new products will be released in Q4, and space and intelligence will lead the Japanese system
- TCP拥塞控制详解 | 1. 概述
- 1-12Vmware新增SSH功能
- 油田勘探问题
- Redis的ACID
- Scala 基礎 (二):變量和數據類型
- JS tutorial using electron JS build native desktop application ping pong game
- Develop operator based on kubebuilder (for getting started)
- R language generalized linear model function GLM, GLM function to build logistic regression model, analyze whether the model is over discrete, and use the ratio of residual deviation and residual degr
猜你喜欢
![[understanding of opportunity -31]: Guiguzi - Daoyu [x ī] Crisis is the coexistence of danger and opportunity](/img/e8/9c5f1658a252c3c80503b5021917f6.jpg)
[understanding of opportunity -31]: Guiguzi - Daoyu [x ī] Crisis is the coexistence of danger and opportunity

大话领域驱动设计——表示层及其他

基於Kubebuilder開發Operator(入門使用)

SAP OData 开发教程 - 从入门到提高(包含 SEGW, RAP 和 CDP)

用Attention和微调BERT进行自然语言推断-PyTorch

TCP拥塞控制详解 | 1. 概述

清华“神奇药水”登Nature:逆转干细胞分化,比诺奖成果更进一步,网友:不靠精子卵子就能创造生命了?!...
Practice of federal learning in Tencent micro vision advertising

The first batch in the industry! Tencent cloud security and privacy computing products based on angel powerfl passed CFCA evaluation

【力扣刷题】单调栈:84. 柱状图中最大的矩形
随机推荐
day10每日3题(1):逐步求和得到正数的最小值
Redis Guide (8): principle and implementation of Qianfan Jingfa distributed lock
【蓝桥杯集训100题】scratch辨别质数合数 蓝桥杯scratch比赛专项预测编程题 集训模拟练习题第15题
How can I get the stock account opening discount link? Is online account opening safe?
《软件工程》期末重点复习笔记
Arduino uno + DS1302 simple time acquisition and serial port printing
网页课程设计大作业——华山旅游网
(DFS search) acwing 2005 horseshoe
Redis 迁移(操作流程建议)1
【力扣刷题】11.盛最多水的容器//42.接雨水
STM32F103C8T6实现呼吸灯代码
Solidus Labs欢迎香港前金融创新主管赵嘉丽担任战略顾问
Mono 的一些实例方法
Which position does Anxin securities rank? Is it safe to open an account?
Notes on key review of software engineering at the end of the term
Failed to upload hyperf framework using alicloud OSS
基于Kubebuilder开发Operator(入门使用)
Codeforces Round #802 (Div. 2)
【小5聊】毕业8年,一直在追梦的路上
"C language" question set of ⑩
