当前位置:网站首页>Implementation of queue (C language)
Implementation of queue (C language)
2022-06-11 07:31:00 【m0_ fifty-two million twelve thousand six hundred and fifty-six】
Implementation of queues
A queue is a first in, first out (First in First Out) The linear table , abbreviation FIFO. Unlike stacks , A stack is a last in, first out ( First in, then out ) The linear table . In the queue , The end allowed to be inserted is called the end of the queue , The end allowed to be deleted is called the team leader . Suppose the queue is q=(a1,a2,…,an), that a1 It's the team leader element , and an It's the tail of the team . So we can delete , Always from a1 Start , And when inserted , Listed last . This is also more in line with our usual habits in life , The first priority , The last one came, of course, at the end of the team . Queues are divided into sequential queues and cyclic queues . Sequential queue can be realized by array or linked list . here , We choose to use linked list to realize sequential queue .
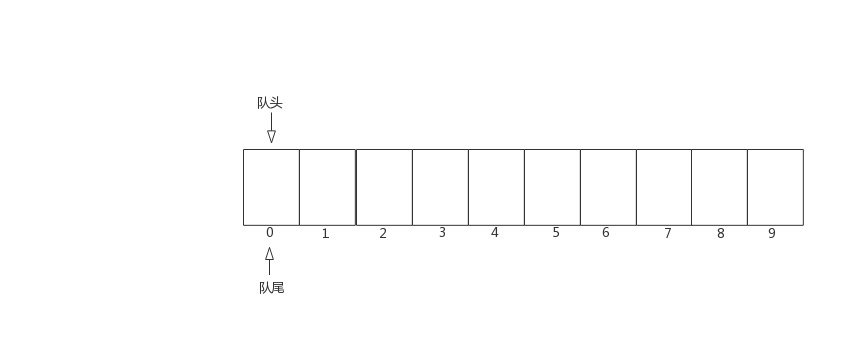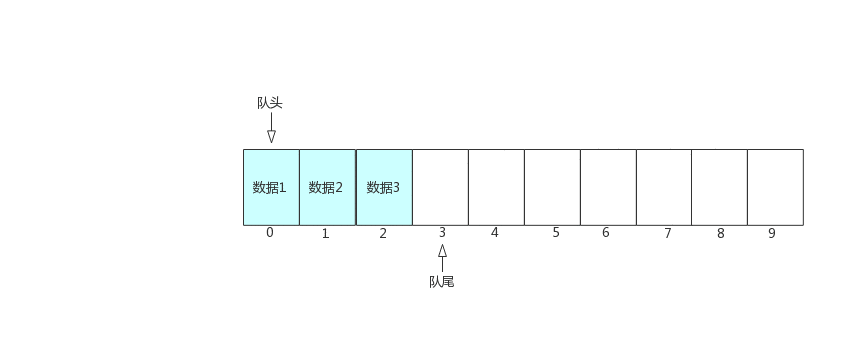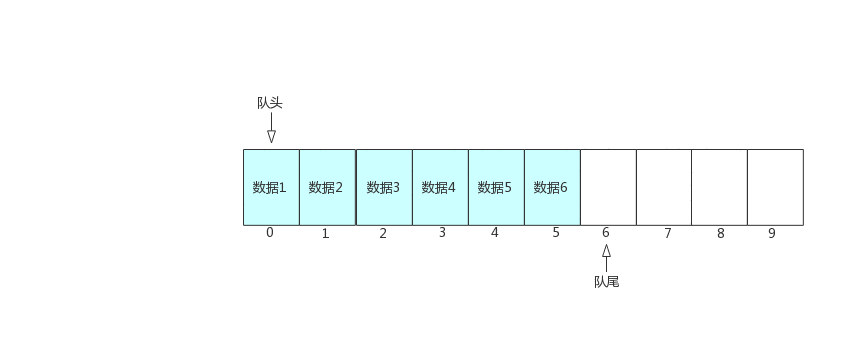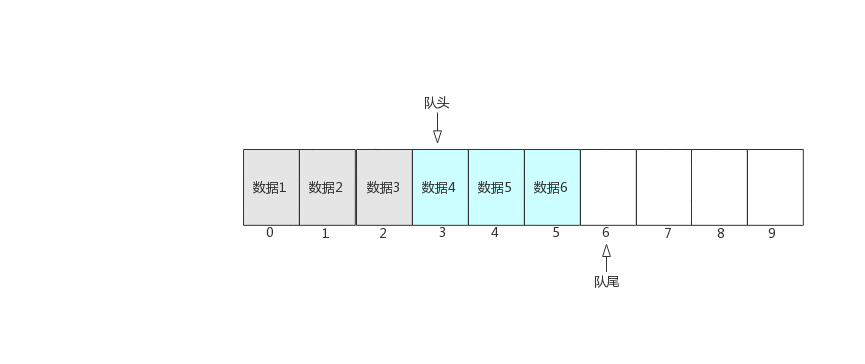
Today, we mainly introduce the queue and circular queue implemented by linked list
Chain queues
What are the main basic operations of a queue
// Initialize queue
void QueueInit(Queue* q);
// Tail in queue
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType data);
// Team leader out of line
void QueuePop(Queue* q);
// Get queue header elements
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q);
// Get queue tail element
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q);
// Get the number of valid elements in the queue
int QueueSize(Queue* q);
// Check if the queue is empty , If NULL, return non-zero result , If not null, return 0
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q);
// Destroy queue
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q);Definition of chain queue
typedef int QDataType;
// The chain structure : Represents a queue
typedef struct QListNode
{
struct QListNode* _next;
QDataType _data;
}QNode;
// The structure of the queue
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* _front;
QNode* _rear;
}Queue;The implementation of chain queue
1、 Initialize queue
void QueueInit(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
q->_front = NULL;
q->_rear = NULL;
