当前位置:网站首页>[advanced C language] advanced pointer [Part 1]
[advanced C language] advanced pointer [Part 1]
2022-06-10 19:35:00 【You and I are all mortals】
author : You and I are all mortals
Blog home page : You and I are all mortal blogs
Aphorisms : Time will not stay for anyone , And things and people , It's changing all the time . Every one of us , Also keep moving forward !
If you think the blogger's article is good , I hope you'll make it three times in a row ( Focus on , give the thumbs-up , Comment on ), Give me more support !!
series :
List of articles
Catalog
Array parameter passing and pointer parameter passing
One dimensional array parameters
Two dimensional array parameters
First level pointer parameter transfer
The secondary pointer transmits parameters
Preface
This article explains the character pointer in the advanced level of pointer , Array pointer , Pointer array , Array parameter passing and pointer parameter passing , illustrated , So that you can understand and understand
Tips : The following is the main body of this article , The following cases can be used for reference
Character pointer
We have learned some knowledge about the primary pointer in the previous learning process , Know the concept of pointer :
1. A pointer is a variable , It's used to store the address , The address uniquely identifies a piece of memory space .2. The size of the pointer is fixed 4/8 Bytes (32 Bit platform /64 Bit platform ).3. Pointers are typed , The type of pointer determines the type of pointer +- Integer step size , The permission of pointer dereference operation .4. The operation of the pointer .Let's move on to the advanced topic of pointersAmong the pointer types, we know that one pointer type is character pointer char*as follows :
int main()
{
char ch = 'w';
char* pc = &ch;
*pc = 'b';
printf("%c\n", ch);
return 0;
}
Like the above, a character is put into a pointer , You have seen another kind of
as follows :
The following is the abcdef The first element of this string a The address of is assigned to p in , Not the whole string p, And the first element address is printed , By the way, I printed out the last string
int main()
{
char* p = "abcdef";
// Put the first element of the string a The address of is assigned to p in
printf("%s\n", p);
return 0;
}Next, let's look at an interview question to solve our problems , By the way, understand the above :
int main()
{
const char* p1 = "abcdef";
const char* p2 = "abcdef";
char arr1[] = "abcdef";
char arr2[] = "abcdef";
if (p1 == p2)
printf("p1==p2\n");
else
printf("p1!=p2\n");
if (arr1 == arr2)
printf("arr1 == arr2\n");
else
printf("arr1 != arr2\n");
return 0;
} 
Why is this the case ?
p1 And p2 Are character pointers , and const Modifiers cannot change the pointer , and “abcdef” Is a constant string , Put the first element address a Give it to p1 And p2, Since it's a constant string , Can't modify , Only read , It seems useless to store multiple copies in memory , So there is a space , and p1 And p2 It points to the same space , So the printing is equal
