当前位置:网站首页>[Verilog] HDLBits Problem Solution - Circuits/Sequential Logic/Latches and Flip-Flops
[Verilog] HDLBits Problem Solution - Circuits/Sequential Logic/Latches and Flip-Flops
2022-08-03 12:11:00 【wjh776a68】
Sequential Logic
Latches and Flip-Flops
D flip-flop
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk, // Clocks are used in sequential circuits
input d,
output reg q );//
// Use a clocked always block
// copy d to q at every positive edge of clk
// Clocked always blocks should use non-blocking assignments
always @ (posedge clk) begin
q <= d;
end
endmodule
D flip-flops
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input [7:0] d,
output [7:0] q
);
always @ (posedge clk) begin
q <= d;
end
endmodule
DFF with reset
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset, // Synchronous reset
input [7:0] d,
output [7:0] q
);
always @ (posedge clk) begin
if (reset)
q <= 0;
else
q <= d;
end
endmodule
DFF with reset value
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset,
input [7:0] d,
output [7:0] q
);
always @ (negedge clk) begin
if (reset)
q <= 8'h34;
else
q <= d;
end
endmodule
DFF with asynchronous reset
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input areset, // active high asynchronous reset
input [7:0] d,
output [7:0] q
);
always @ (posedge clk or posedge areset) begin
if (areset)
q <= 0;
else
q <= d;
end
endmodule
DFF with byte enable
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input resetn,
input [1:0] byteena,
input [15:0] d,
output [15:0] q
);
always @ (posedge clk) begin
if (~resetn) begin
q <= 16'b0;
end
else begin
q <= {
(({
8{
byteena[1]}} & d[15:8]) | ({
8{
~byteena[1]}} & q[15:8])), (({
8{
byteena[0]}} & d[7:0]) | ({
8{
~byteena[0]}} & q[7:0]))};
end
end
endmodule
D Latch
题目链接
module top_module (
input d,
input ena,
output q);
reg q_reg;
assign q = q_reg;
always @ (*) begin
if (ena)
q_reg <= d;
end
endmodule
DFF
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input d,
input ar, // asynchronous reset
output q);
always @ (posedge clk or posedge ar) begin
if (ar)
q <= 0;
else
q <= d;
end
endmodule
DFF
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input d,
input r, // synchronous reset
output q);
always @ (posedge clk) begin
if (r) begin
q <= 0;
end
else begin
q <= d;
end
end
endmodule
DFF + Gate
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input in,
output out);
always @ (posedge clk) begin
out <= (in ^ out);
end
endmodule
Mux and DFF
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input L,
input r_in,
input q_in,
output reg Q);
wire ff_in = L ? r_in : q_in;
always @ (posedge clk) begin
Q <= ff_in;
end
endmodule
Mux and DFF
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input w, R, E, L,
output Q
);
wire ff_in_1 = E ? w : Q;
wire ff_in = L ? R : ff_in_1;
always @ (posedge clk) begin
Q <= ff_in;
end
endmodule
DFFs and gates
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input x,
output z
);
reg Q_ff1 = 0, Q_ff2 = 0, Q_ff3 = 0;
wire D_ff1, D_ff2, D_ff3;
assign D_ff1 = x ^ Q_ff1;
assign D_ff2 = ~Q_ff2 & x;
assign D_ff3 = ~Q_ff3 | x;
assign z = ~(Q_ff1 | Q_ff2 | Q_ff3);
always @ (posedge clk) begin
Q_ff1 <= D_ff1;
Q_ff2 <= D_ff2;
Q_ff3 <= D_ff3;
end
endmodule
Create circuit from truth table
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input j,
input k,
output Q);
reg Q_old;
always @ (posedge clk) begin
case({
j,k})
2'b00: Q <= Q_old;
2'b01: Q <= 0;
2'b10: Q <= 1;
2'b11: Q <= ~Q_old;
endcase
end
always @ (*) begin
Q_old <= Q;
end
endmodule
Detect an edge
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input [7:0] in,
output [7:0] pedge
);
reg [7:0] in_old = 8'b0;
always @ (posedge clk) begin
pedge <= (in & ~in_old);
in_old <= in;
end
endmodule
Detect both edges
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input [7:0] in,
output [7:0] anyedge
);
reg [7:0] in_old;
always @ (posedge clk) begin
anyedge <= in_old ^ in;
in_old <= in;
end
endmodule
Edge capture register
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset,
input [31:0] in,
output [31:0] out = 32'b0
);
reg [31:0] in_old = 32'b0;
//reg reset_old = 0;
reg [31:0] out_last = 32'b0;
always @ (posedge clk) begin
if (reset) begin
out <= 'b0;
end
else begin
out <= (in_old & ~in) | out_last;
end
in_old <= in;
end
always @ (*) begin
out_last <= out;
end
endmodule
Edge capture register
题目链接
module top_module (
input clk,
input d,
output q
);
reg q_1, q_2;
assign q = clk ? q_1 : q_2;
always @ (posedge clk) begin
q_1 <= d;
end
always @ (negedge clk) begin
q_2 <= d;
end
endmodule
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
622. 设计循环队列
深度学习中数据到底要不要归一化?实测数据来说明!
