当前位置:网站首页>File processing examples of fopen, FREAD, fwrite, fseek
File processing examples of fopen, FREAD, fwrite, fseek
2022-07-04 18:24:00 【Hua Weiyun】
Like any operating system , File processing is Linux Core concepts in . Any system programmer will regard it as him / One of her initial programming tasks is learning . This aspect of programming involves system files .
Through file processing , You can create system files 、 modify 、 Delete and other operations . In this paper , Try to introduce very basic file processing .
File processing function
In this paper , We will introduce the following functions commonly used in file processing :
fopen()
FILE *fopen(const char *path, const char *mode);fopen() Function to open a file and put I/O Flow and its association . This function has two arguments . The first parameter is a pointer to the string containing the file name to open , The second parameter is the mode to open the file . The pattern can be :
- 'r' : Open a text file to read . The stream is at the beginning of the file .
- 'r+' : Turn on read write . The stream is at the beginning of the file .
- 'w' : Truncate the file to zero length or create a text file for writing . The stream is at the beginning of the file .
- 'w+' : Turn on read write . If the file doesn't exist , Then create the file , Otherwise, cut it off . The stream is at the beginning of the file .
- 'a' : Open for attachment ( Write... At the end of the file ). If the file doesn't exist , Then create the file . The stream is at the end of the file .
- 'a+' : Open for reading and attaching ( Write... At the end of the file ). If the file doesn't exist , Then create the file . The initial file position read is at the beginning of the file , But the output is always appended to the end of the file .
fopen() The function returns... On success FILE Flow pointer , And when it fails, it returns NULL.
fread() and fwrite()
size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream);size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream);fread/fwrite The function is used from fopen Function to open the file / Write data . These functions take three parameters . The first parameter is for reading / Pointer to the buffer where data is written . Read / The written data adopts “nmemb” Element form , Every “size” Byte length .
If it works ,fread/fwrite Return from fopen Function to actually read from the stream opened / Bytes written . If you fail , Returns a smaller number of bytes ( Then request to read / Write ).
fseek()
