当前位置:网站首页>线程基础(一)
线程基础(一)
2022-08-02 05:11:00 【谁是黄黄】
活动地址:CSDN21天学习挑战赛
文章目录
一.并发与并行的概念
1.程序:一个固定逻辑与数据的集合就是程序 例如 俄罗斯方块 贪吃蛇
2.cpu:中央处理器 主要用于协调程序与硬件的工作
那什么是并发与并行?
先来一张图浅显了解一下并发和并行的区别吧。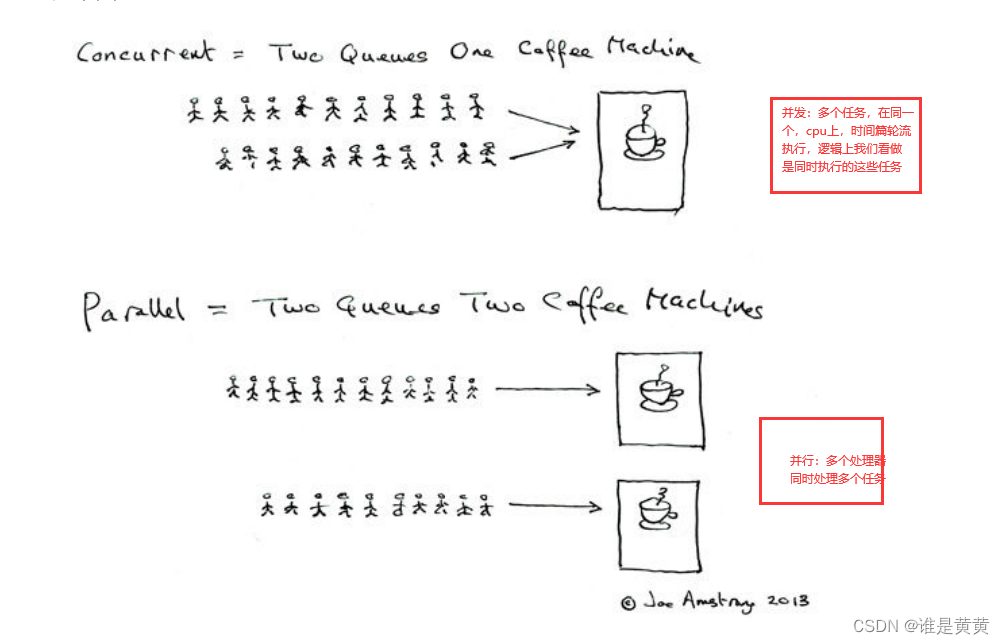
大体上的解释是:
并发(又称高并发):是同一个时间段执行两个,或者两个以上程序的,单核cpu交互(上面所说的时间片轮转是一种)的执行,由于cpu切换的速度很快,逻辑上我们任务并发是同时执行多个任务,实际上是交替执行。
例子:两个队伍的人在一个窗口打菜。
并行:在同一时刻,执行两个或者是多个程序的时候,多核cpu同时执行(现象的电脑都是多核cpu)
例子:多个人在多个咖啡机前排队。

二.线程与进程
概念:
进程:运行在内存中的程序就是进程.