arr1 Is an array , Initialization will open up a space ,arr2 It's also an array , Initialize to open up a space , therefore arr1 And arr2 It's not equal
Pointer array
Pointer arrays are arrays , Is an array used to store pointers
int main()
{
int arr[10]; // integer array , Store plastic
char arr1[10];// A character array , To store characters
int* arr2[10];// Integer pointer array , Store the integer pointer
char* arr3[10];// Character pointer array , Storing character pointers
return 0;
}The name of the array is equivalent to the address of the first element , So can we put the array in the array , Accept with a pointer , This is just a pointer array ? The following code :
int main()
{
int arr1[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
int arr2[] = { 2,3,4,5,6 };
int arr3[] = { 3,4,5,6,7 };
int* parr[3] = { arr1,arr2,arr3 };
return 0;
}Drawing interpretation :
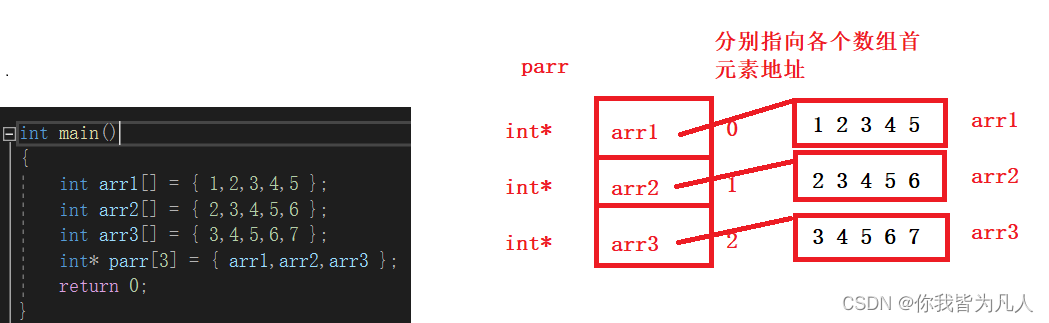
In fact, we found that we simulated a two-dimensional array , We can also take it out , Simulate a two-dimensional array to get the value of a one-dimensional array
int main()
{
int arr1[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
int arr2[] = { 2,3,4,5,6 };
int arr3[] = { 3,4,5,6,7 };
int* parr[3] = { arr1,arr2,arr3 };
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
// Because we knew before ,*(p+i) -- p[i]
printf("%d ", *(parr + i) + j);
//printf("%d ", *(parr[i] + j));
//printf("%d ", parr[i][j]);
// So the latter ones are actually equivalent
}
}
return 0;
}Array pointer
Definition of array pointer
Is the array pointer a pointer or an array ?
The answer is the pointer
Integer pointer : Pointer to shaping data
Character pointer : Pointer to character data
Array pointer : Pointer to array data
Which of the following is an array pointer ?
int *p1[10];
int (*p2)[10]; explain :
int *p1[10];
p1 The first and 【】 combination , Priority application , Represents the p1 Is an array , The type is int* Of , It's an array of Pointers
int (*p2)[10];
p2 The first and * The union representation is a pointer , because () High priority , And then store 10 Elements , The type of each element is int type , Represents an array pointer that holds an array
/ Pay attention here :[] Priority is higher than * The no. , So we have to add () To guarantee p The first and * combination .
& Array name VS Array name
Let's talk about array names again :
For the following array :
int arr【10】;
there arr And &arr What's the difference? , What are they ?
We know arr It's an array name , The array name indicates the address of the first element of the array , that &arr What is the array name ?
Let's take a look at a piece of code :
int main()
{
int arr[10] = { 0 };
printf("%p\n", arr);
printf("%p\n", &arr[0]);
printf("%p\n", &arr);
return 0;
}The operation results are as follows :