int fseek(FILE *stream, long offset, int wherece);fseek() The function is used to set the file location indicator of the stream to the new location . This function takes three arguments . The first parameter is fopen() Function return FILE Flow pointer . The second parameter 'offset' Tell us the number of bytes to find . The third parameter “whence” Tell me where to look “offset” Number of bytes .wherece The available values of are SEEK_SET、SEEK_CUR or SEEK_END. These three values ( According to the order ) Describes the beginning of the file 、 Current location and end of file .
success , This function returns 0, Otherwise return to -1.
fclose()
int fclose(FILE *fp);fclose() Function first refreshes fopen() Open stream , Then close the underlying descriptor . After successful completion , This function returns 0, Otherwise, it returns to the end of the file (eof). In the event of failure , If you further access the stream , Then the behavior remains undefined .
Code
#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>#define SIZE 1#define NUMELEM 5int main(void){ FILE* fd = NULL; char buff[100]; memset(buff,0,sizeof(buff)); fd = fopen("test.txt","rw+"); if(NULL == fd) { printf("\n fopen() Error!!!\n"); return 1; } printf("\n File opened successfully through fopen()\n"); if(SIZE*NUMELEM != fread(buff,SIZE,NUMELEM,fd)) { printf("\n fread() failed\n"); return 1; } printf("\n Some bytes successfully read through fread()\n"); printf("\n The bytes read are [%s]\n",buff); if(0 != fseek(fd,11,SEEK_CUR)) { printf("\n fseek() failed\n"); return 1; } printf("\n fseek() successful\n"); if(SIZE*NUMELEM != fwrite(buff,SIZE,strlen(buff),fd)) { printf("\n fwrite() failed\n"); return 1; } printf("\n fwrite() successful, data written to text file\n"); fclose(fd); printf("\n File stream closed through fclose()\n"); return 0;}The above code assumes that you have a test file “test.txt” Put it in the same location where the executable is running .
The content of the original document is :
$ cat test.txthello everybodyNow? , Run code :
$ ./fileHandling File opened successfully through fopen() Some bytes successfully read through fread() The bytes read are [hello] fseek() successful fwrite() successful, data written to text file File stream closed through fclose()Check the file again test.txt The content of . As shown below , The contents of the file have been modified .
$ cat test.txthello everybodyhello边栏推荐
- Superscalar processor design yaoyongbin Chapter 7 register rename excerpt
- 12 - explore the underlying principles of IOS | runtime [isa details, class structure, method cache | t]
- Russia arena data releases PostgreSQL based products
- [proteus simulation] printf debugging output example based on VSM serial port
- 力扣刷题日记/day3/2022.6.25
- 【系统盘转回U盘】记录系统盘转回U盘的操作
- 【每日一题】871. 最低加油次数
- Numpy 的仿制 2
- 【Hot100】32. Longest valid bracket
- 被忽视的问题:测试环境配置管理
猜你喜欢
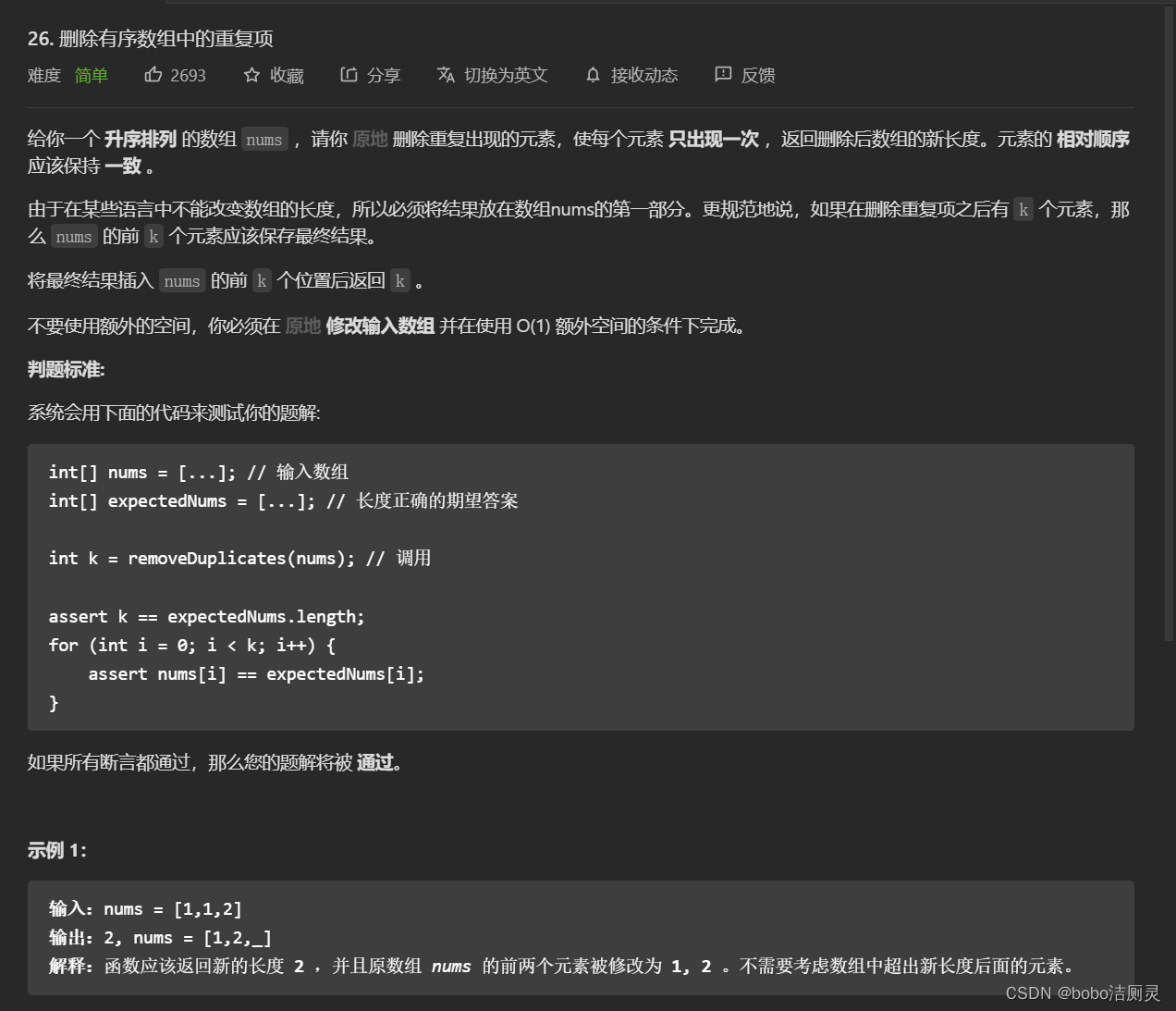
力扣刷题日记/day6/6.28
【Go语言刷题篇】Go完结篇|函数、结构体、接口、错误入门学习
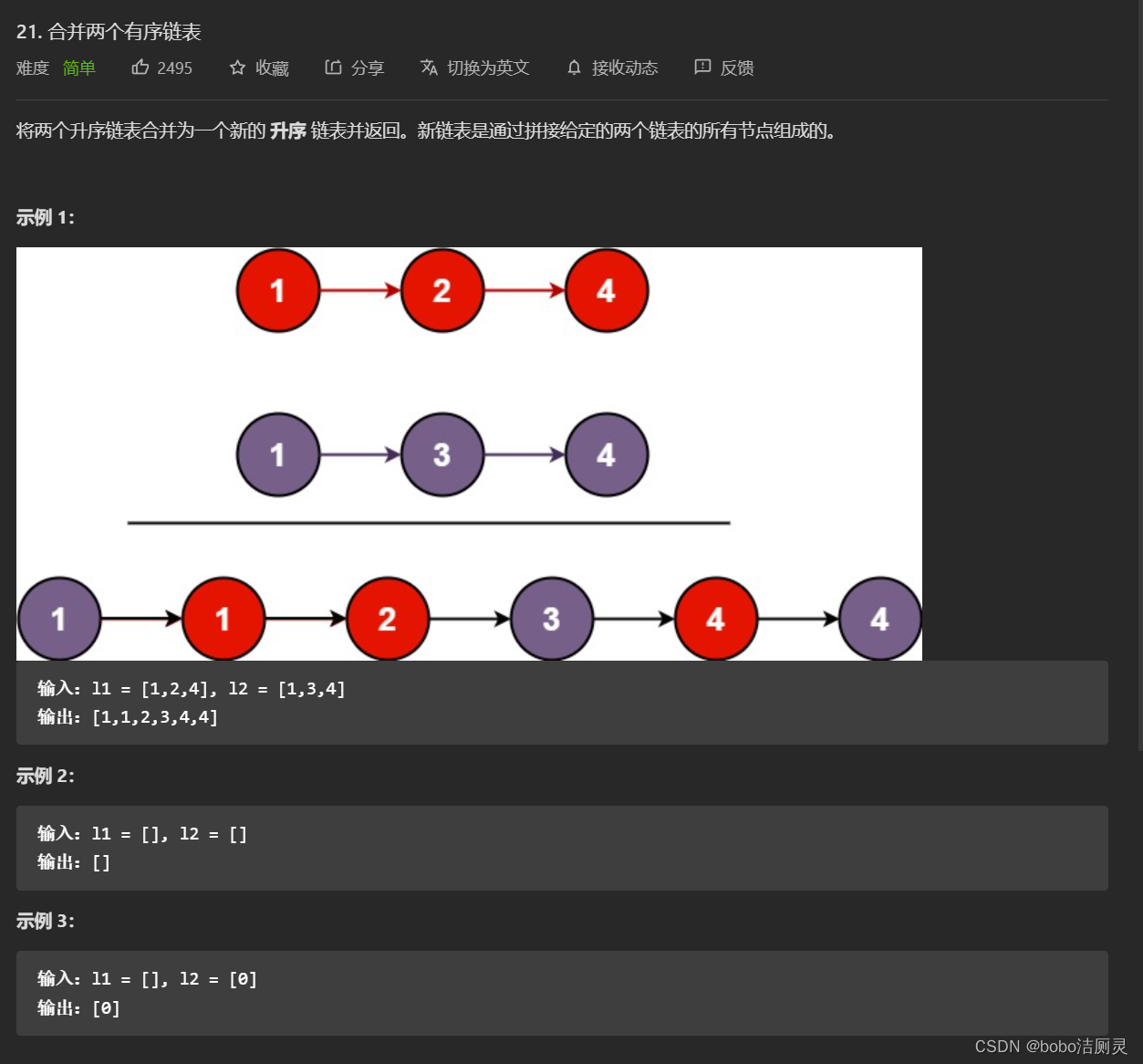
力扣刷题日记/day7/2022.6.29