每个进程都有⼀个独⽴的内存空间,⼀个应⽤程序可以同时运⾏多个进程;进程也是程序的⼀次执⾏过程,是系统运⾏程序的基本单位;系统运⾏⼀个程序即是 ⼀个进程从创建、运⾏到消亡的过程
线程: 通向cpu的执行的路径就是线程。
线程又分为单线程和多线程
单线程:只有一条通向cpu的执行的路径
多线程:多条通向cup的执行的路径
注意:
1.一个进程中能包含多个线程
2.一个线程只能存在一个进程中。
3.任务管理器里关闭的那个玩意就叫做进程

多线程的进程运行的流程图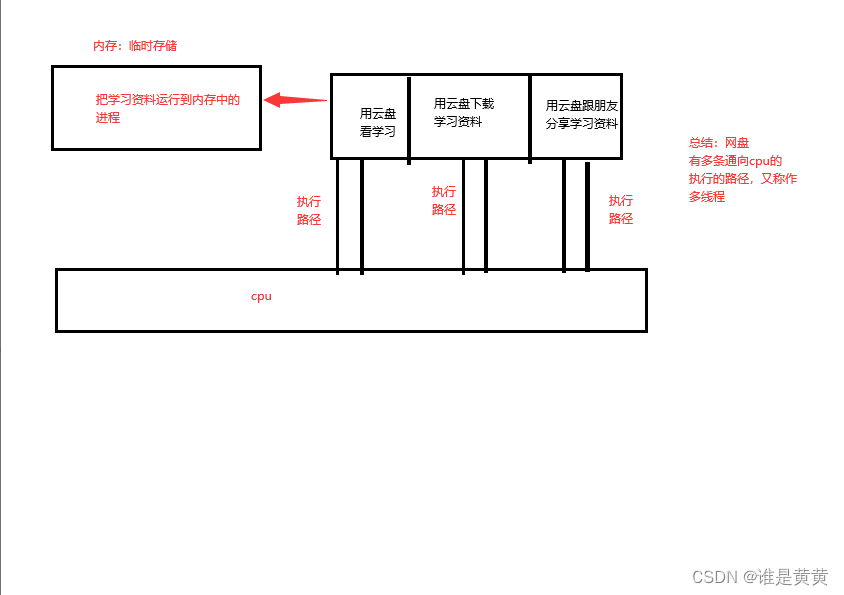
三. 主线程与子线程

3.1主线程:
主方法中,例如运行main方法函数的线程
负责管理子线程,即子线程的启动、挂起、停止等等操作
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread mainThread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println("我是主线程");
}
}
3.2子线程:
只能是理解为由主线程负责管理,即主线程负责启动,挂起,停止的线程为子线程
3.3进程,主线程,子线程的关系图

四.线程的三种创建方法
4.1 第一种 继承Thread重写run方法
步骤:
1.定义一个类去继承Thread
2.重写run()方法,执行线程的操作
3.实例化这个线程类的独享
4.调用start()方法,开启线程
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=1;i<=10;i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
测试类
public class Testhuang {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实例化对象
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
myThread.start();
}
}
输出结果:
4.2第二种 实现Runnable接口
步骤:
1.定义一个类 实现 Runnable
2.实现run()
3.实例化线程对象 Thread 传递一个参数 Runnable 的实现类
4.调用方法开启线程 start()
线程定义类
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + i);
}
}
}
测试类
public class Testhuang {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实例化Runnable对象的实现类
MyRunnable r = new MyRunnable(); //实例化线程类
Thread th = new Thread(r); //开启线程
th.start();
}
}
结果
4.3第三种 实现Callable接口
步骤:
1.定义一个类实现接口 Callable
2.重写call()方法
3.实例化 任务对象 FutureTask 构建一个Callable的实现类
4.实例化线程对象 Thread 构建一个任务对象
5.开启线程
6.调用任务对象的get() 获取其返回值
实现线程类
public class MyCallAble implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
Integer sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
}
测试类
public class Testhuang {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
MyCallAble call = new MyCallAble();
FutureTask<Integer> f = new FutureTask<>(call);
Thread t = new Thread(f);
t.start();
Integer c = f.get();
System.out.println(c);
}
}
结果
4.4 最常用的创建线程的方式
使用Runnable的匿名内部类来创建线程
public class Testhuang {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//第一种方式
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}).start();
//第二种方式
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}.start();
}
}
结果
4.5 线程调度的方式
线程调度的方式有两种:
1.分配式调度:多个线程执行任务的时间,都是评价分配,每一个线程执行的周期都是相同的
2.抢占式调度:线程的优先级越高,获取cpu执行权越高,线程抢到cpu的概率就越搞,优先执行的概率就越高,而我们的java中的多线程就是抢占式调度