We see the array name and & The array name and the address of the first element of the array are exactly the same , Are these three the same ?
The array name usually represents the address of the first element of the array
But there are 2 Exceptions :
1,sizeof( Array name ), The array name here represents the entire array , It calculates the size of the entire array
2,& Array name , The array name here still represents the whole array , therefore & The array name takes out the address of the whole array
Let's take another look at the code :
int main()
{
int arr[10] = { 0 };
printf("%p\n", arr);
printf("%p\n", arr+1);
printf("%p\n", &arr[0]);
printf("%p\n", &arr[0]+1);
printf("%p\n", &arr);
printf("%p\n", &arr+1);
return 0;
}The analysis results are as follows :
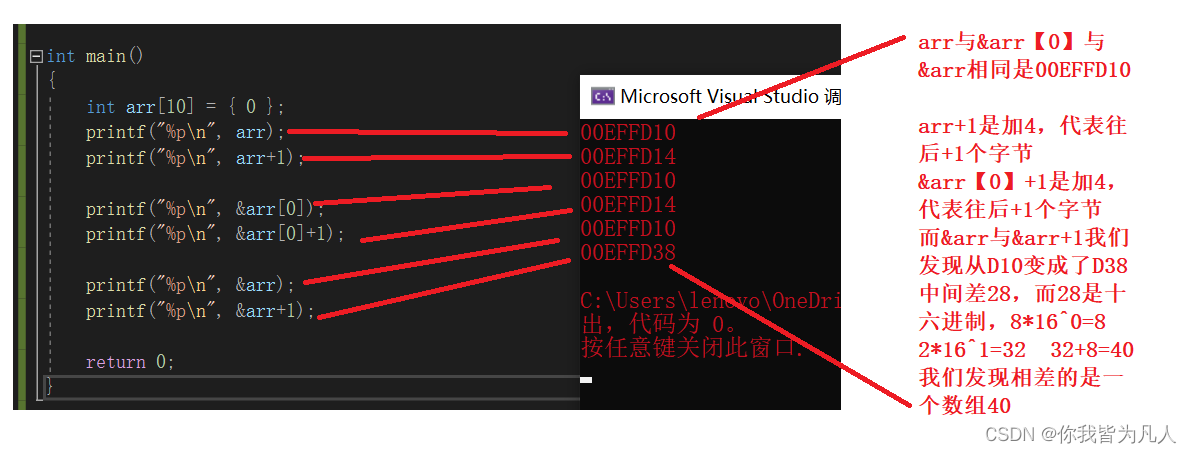
According to the above code, we find that , Actually &arr and arr, Although the values are the same , But the meaning should be different .
actually :&arr It means Address of array , Instead of the address of the first element of the array .In this case &arr The type is : int(*)[10] , Is an array pointer typeAddress of array +1, Skip the size of the entire array , therefore &arr+1 be relative to &arr The difference is 40.As shown in the following figure :
int main()
{
int arr[10] = { 0 };
int* p = arr;
int(*p)[10] = &arr;
// p With the first * Union is a pointer , Then there is an array of ten elements , The type is int, Deposit is arr Address of array
// The integer pointer is used to store the address of the integer
// A character pointer is an address used to store characters
// Array pointer is the address used to store the array
return 0;
}
The use of array pointers
So how exactly are array pointers used ?
Since the array pointer points to an array of numbers , Then the address of the array should be stored in the array pointer
Remember not to confuse it with a second level pointer , The second level pointer is the address where the first level pointer variable is stored
int main()
{
char* arr[5] = { 0 };
char* (*pc)[5] = &arr;// Array pointer
char ch = 'w';
char* p1 = &ch; // First level pointer
char** ph = &p1;// The secondary pointer
return 0;
}The use of an array pointer is as follows :
#include <stdio.h>
void print_arr1(int arr[3][5], int row, int col) {
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void print_arr2(int(*arr)[5], int row, int col) {
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[3][5] = { 1,2,3,4,5,2,3,4,5,6,3,4,5,6,7};
print_arr1(arr, 3, 5);
// Array name arr, Represents the address of the first element
// But the first element of a two-dimensional array is the first row of a two-dimensional array
// So the message here is arr, It's actually equivalent to the address on the first line , Is the address of a one-dimensional array
// You can use an array pointer to receive
print_arr2(arr, 3, 5);
return 0;
}After learning pointer array and array pointer, let's review the meaning together and see the meaning of the following code :
int main()
{
int arr[5];
int* parr1[10];
int(*parr2)[10];
int(*parr3[10])[5];
return 0;
}int arr[5];
arr Is an integer array , Yes 5 Elements , The type is int
int* parr1[10];parr1 Is an array of integer pointers , Yes 10 Elements , Each type is int*
int(*parr2)[10];parr2 Is an integer array pointer , With the first * Combination is a pointer , Then there is 10 Elements , Each type is int
int(*parr3[10])[5];parr3 Is an array that holds array pointers ,parr3 With the first 【】 The combination is an array , And then the rest int * 【5】 It's the type , It is an array of pointers , So it's an array that holds array pointers , Array pointer array for short
Array parameter passing and pointer parameter passing
When writing code, it's hard to avoid 【 Array 】 perhaps 【 The pointer 】 Pass to function , So how to design the parameters of the function ?
One dimensional array parameters
Code :
#include <stdio.h>
void test(int arr[])//ok?
{}
void test(int arr[10])//ok?
{}
void test(int* arr)//ok?
{}
void test2(int* arr[20])//ok?
{}
void test2(int** arr)//ok?
{}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = { 0 };
int* arr2[20] = { 0 };
test(arr);
test2(arr2);
}
Drawing analysis :

