当前位置:网站首页>Summary of common methods of ArrayList, LinkedList and vector, and analysis of source code learning
Summary of common methods of ArrayList, LinkedList and vector, and analysis of source code learning
2022-06-25 15:27:00 【BlackPenguin】
ArrayList
ArrayList It's essentially a The dynamic array , The main difference between it and array is : There is no need to give the exact length in advance , And it can be dynamically expanded , More flexible than arrays .
One 、 Common methods
| Method | meaning |
|---|---|
| .add(Object element) | add to Elements value |
| .add(int index, Object element) | At the specified subscript position index Additive elements value |
| .size() | Number of return elements , namely ArrayList length |
| .get(int index) | obtain Subscript to be index Value |
| .set(int index, Object element) | Replace Subscript index The value of is element, And return the original element value |
| .isEmpty() | Judge Is it empty . empty , Then return to true, Otherwise return to false |
| .contains(Object element) | whether contain Elements element. There is , return true, otherwise , return false |
| .remove(int index) | Delete Subscript index The elements of , And return the element |
| .remove(Object element) | Delete the first time appear element The elements of , Removed successfully , return true; otherwise , return false |
Two 、 Source code
Parameters
// Default initial capacity. Initialize capacity size
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
// Shared empty array instance used for empty instances. Shared empty array for empty instances
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {
};
// Share empty array instances , And EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA Differentiate
// The goal is to see how much more capacity is needed to add the first element
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {
};
// Where real data objects are stored , Does not participate in serialization
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
// The capacity of the list
private int size;
Constructors
// The create capacity size is initialCapacity A list of
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity);
}
}
// Create an empty list
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
// Set Collection The elements of copy Go to the list , And update the size value
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
// If size The length is not 0
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// The length is 0, Then the assignment is null {}
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
add to add
- For each addition, first determine whether there will be out of bounds
- After adding the element for the first time ,ArrayList The capacity of becomes the default initial value 10
- After that, each expansion = Original capacity *1.5 ( In the code, it is expressed as oldCapacity + oldCapacity >> 1)
- List full , Reload all data into a new list , More time-consuming
// Additive elements e
public boolean add(E e) {
// Make sure the capacity after adding the element :size + 1 Will not cross the border
// Capacity expansion , Additive elements
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
// DEFAULT_CAPACITY The initial value is 10
// After adding the element for the first time ,minCapacity Value to 10
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// Dynamic capacity
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// Get the new capacity size dynamically , And change elementData list
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
// The subscript for index Add element at element
public void add(int index, E element) {
// Make sure index No boundaries
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
// Capacity expansion
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);
// Empty the original array index Location
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index);
// Additive elements
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
obtain get
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
// The return subscript is index The elements of
return elementData(index);
}
// Make sure index No boundaries
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
Replace set
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index); // index Don't cross the border
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
// Return old value
return oldValue;
}
Does it include contains
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
3、 ... and 、FailFast Mechanism
Source code has modCount++;, If there are two threads operating on the same ArrayList, May lead to modCount atypism , Concurrency problems occur . therefore , Put forward FailFast Fast failure mechanism , To ensure that there will be Concurrency issues And a protective measure for the internal structure , It throws an exception java.util.ConcurrentModificationException.
LinkedList
LinkedList The essence is Double linked list , Search efficiency is not ArrayList high , But delete 、 High insertion efficiency , because LinkedList No need to move elements .
One 、 Common methods
| Method | meaning |
|---|---|
| .size() | Number of return elements , namely LinkedList length |
| .add(Object element) | add to Elements element ( The queue is pushed in ) |
| .addFirst(Object element) | add to Elements element To the head of the list |
| .addLast(Object element) | add to Elements element To the end of the list |
| .get(int index) | obtain Subscript to be index Value |
| .getFirst(int index) | obtain The first value in the list |
| .getLast(int index) | obtain The last value in the list |