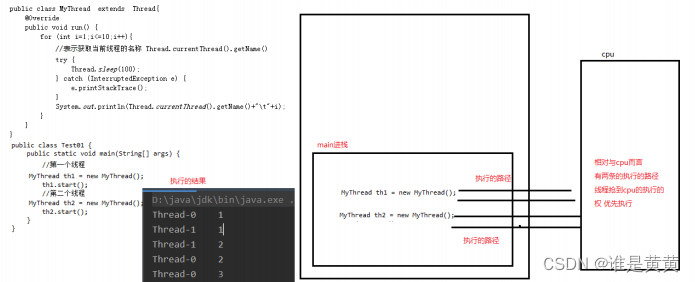
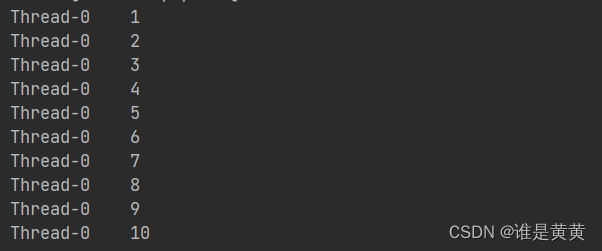
例子:
创建线程类
public class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
try {
//sleep方法是休眠方法,这里间隔0.1s
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//.getName方法获取当前线程的名称
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + i);
}
}
}
测试类:
public class Testhuang {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//开启第一个线程
MyThread th1 = new MyThread();
th1.start();
//开启第二个线程
MyThread th2 = new MyThread();
System.out.println(th2);
}
}
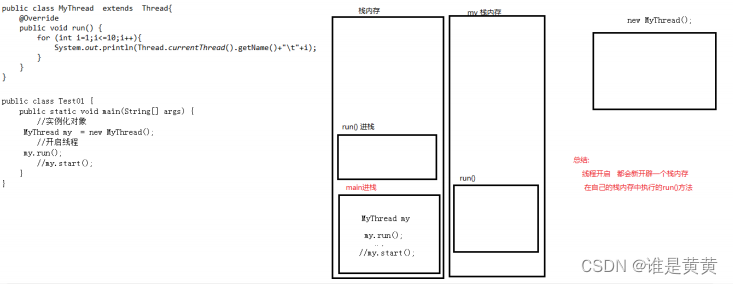
4.5线程的内存图
4.7 线程的常见方法
4.7.1 获取线程名
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| public final String getName() | 返回该线程的名称 |
| public static Thread currentThread() | 返回对当前正在执行的线程对象的引用 |
线程创建类
public class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run(){
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(getName() + "\t" + i);
}
}
}
测试类
public class Testhuang {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实例化线程对象
MyThread th = new MyThread();
th.start();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + i);
}
}
}
结果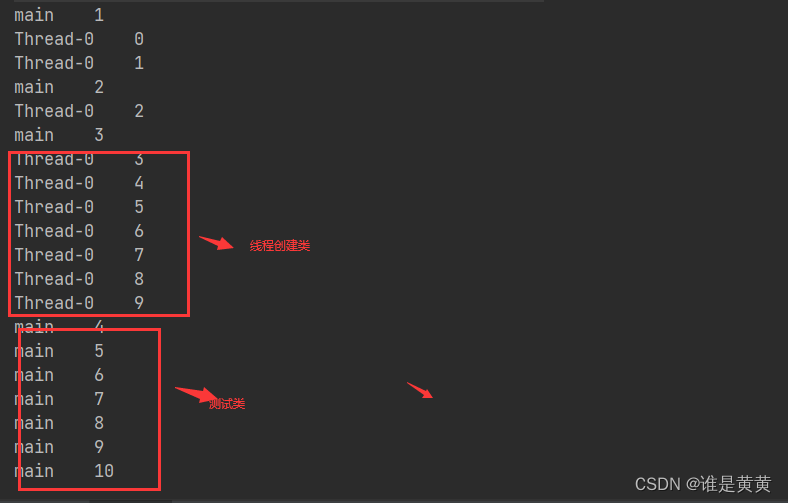
4.7.2 线程休眠
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| public static void sleep(long millis) | 线程休眠 |
线程创建类
public class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 60; i >= 1; i--) {
System.out.println("还剩下" + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
测试类
public class Testhuang {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实例化线程对象
MyThread th = new MyThread();
th.start();
}
}
结果

4.7.3 守护线程
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| public final void setDaemon(boolean on) | 设置为守护线程 |
| public final boolean isDaemon() | 测试该线程是否为守护线程 |
线程创建类
public class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//休眠五秒
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
OutputStream is = new FileOutputStream("3.txt");
is.write(97);
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
测试类
public class Testhuang {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实例化线程对象
MyThread my = new MyThread();
//设置为守护线程
my.setDaemon(true);
//获取其状态
System.out.println(my.isDaemon());
my.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(6000);
} catch (
InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
结果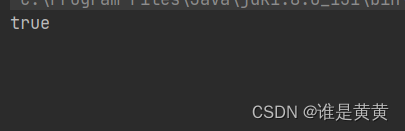
显示开启了守护线程
4.7.4 设置线程的优先级
4.7.4.1 常量
| 常量名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| public static final int MAX_PRIORITY | 线程可以具有的最高优先级 |
| public static final int MIN_PRIORITY | 线程可以具有的最低优先级 |
| public static final int NORM_PRIORITY | 分配给线程的默认优先级 |

注意点:
1.线程的
最高优先级是10,最低优先级是1,范围1-10
2.线程优先级越高表示获取cpu执行权越大即被执行的概率越高,但是并不一定会执行,因为java是抢占式调度
4.7.4.2 方法
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| public final int getPriority() | 返回的是线程的优先级 |
| public final void setPriority(int newPriority) | 更改线程的优先级 |
线程创建类
public class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
System.out.println(getName() + "\t" + i);
}
}
}
测试类
public class Testhuang {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实例化第一个线程
MyThread t = new MyThread();
t.setPriority(8);
t.start(); //
// 实例化第二个线程
MyThread th = new MyThread();
th.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
th.start();
}
}
结果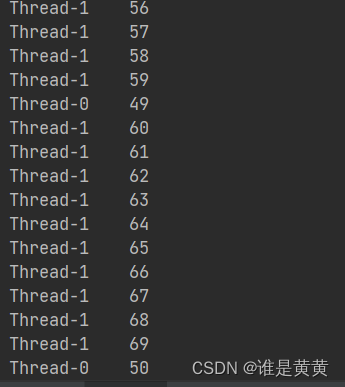
边栏推荐
- 51 microcontroller peripherals article: dot-matrix LCD
- Mysql implements optimistic locking
- What do interview test engineers usually ask?The test supervisor tells you
- [PSQL] 窗口函数、GROUPING运算符
- Go language study notes - grpc serverclient protobuf Go language from scratch
- JUC(二)原子类:CAS、乐观锁、Unsafe和原子类
- MySQL数据表的基本操作和基于 MySQL数据表的基本操作的综合实例项目
- OAuth 授权协议 | 都云原生时代了,我们应该多懂一点OAuth ?
- Google notes cut hidden plug-in installation impression
- Introduction to coredns
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Shuttle + Alluxio 加速内存Shuffle起飞
Polar Parametrization for Vision-based Surround-View 3D Detection 论文笔记
测试技术之APP蓝牙连接测试
leetcode括号匹配问题——32.最长有效括号
Linux CentOS8安装Redis6
Cyber Security Learning - Intranet Penetration 4
OAuth 授权协议 | 都云原生时代了,我们应该多懂一点OAuth ?
腾讯大咖分享 | 腾讯Alluxio(DOP)在金融场景的落地与优化实践
【C语言】LeetCode26.删除有序数组中的重复项&&LeetCode88.合并两个有序数组
Meta公司新探索 | 利用Alluxio数据缓存降低Presto延迟
如何进行并发数计算(稳定性测试和压力测试)?
家用 NAS 服务器(4)| MergerFS和SnapRaid数据定时备份
Detailed explanation of interface in Go language
51单片机外设篇:点阵式LCD
Redis-----非关系数据库
TikTok平台的两种账户有什么区别?
PSQL function, predicate, CASE expression and set operations
关于web应用的目录结构
C语言基础知识梳理总结:零基础入门请看这一篇
LeetCode刷题系列 -- 787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班