}2、 Destroy queue
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
QNode* cur = q->_front;
while (cur != NULL)
{
QNode* next = cur->_next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
q->_front = q->_rear = NULL;
}3、 Queue empty
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
//if (q->_front == NULL)
//{
// return 1;
//}
//else
//{
// return 0;
//}
return q->_front == NULL;
}
4、 Joining operation
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType data)
{
assert(q);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
exit(-1);
}
newnode->_data = data;
newnode->_next = NULL;
if (q->_front == NULL)
{
q->_front = q->_rear = newnode;
}
else
{
q->_rear->_next = newnode;
q->_rear = newnode;
}
}5、 Out of line operation
void QueuePop(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
QNode* next = q->_front->_next;
free(q->_front);
q->_front = next;
if (q->_front == NULL)
{
q->_rear = NULL;
}
}6、 Take the team leader element
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->_front->_data;
}7、 End of queue operation
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->_rear->_data;
}
8、 The number of effective elements in the team
int QueueSize(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
int size = 0;
QNode* cur = q->_front;
while (cur)
{
size++;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return size;
}Circular queue
Circular queue is to wrap the last position of queue storage space to the first position , Form a logical ring space , For queue recycling . In the circular queue structure , When the last position of the storage space has been used and it is necessary to enter the queue operation , Only the first location of the storage space is free , You can add the element to the first position , The first location of the storage space will be used as the tail of the team . Circular queues can more easily prevent pseudo overflow , But the queue size is fixed . In the loop queue , When the queue is empty , Yes front=rear, And when all the queue space is full , Also have front=rear. To distinguish between these two situations , Specifies that the circular queue can have at most MaxSize-1 Queue elements , When there is only one empty storage unit left in the circular queue , The queue is full . therefore , The condition of empty queue is front=rear, The condition for the queue to be full is front=(rear+1)%MaxSize.