| .set(int index, Object element) | Replace Subscript index The value of is element, And return the original element value |
| .remove(int index) | Delete Subscript index The elements of , And return the element |
| .remove(Object element) | Delete the first time appear element The elements of , Removed successfully , return true; otherwise , return false |
| .removeFirst(int index) | Delete And return the first element |
| .removeLast(Object element) | Delete And return the last element |
| .isEmpty() | Judge Is it empty . empty , Then return to true, Otherwise return to false |
| .contains(Object element) | whether contain Elements element. There is , return true, otherwise , return false |
| .push(Object element) | Elements element Push into the stack |
| .pop() | Pop up stack |
| .peek() | Get stack header Elements |
| .poll() | queue The first eject First element |
Two 、 Source code
Node class
Node classes in the linked list , contain prev Pointer to the previous 、next Pointer to the next 、item Element value
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next; // Next node
Node<E> prev; // Last node
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
add to add、push
add And push Different
add Method to perform tail interpolation , and push It's a head plug ,push Often used Stack The implementation of the .
- add
public boolean add(E e) { // linkLast Add... At the end of the list linkLast(e); return true; } // linkLast Add... At the end of the list void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; } - push
public void push(E e) { addFirst(e); } public void addFirst(E e) { linkFirst(e); } private void linkFirst(E e) { final Node<E> f = first; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); first = newNode; if (f == null) last = newNode; else f.prev = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
obtain get
Find by dichotomy to reduce time . It is essentially traversal .
If index Less than size/2, Start from the head ; conversely , Greater than size/2, Start from the tail
public E get(int index) {
// Make sure index Don't cross the border
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
Node<E> node(int index) {
// get The core of the acquisition method
// Find by dichotomy to reduce time .
// If index Less than size/2, Start from the head
// conversely , Greater than size/2, Start from the tail
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
Vector
Vector Be similar to ArrayList, It's also a dynamic array . But it has obsolete , because Vector Every operation method in the is synchronized , very Time consuming (Vector It's thread safe ).
For example, the following Vector Of add Method , And ArrayList be similar , But it uses synchronized To modify .Vector Many of the operation methods of are synchronized modification .
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
A small summary
Through the above study, we can know ArrayList、LinkedList It's not thread safe , and Vector Thread safety . But because of Vector A lot of use
synchronizedMethod , Resulting in low performance , therefore Vector It is not recommended to use .The need to Handle synchronization issues with lists when , You can use the collection tool class Collections Turn the thread unsafe list into thread safe .
List syncList = Collections.synchronizedList(list);The method of this tool class is essentially to add synchronized code blocks to the list operation to make it thread safe .Use LinkedList Stack can be implemented 、 The data structure of the queue
Stack The implementation of the
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(3); int var = stack.pop();queue The implementation of the
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.add(3); int var = queue.poll();
边栏推荐
- Esp8266 building smart home system
- Leetcode122 timing of buying and selling stocks II
- [untitled] PTA check password
- Usage of qlist
- Installing QT plug-in in Visual Studio
- [paper notes] overview of case segmentation
- QT pop up open file dialog box QFileDialog
- p1408
- Architecture evolution of high-performance servers -- Suggestions
- QT database connection
猜你喜欢
![[paper notes] poly yolo: higher speed, more precise detection and instance segmentation for yolov3](/img/28/6d58759a4a4b18923a5ed5ed573956.jpg)
[paper notes] poly yolo: higher speed, more precise detection and instance segmentation for yolov3
Advertising effect cluster analysis (kmeans)

System Verilog - thread

QT set process startup and self startup

Learning notes on February 18, 2022 (C language)

Summary of four parameter adjustment methods for machine learning
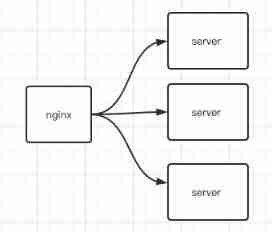
Websocket (WS) cluster solution
Summary of regularization methods

Iterator failure condition
Graphic control and layout basis of R visualization
随机推荐
Solve valueerror: invalid literal for int() with base 10
Generation method and usage of coredump
[paper notes] contextual transformer networks for visual recognition
Business layer - upper and lower computer communication protocol
Usage of qlist
Dynamic memory allocation
Learning notes on February 8, 2022 (C language)
System Verilog - function and task
Some usage records about using pyqt5
Design and implementation of timer
QT article outline
2.18 codeforces supplement
Go language modifies / removes multiple line breaks in strings
CV pre training model set
Modal and modeless dialogs for QT
A deformation problem of Hanoi Tower
QT database connection deletion
(translation) json-rpc 2.0 specification (Chinese version)
The difference between sizeof and strlen
Yolov5 Lite: fewer parameters, higher accuracy and faster detection speed