当前位置:网站首页>Lex and yacc based lexical analyzer + parser
Lex and yacc based lexical analyzer + parser
2022-07-04 18:58:00 【biyezuopinvip】
Resource download address :https://download.csdn.net/download/sheziqiong/85895082
Resource download address :https://download.csdn.net/download/sheziqiong/85895082
C-- Compiler implementation
One 、 Instructions
Running environment :Ubuntu 14.04 Ubuntu 16.04
Please refer to Section 2 and section 3 for the morphology and syntax supported by this compiler
Decompress the package Run the command
unzip compiler.zip
Enter the folder and run the command
./compiler test.cmm
among test.cmm It can be replaced with other files
If you make a mistake , Then output the error line number and output the syntax tree
Derivation of the production used to generate the syntax tree / Protocol sequence
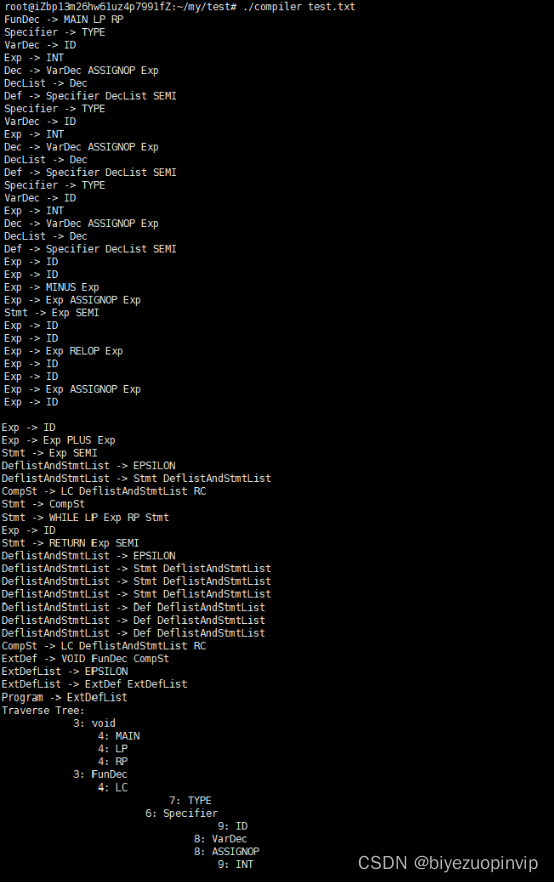
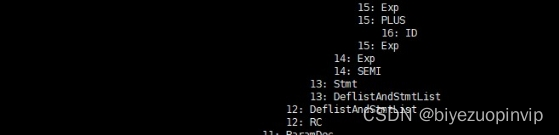
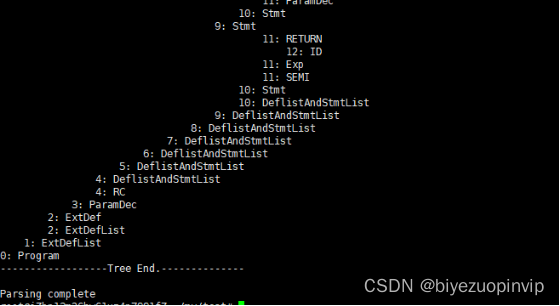
Two 、 Lexical analysis
1. summary
The function of lexical analyzer is to read the source program and generate lexical units , And filter out comments and whitespace . Lexical analysis in the project uses lex .
2. Word element type description
INT
INT Represents an integer constant . A decimal integer consists of 0~9 Ten figures make up , There is no space between numbers The delimiter .
except 0 outside , The first digit of decimal integer is not 0.
Octal or hexadecimal form . Octal integer consists of 0-7 It consists of eight numbers and is represented by numbers 0 start . Hexadecimal integers consist of 0-9、a-f It consists of sixteen numbers and is represented by 0x start .
FLOAT
FLOAT Represents a floating-point constant . A floating-point number consists of a string of numbers and a decimal point , Numbers must appear before and after the decimal point .
Floating point constants can also be expressed in exponential form . Floating point numbers in exponential form must include Radix 、 Index sign and index three part , And the three parts appear in turn . The base part consists of a series of numbers (0~9) And a decimal point , The decimal point can be Now anywhere in the string ; The exponent sign is E or e; The index part consists of a band - Or a string of numbers without ,- have to Must appear before the number string .
ID
ID Represents an identifier . The identifier consists of upper and lower case letters 、 Numbers and underscores , But it must be in letters or underlined start .