The space of the circular queue can be reused , It solves the problem of space waste of ordinary queues
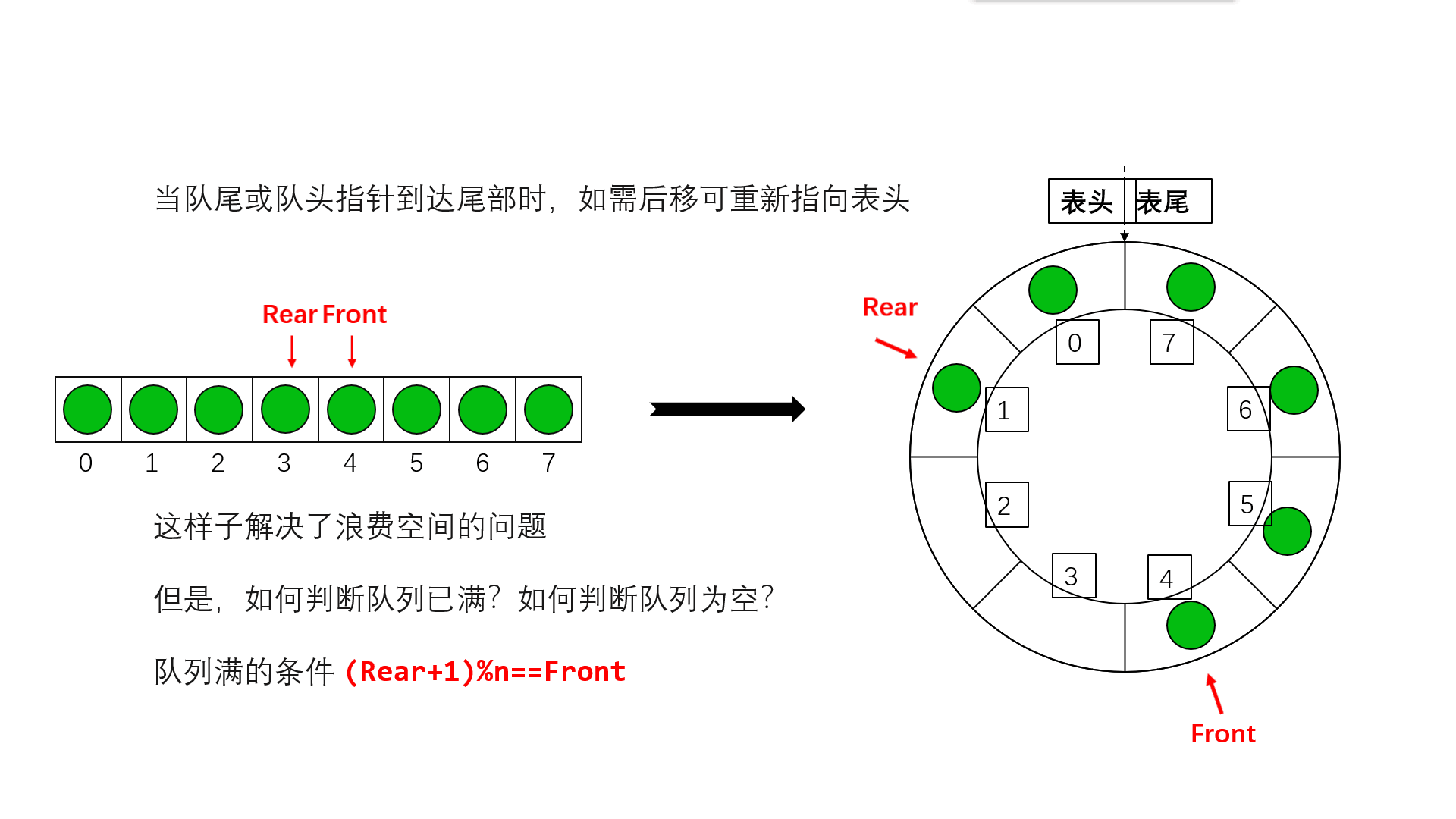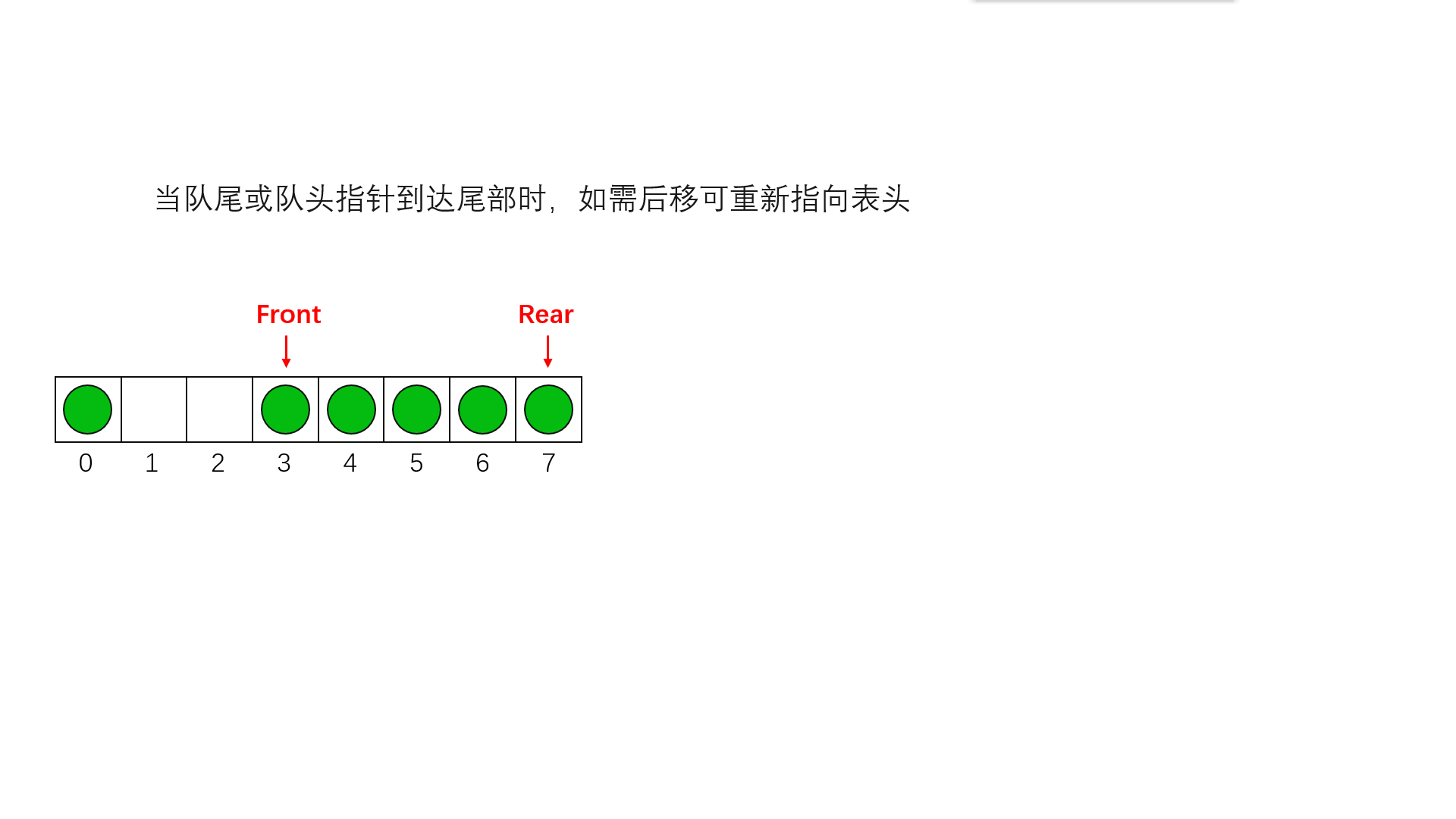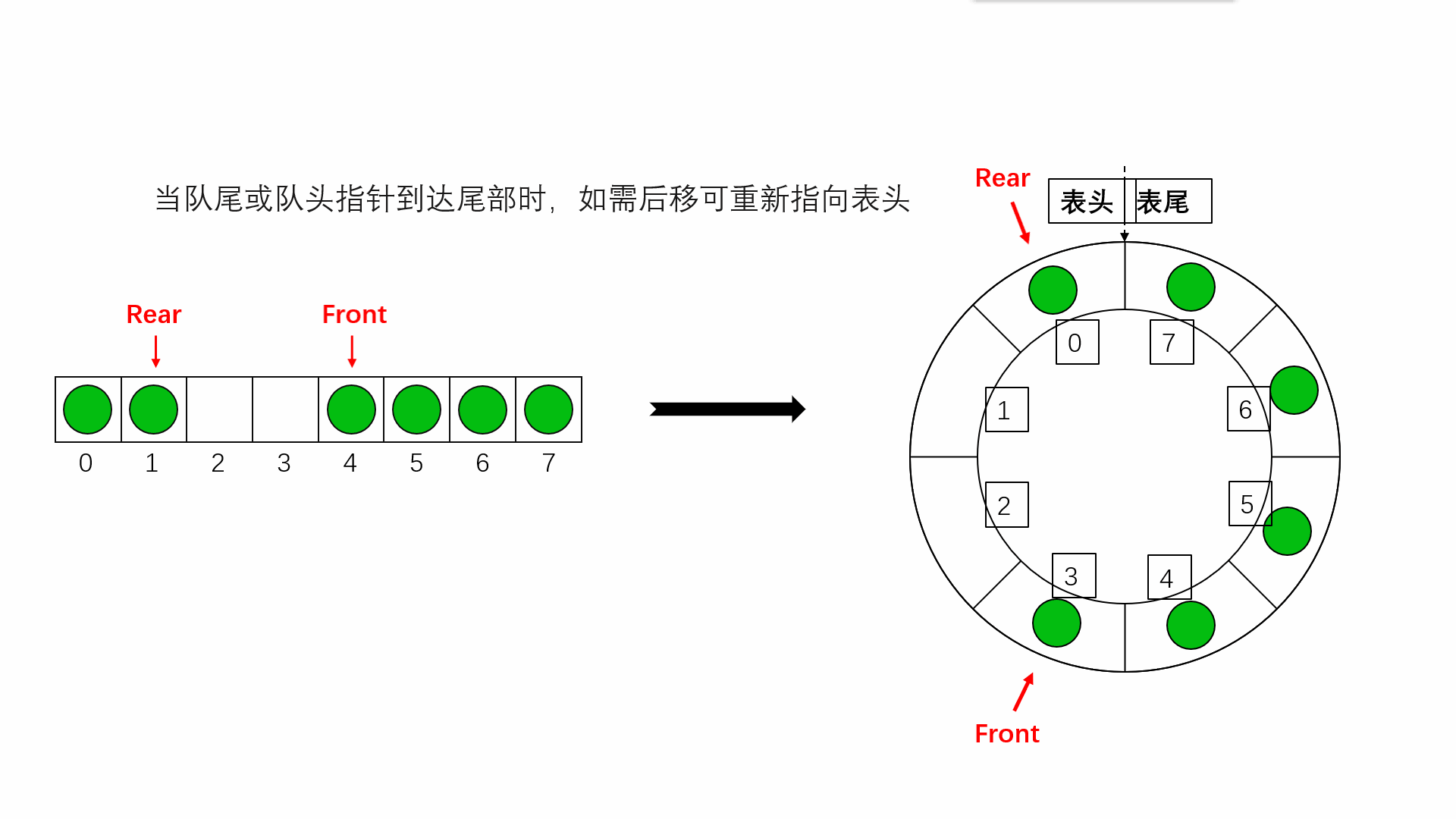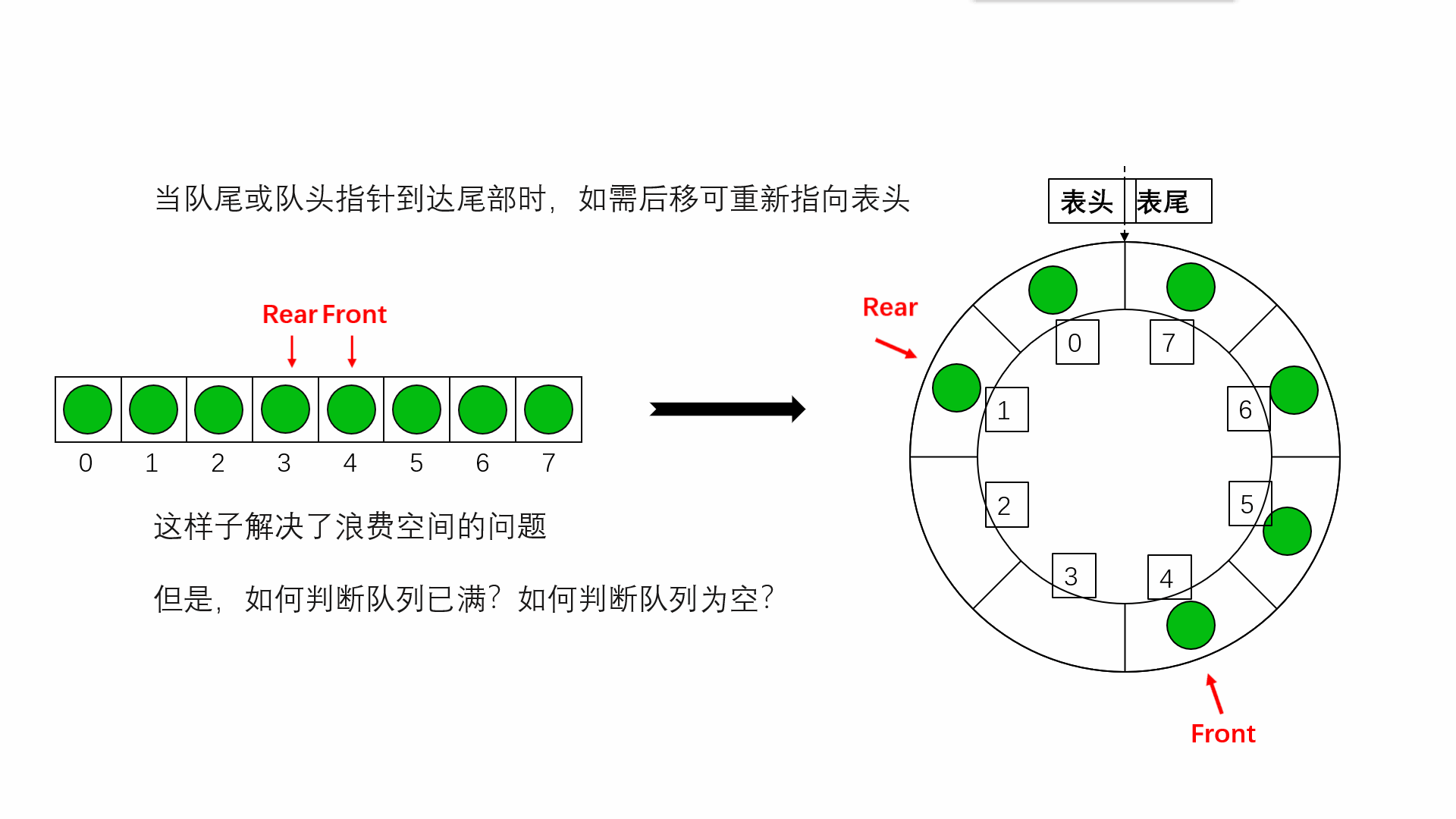
Implementation of circular queue
typedef struct {
int *a;
int front;
int tail;
int k;
} MyCircularQueue;
// Declare in advance that the sentence is empty and the sentence is full
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj);
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj);
// Create circular queue
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
MyCircularQueue* cq=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
cq->a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));
cq->front=cq->tail=0;