Two dimensional array parameters
Code :
void test(int arr[3][5])//ok?
{}
void test(int arr[][])//ok?
{}
void test(int arr[][5])//ok?
{}
// summary : Two dimensional array parameters , Function parameter design can only omit the first [] The number of .
// Because for a two-dimensional array , I don't know how many lines there are , But you have to know how many elements in a row .
// So it's easy to calculate .
void test(int *arr)//ok?
{}
void test(int* arr[5])//ok?
{}
void test(int (*arr)[5])//ok?
{}
void test(int **arr)//ok?
{}
int main()
{
int arr[3][5] = {0};
test(arr);
}Drawing analysis :

First level pointer parameter transfer
Code :
#include <stdio.h>
void print(int *p, int sz) {
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i<sz; i++)
{
printf("%d\n", *(p+i));
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int *p = arr;
int sz = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
// First level pointer p, Pass to function
print(p, sz);
return 0; }Drawing analysis :

Think about a problem : Push backwards , If the parameter part of the function has been fixed, it is a first-order pointer , So what can be used to transmit parameters
Such as void print(int* p)
{}
If int a = 10;
print(&a); You can pass it on , Because it's the address , Receive... With a pointer
If int* ptr = &a;
print(ptr); You can pass the pointer to receive the pointer
If int arr【10】
print(arr); You can pass it on ,arr Represents the address of the first element of the array , Pointer reception
The secondary pointer transmits parameters
Code :
#include <stdio.h>
void test(int** ptr)
{
printf("num = %d\n", **ptr);
}
int main()
{
int n = 10;
int*p = &n;
int **pp = &p;
test(pp);
test(&p);
return 0;
}Drawing analysis :

Think about a problem : Push backwards , If the parameter part of the function has been fixed, it is a second-order pointer , So what can be used to transmit parameters
such as :test(int** p)
{}
If int *p1;
test(&p1); The address of the first level pointer and the second level pointer can be used to receive
If int**p2;
test(p2); The second level pointer can be passed to the second level pointer to receive
If int* arr【10】;
test(arr);
The pointer array name is the address of the first element , Each element is int* type , The second level pointer reception is OK
Entrance to exercises
After reading these specific operations, it is not allowed , You can click on the top to practice some exercises , You can also have a casual look C Some language exercises , Practice multiple-choice questions and programming questions , Let your knowledge be consolidated , Click directly into the title to go directly to , In addition, if you want to get the qualification of internal promotion of large factories, you can also go and have a look :
边栏推荐
- LeetCode_并查集_中等_399. 除法求值
- 一文带你了解J.U.C的FutureTask、Fork/Join框架和BlockingQueue
- MySQL (17 after class exercises)
- 【代理】10分钟掌握正向代理和反向代理的本质区别
- Explain the interview questions by holding chestnuts (interview, review and study)
- Analysis of Muduo source code -- an analysis of the rigor, efficiency and flexibility of Muduo library code design with three slices
- Developers changing the world - Yao Guang teenagers playing Tetris
- 专项测试之「 性能测试」总结
- China pufuteng hotels and resorts launched new spa products to celebrate the global health day on June 11
- C知识练习
猜你喜欢
SAR回波信号基本模型与性质

【代理】10分钟掌握正向代理和反向代理的本质区别

【C语言进阶】数据的存储【下篇】【万字总结】

VS从txt文件读取中文汉字产生乱码的解决办法(超简单)

Tencent cloud database tdsql- a big guy talks about the past, present and future of basic software

【 random talk 】 congratulations on getting the title of CSDN expert. Your efforts will eventually pay off

Basic model and properties of SAR echo signal

ESP8266 系统环境搭建

Lingo12 software download and lingo language introduction resources

单纯形法代码求解(含超详细代码注释和整个流程图)
随机推荐
WordPress 6.0 "Arturo Arturo" release
第6章 关系数据理论练习
[web] personal homepage web homework "timetable", "photo album" and "message board"
DDD落地实践复盘 - 记理论培训&事件风暴
一文带你了解J.U.C的FutureTask、Fork/Join框架和BlockingQueue
一文帶你了解J.U.C的FutureTask、Fork/Join框架和BlockingQueue
lingo12软件下载及lingo语言入门资源
mysql(17-觸發器)
Array signal processing simulation part IV -- Z-transform analysis array polynomial
【C语言进阶】数据的存储【下篇】【万字总结】
云图说|每个成功的业务系统都离不开APIG的保驾护航
VS从txt文件读取中文汉字产生乱码的解决办法(超简单)
frp reverse proxy
Design and implementation of online ordering system based on SSM Rar (project source code)
Low carbon data center construction ideas and future trends
Design and development of hospital reservation registration platform based on JSP Zip (thesis + project source code)
Monotonic stack structure
Chapter 6 relational data theory exercise
Analysis of Muduo source code -- an analysis of the rigor, efficiency and flexibility of Muduo library code design with three slices
c(指针-02)