3、 ... and 、 Syntax analysis
1. summary
The parser receives the token string provided by the lexical analyzer , Check whether the token string can be used by c-- The prescribed grammar produces , And prompt the error message .
2. Rule of grammar
And C The difference of language :
- The program does not have to meet the requirement that there is only one main The condition of a function
- There is no need to declare functions before using
- for The first expression of the loop , Declaring local variables is not supported
3. Syntax tree output implementation
Use a multi fork tree and a single linked list to construct and output a syntax tree
Implementation of multi fork tree : The main function of multi fork tree is to construct each sub syntax tree ( In units of non terminators )
type: Node type .type=0, Represents the intermediate node ,type=1, Represents a leaf node data: Node values ( Terminator or or nonterminal )
length: Number of child nodes
leaves Is an array of node pointers , Length fixed to 9, The number of valid values is length individual , Store points to Pointer to the child node
// Tree node
typedef struct TreeNode{
int type;
int length;
struct TreeNode\* leaves[9]; char\* data;
}TreeNode, \*Tree;
Multi tree operation
For terminators , Create a leaf node , The parameter is the value of the terminator . Default type=1 ,length=0, Leaf node pointers all point to null
// Create leaf nodes
Tree createLeaf(char\* rootData){
int i = 0;
Tree T = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode)); if (T != NULL){
T -> type = 1;
T -> data = rootData; T -> length = 0;
for (i = 0 ; i < 9 ; i++){
T -> leaves[i] = NULL;
}
}else{
exit(-1);
}
return T;
}
For non terminators , Create an intermediate node , And connect the corresponding child nodes . The parameter is a non terminal value 、 Child node Pointer array 、 Number of child nodes ,type = 0
// Link leaf node and root node
Tree createTree(char\* root, TreeNode\*\* leaves, int length){
int i = 0;
Tree T = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode)); if (T == NULL){
exit(-1);
}else{
T -> type = 0;
T -> data = root;
T -> length = length;
for (i = 0 ; i < 9 ; i++){
T -> leaves[i] = leaves[i];
}
}
}
Linked list implementation : The main function of linked list is to analyze according to grammar ( Bottom up ) Sequentially store the terminator sub syntax tree , To connect Connect all sub syntax trees
data: Pointer to the root node of a grammar tree
next: Point to the next node in the linked list
// List nodes
typedef struct ListNode{
struct TreeNode\* data; struct ListNode\* next;
}ListNode, \*LinkList;
List operation :
