当前位置:网站首页>属性动画的用法 以及ButterKnife的用法
属性动画的用法 以及ButterKnife的用法
2022-08-04 05:28:00 【N_Y_S】
重点
1.属性动画 2.黄油刀ButterKnife
内容
什么是属性动画:属性动画是从3.0及以后出现的(如果要兼容低版本,可以使用一个民间版第三方的一个jar NineOldAndroid.jar,用法跟系统的用法差不多)。
不断地控制控件的属性变化达到动画的效果,一般我们是一些组合的属性动画达到复杂的效果。
属性动画的用法
1.在xml文件中添加控件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="15dp"
android:id="@+id/lv_root"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_1"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="动画一" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_2"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="动画二" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_3"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="动画三" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_4"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="动画四" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_5"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="动画五" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/img"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:background="@mipmap/a006" />
</LinearLayout>2.在ActivityJava文件中设置按钮的点击事件
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private Button btn_1;
private Button btn_2;
private Button btn_3;
private Button btn_4;
private Button btn_5;
private ImageView img;
private LinearLayout lv_root;
int width,height;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
btn_1=findViewById(R.id.btn_1);
btn_2=findViewById(R.id.btn_2);
btn_3=findViewById(R.id.btn_3);
btn_4=findViewById(R.id.btn_4);
btn_5=findViewById(R.id.btn_5);
img=findViewById(R.id.img);
lv_root=findViewById(R.id.lv_root);
btn_1.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_2.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_3.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_4.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_5.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
switch (view.getId()){
case R.id.btn_1:
break;
case R.id.btn_2:
case R.id.btn_3:
break;
case R.id.btn_4:
break;
case R.id.btn_5:
break;
}
}
}3.设置图片的移动动画,(这里是从上到下移动)
switch (view.getId()){
case R.id.btn_1:
width = lv_root.getWidth();
height = lv_root.getHeight();
ValueAnimator valueAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofInt(0, height / 4, height / 2, height / 4 * 3, height);
valueAnimator.setDuration(3000L);
valueAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
int y= (Integer) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();
int x=width/2;
moveView(img,x,y);
}
});