cq->k=k;
return cq;
}
// Loop queue in
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj)){
return false;
}
obj->a[obj->tail]=value;
obj->tail++;
obj->tail%=(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
// Loop queue out
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){
return false;
}
obj->front++;
obj->front%=(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
// Loop queue fetch header
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){
return -1;
}
return obj->a[obj->front];
}
// End of loop queue
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){
return -1;
}
int i=(obj->tail+obj->k)%(obj->k+1);
return obj->a[i];
}
// Circular queue null
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return obj->front==obj->tail;
}
// The loop queue is full
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return (obj->tail+1)%(obj->k+1)==obj->front;
}
// Destroy circular queue
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
free(obj->a);
free(obj);
}
边栏推荐
- Directrix of ellipse
- [STL source code analysis] summary note (2): overview of containers
- Deux diplômés, la Banque a externalisé le travail d'essai pendant plus de quatre mois. Parler de vrais sentiments...
- Software testing weekly (issue 75): only when you look down, can you see your true self.
- 【HDU6357】Hills And Valleys(DP)
- Create a form whose client area is 800 pixels by 600 pixels
- Import on CSDN MD file
- May 30-June 5, 2022 AI industry weekly (issue 100): three years
- MFC custom string linked list
- The rotation of the earth and the moon (II)