Create a linked list , Return to header node (data It's empty ,next Point to the first node )
// Create the chain header node ( Point to the first node ) LinkList createLinkList(){
ListNode\* L = (ListNode\*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode)); if ( L == NULL ){
exit(-1);
}
L -> next = NULL; return L;
}
Head insertion , Return the inserted chain header node
// Insert node into the chain header
LinkList linkListInset(LinkList L, TreeNode\* newNode){
ListNode\* temp = (ListNode\*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode)); if ( temp == NULL ){
exit(-1);
}
temp -> data = newNode; temp -> next = L -> next; L -> next = temp;
return L;
}
Construct syntax tree
Declare the variables used in the construction process
LinkList list = NULL; // Chain header node
LinkList head = NULL; // The first node in the linked list
Tree T; // The root node of the sub syntax tree
TreeNode\* child[9]; // Array of child node pointers
stay main Function to initialize it
list = createLinkList();
T = NULL;
for (i = 0 ; i < 9 ; i++){
child[i] = NULL;
}
For all production , Add the following semantics
ExtDef: Specifier ExtDecList SEMI
{
printf("ExtDef -> Specifier ExtDefList SEMI\n"); // Output production head = list -> next; // initialization head
alloc(child); // Allocate space for the array of child node pointers
child[0] = (head->next) -> data; // For production right-hand non terminator , Give it the root node pointer of the sub syntax tree stored in the linked list , The first non terminator appears after the linked list
child[1] = head -> data;
child[2] = createLeaf("SEMI"); // For production right terminator , Create leaf nodes T = createTree("ExtDef", child, 3); // Join the sub syntax tree
list -> next = (head -> next) -> next; // Remove the sub syntax tree corresponding to the non terminator at the right end of this production from the linked list
linkListInset(list, T); // Insert the newly constructed sub syntax tree
}
among :
// by child Allocate memory space
void alloc(TreeNode\*\* child){
int i;
for (i = 0 ; i < 9 ; i++){
child[i] = (TreeNode\*)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode)); if(child[i] == NULL){
exit(-1);
}
}
}
Output syntax tree
Define global variables level, Store the number of layers of the current tree ( from 0 Start )
Post order traversal syntax tree
// After the sequence traversal
void traverseTree(Tree T, int level){
int i = 0;
if (T == NULL){
return;
}else{
if (T -> type == 1){
// Leaf node
if (T -> data != ""){
//epsilon No output
for ( i = 0 ; i < level ; i++){
// According to the number of layers , Output 4\* Several spaces in the layer