力扣刷题日记/day7/6.30

能源行业的数字化“新”运维

【Hot100】32. Longest valid bracket

Weima, which is going to be listed, still can't give Baidu confidence
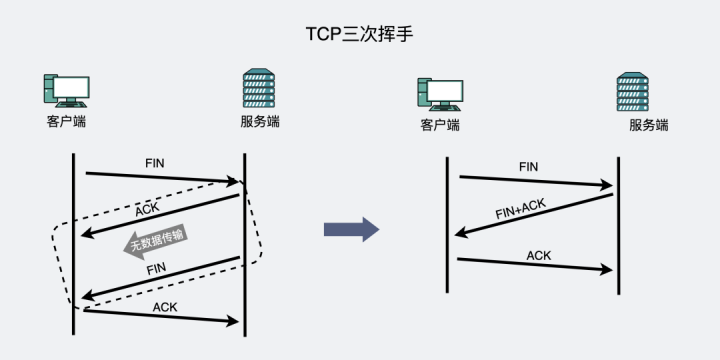
TCP waves twice, have you seen it? What about four handshakes?

五千字讲清楚团队自组织建设 | Liga 妙谈
Reptile elementary learning
随机推荐
Li Kou brush question diary /day7/6.30
Li Kou brush question diary /day7/2022.6.29
Li Kou brush question diary /day6/6.28
[system analyst's road] Chapter 7 double disk system design (structured development method)
Superscalar processor design yaoyongbin Chapter 6 instruction decoding excerpt
.NET ORM框架HiSql实战-第二章-使用Hisql实现菜单管理(增删改查)
【209】go语言的学习思想
力扣刷题日记/day4/6.26
[210] usage of PHP delimiter
Easy to use map visualization
MVC mode and three-tier architecture
五千字讲清楚团队自组织建设 | Liga 妙谈
Is it science or metaphysics to rename a listed company?
ITSS运维能力成熟度分级详解|一文搞清ITSS证书
股价大跌、市值缩水,奈雪推出虚拟股票,深陷擦边球争议
Is it safe to open an account online? is that true?
能源行业的数字化“新”运维
12 - explore the underlying principles of IOS | runtime [isa details, class structure, method cache | t]
2022年全国CMMI认证补贴政策|昌旭咨询
fopen、fread、fwrite、fseek 的文件处理示例