猜你喜欢

Classification of MNIST datasets with keras

【AtCoder1980】Mysterious Light(数学模拟)

二本畢業,銀行外包測試工作 4 個月有餘。聊聊一些真實感受 ...
![Uoj 554 [unr 4] challenges Hamilton [find Hamilton path (adjustment method)]](/img/f0/9d4609a53f398636b8062c625f7d3c.jpg)
Uoj 554 [unr 4] challenges Hamilton [find Hamilton path (adjustment method)]

【编译原理】05-语法制导的语义计算——基于翻译模式的语义计算
![[STL source code analysis] summary notes (5): a good helper for understanding iterators --list](/img/a7/c54bfb6a03c04e4ffeafdfcf8cedc2.jpg)
[STL source code analysis] summary notes (5): a good helper for understanding iterators --list
QObject usage skills -- control function class

The rotation of the earth and the moon (II)

Raspberry pie builds a full-featured NAS server (07): manage your library & read as you please

2022低压电工操作证考试题模拟考试平台操作
随机推荐
Uoj 554 [unr 4] challenges Hamilton [find Hamilton path (adjustment method)]
【CF#654 (Div. 2)】A. Magical Sticks
Nim product
CRMEB/V4.4标准版打通版商城源码小程序公众号H5+App商城源码
[STL source code analysis] summary notes (1): Opening
【AtCoder1983】BBQ Hard (组合数+巧妙模型转化)
Regular Expression Matching
R language Parallel Computing practice tutorial
MySQL设置管理员密码无法生效的案例一则
RTMP protocol
欧拉定理及扩展(附证明)
Software testing weekly (issue 75): only when you look down, can you see your true self.
R语言并行计算实战教程
模线性方程组(中国剩余定理+通用解法)
Nosqlzoo question brushing-1
测试4年裸辞失业,面试15k的测试岗被按在地上摩擦,结局让我崩溃大哭...
软件测试周刊(第75期):唯有平视,才能看见真实的自己。
20200803 T3 my friends [divide and conquer NTT optimization recursion]
Ffmpe a small demo to understand 80% of common APIs
【AtCoder1981】Shorten Diameter(图论思维)