printf("%-4s", " ");
}
printf("%d: %s\n", level, T -> data); // Output " The layer number : value "
}
}else{
// Intermediate nodes
for (i = 0 ; i < T -> length ; i++){
// Recursively traverse all child nodes , The layer number +1
traverseTree(T -> leaves[i], level + 1);
}
// Then variable the intermediate node
if (T -> data != ""){
for ( i = 0 ; i < level ; i++){
printf("%-4s", " ");
}
printf("%d: %s\n", level, T -> data);
}
}
}
}
Production of initial symbols , After constructing the semantics of the syntax tree , Add the following semantics
head = list -> next; // Reinitialize head
T = head -> data; //T It is the root node of the current start symbol sub syntax tree , That is, the root node of the syntax tree
printf("Traverse Tree: \n");
level = 0;
traverseTree(T, level); // Take the root node as 0 layer , Traverse
printf(" Tree End. \n");
Resource download address :https://download.csdn.net/download/sheziqiong/85895082
Resource download address :https://download.csdn.net/download/sheziqiong/85895082
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

ByteDance dev better technology salon was successfully held, and we joined hands with Huatai to share our experience in improving the efficiency of web research and development
一直以为做报表只能用EXCEL和PPT,直到我看到了这套模板(附模板)
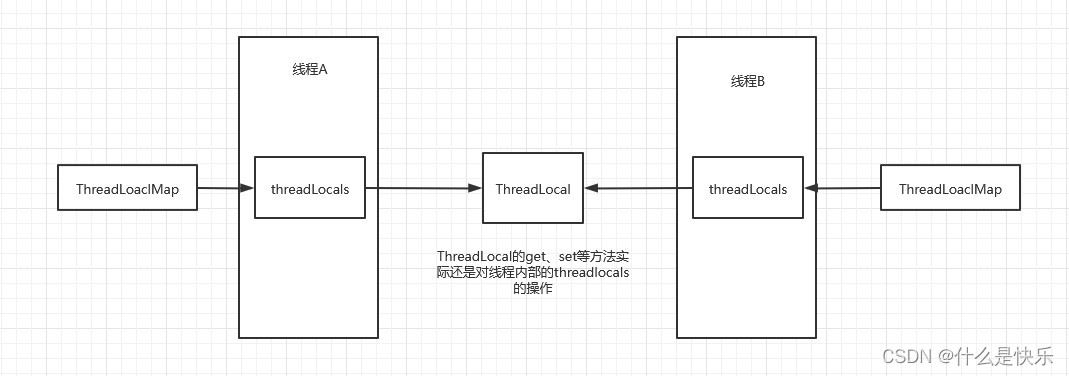
ThreadLocal原理与使用

Halcon template matching
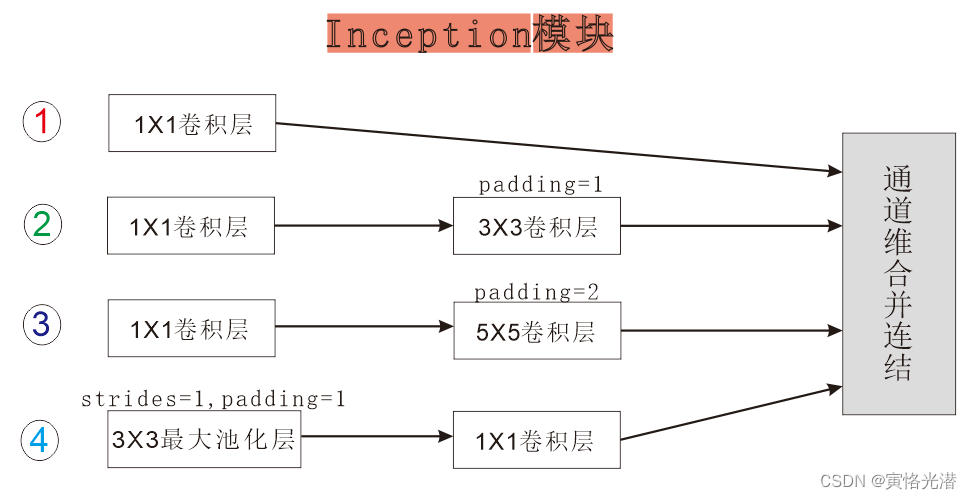
Mxnet implementation of googlenet (parallel connection network)
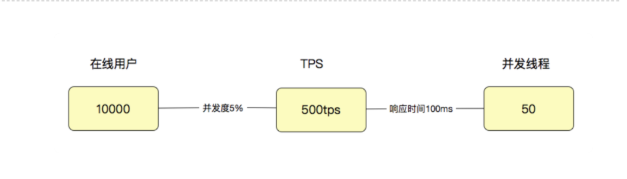
Load test practice of pingcode performance test
![[go ~ 0 to 1] read, write and create files on the sixth day](/img/cb/b6785ad7d7c7df786f718892a0c058.png)
[go ~ 0 to 1] read, write and create files on the sixth day
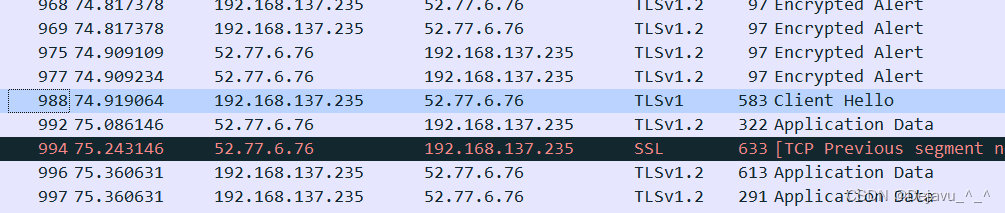
Wireshark抓包TLS协议栏显示版本不一致问题

同事悄悄告诉我,飞书通知还能这样玩
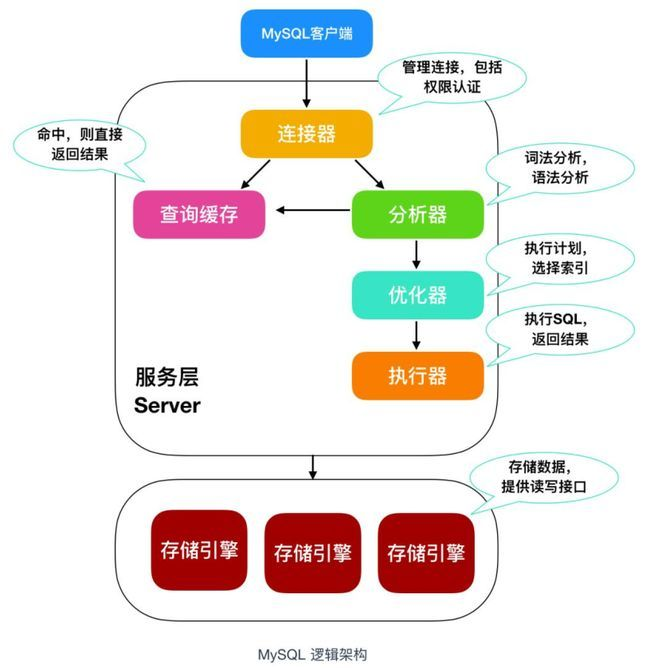
How is the entered query SQL statement executed?
随机推荐
How to open an account is safe,
Scala基础教程--18--集合(二)
Li Kou brush question diary /day7/2022.6.29
2022年字节跳动日常实习面经(抖音)
【211】go 处理excel的库的详细文档
. Net ORM framework hisql practice - Chapter 2 - using hisql to realize menu management (add, delete, modify and check)
Learning path PHP -- phpstudy "hosts file does not exist or is blocked from opening" when creating the project
力扣刷题日记/day6/6.28
android使用SQLiteOpenHelper闪退
大厂面试总结大全二
谷粒商城(一)
【机器学习的数学基础】(一)线性代数(Linear Algebra)(上+)
File processing examples of fopen, FREAD, fwrite, fseek
Scala基础教程--13--函数进阶
vbs或vbe如何修改图标
如何使用 wget 和 curl 下载文件
How to modify icons in VBS or VBE
【2022年江西省研究生数学建模】冰壶运动 思路分析及代码实现
一直以为做报表只能用EXCEL和PPT,直到我看到了这套模板(附模板)
Scala基础教程--20--Akka