苹果发布 AI 生成模型 GAUDI,文字生成 3D 场景
【云原生 · Kubernetes】部署Kubernetes集群

The effects of the background and the Activiti
【一起学Rust 基础篇】Rust基础——变量和数据类型
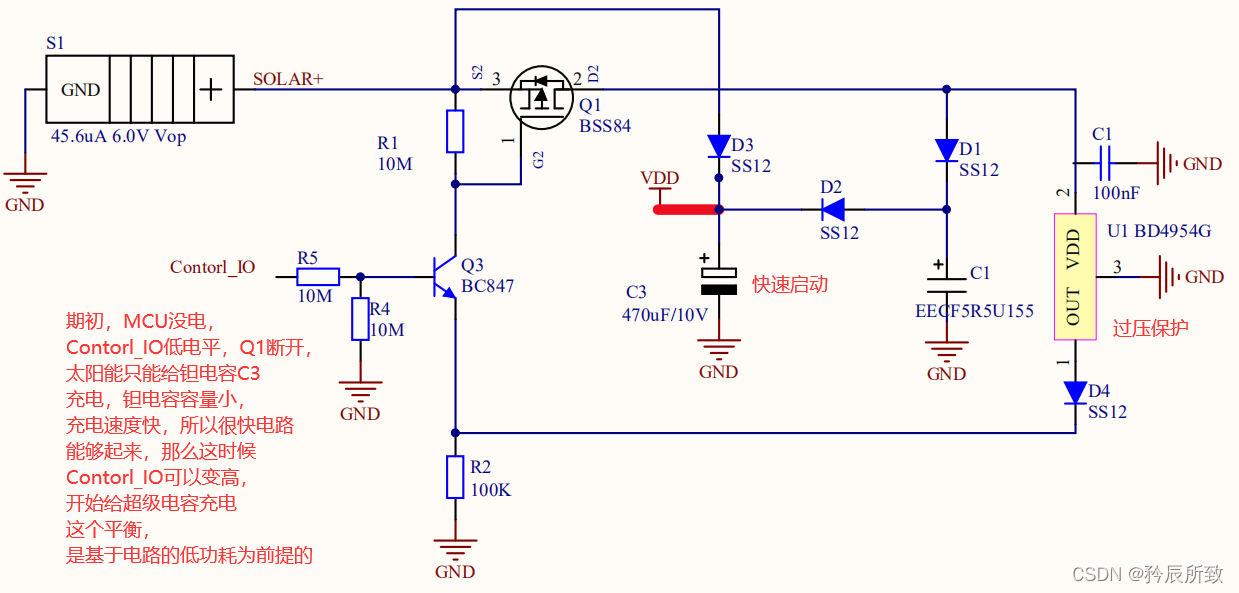
分享一款实用的太阳能充电电路(室内光照可用)
ROS中编译通过但是遇到可执行文件找不到的问题
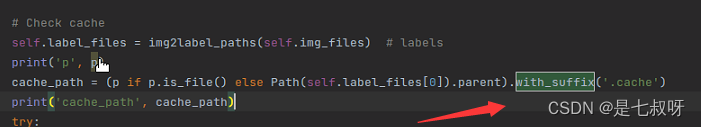
YOLOv5训练数据提示No labels found、with_suffix使用、yolov5训练时出现WARNING: Ignoring corrupted image and/or label
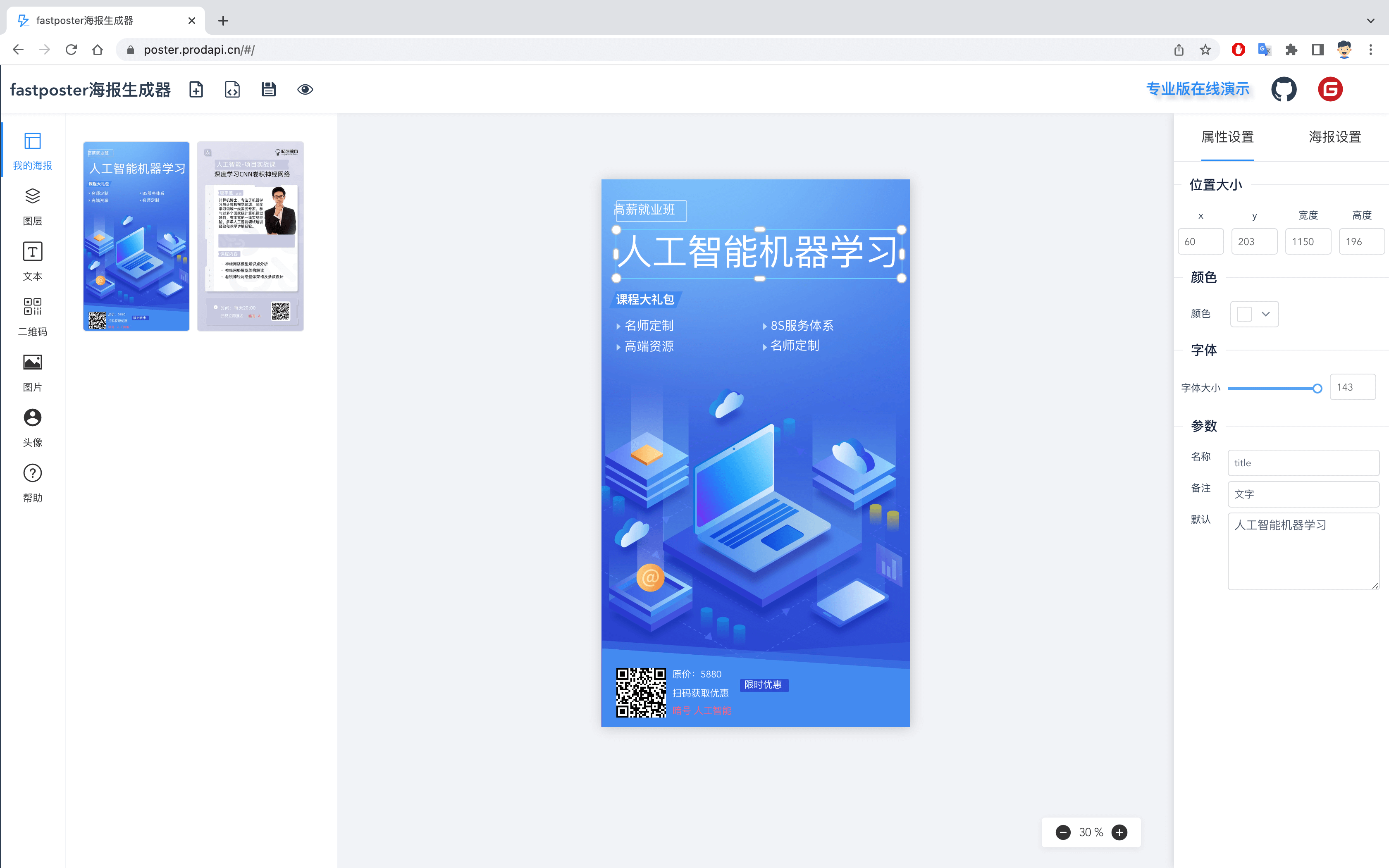
fastposter v2.9.0 程序员必备海报生成器
随机推荐
【Mysql】清理binlog日志的方法
Take you understand the principle of CDN technology
C language advanced article: memory function
第3章 搭建短视频App基础架构
特征工程学习笔记
为什么越来越多的开发者放弃使用Postman,而选择Eolink?
3年软件测试经验,不懂自动化基础...不知道我这种测试人员是不是要被淘汰了?
JUC(三):锁核心类AQS ing
第四周学习 HybridSN,MobileNet V1,V2,V3,SENet
LeetCode-1161. 最大层内元素和
PC client automation testing practice based on Sikuli GUI image recognition framework
流式编程使用场景
零信任架构分析【扬帆】
后台图库上传功能
html网页如何获取后台数据库的数据(html + ajax + php + mysql)
What knowledge points do you need to master to learn software testing?
【HCIP持续更新】STP协议相关保护机制
一个扛住 100 亿次请求的红包系统,写得太好了!!
从器件物理级提升到电路级
常用lambda表达式