valueAnimator.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());
valueAnimator.start();
break;4.设置图片的旋转缩放动画
case R.id.btn_3:
AnimatorSet scaleSet=new AnimatorSet();
ValueAnimator setAnim=ValueAnimator.ofFloat(1.0f,0.5f,1.2f,1.0f,0.6f,1.2f,1.0f);
setAnim.setDuration(2000l);
ValueAnimator ra=ValueAnimator.ofInt(0,360);
ra.setDuration(2000l);
setAnim.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
float scale= (float)valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();
img.setScaleX(scale);
img.setScaleY(scale);
}
});
ra.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
int rotate=(int)valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();
img.setRotation(rotate);
}
});
scaleSet.playTogether(setAnim,ra);
//scaleSet.play(setAnim).after(ra);
scaleSet.start();5.设置图片的旋转渐变动画
case R.id.btn_4:
ValueAnimator raValue=ValueAnimator.ofInt(0,360);
raValue.setDuration(1000l);
raValue.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
int rotate= (int) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();
img.setRotation(rotate);
float alpha=valueAnimator.getAnimatedFraction();
img.setAlpha(alpha);
}
});
raValue.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());
raValue.start();
break;ButterKnife的使用
1.引入依赖
implementation 'com.jakewharton:butterknife:10.2.3'// 添加此依赖 annotationProcessor 'com.jakewharton:butterknife-compiler:10.2.3'// 添加此规则
2.在java文件中使用,绑定控件
@BindView(R.id.button1)
Button button1;
@BindView(R.id.button2)
Button button2;
@BindView(R.id.button3)
Button button3;
@BindView(R.id.button4)
Button button4;3.在orCreate中启动绑定
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2);
ButterKnife.bind(this);
}4.设置点击事件
@OnClick({R.id.button1,R.id.button2,R.id.button3,R.id.button4})
public void onClick(View v){
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.button1:
Toast.makeText(this, "按钮1", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case R.id.button2:
Toast.makeText(this, "按钮2", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case R.id.button3:
Toast.makeText(this, "按钮3", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case R.id.button4:
Toast.makeText(this, "按钮4", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
}
}边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
webrtc中的任务队列TaskQueue
MySql--存储引擎以及索引
自动化运维工具Ansible(1)基础

实际开发中左菜单自定义图标点击切换
npm install dependency error npm ERR! code ENOTFOUNDnpm ERR! syscall getaddrinfonpm ERR! errno ENOTFOUND
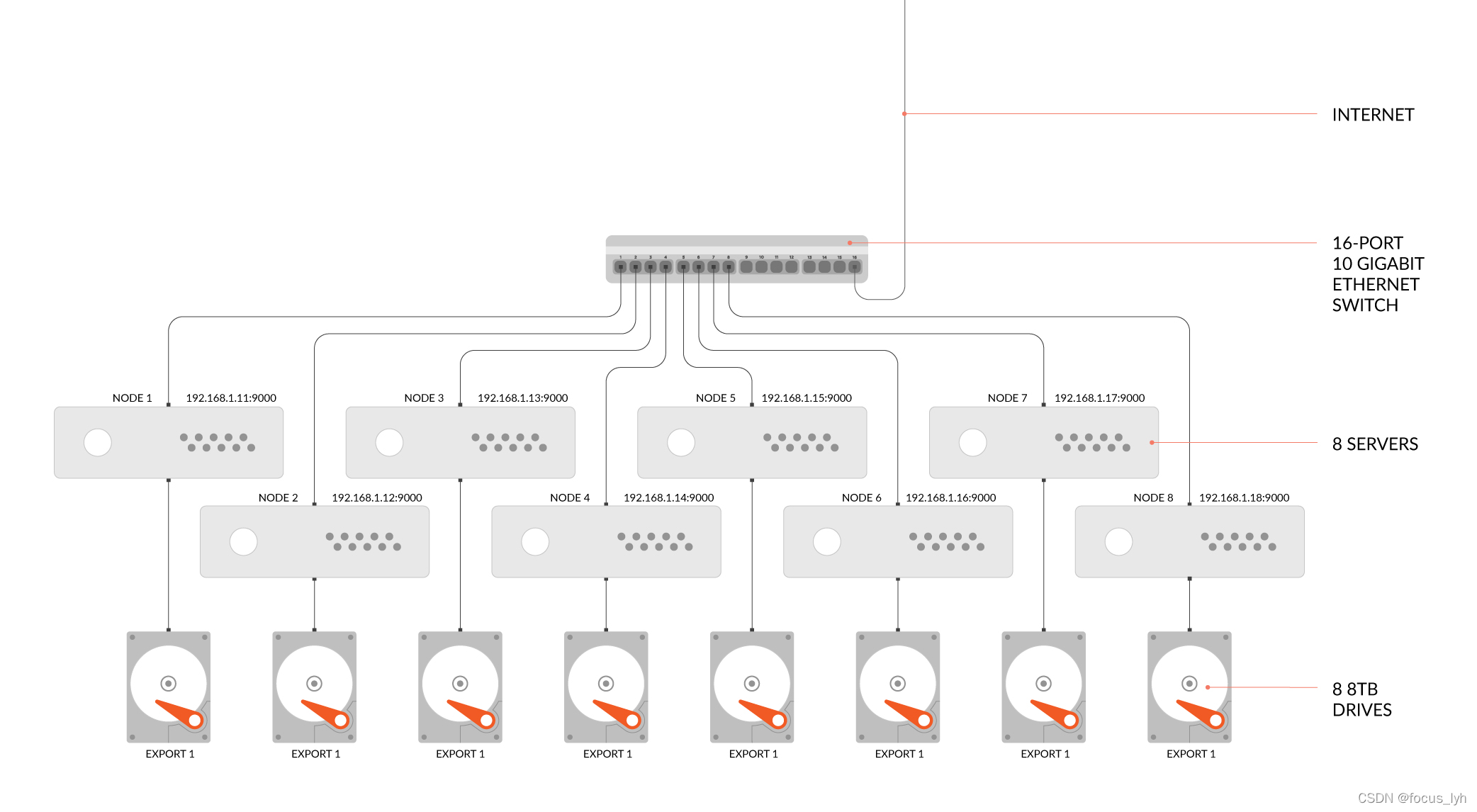
对象存储-分布式文件系统-MinIO-2:服务端部署
Delphi-C side interesting menu operation interface design
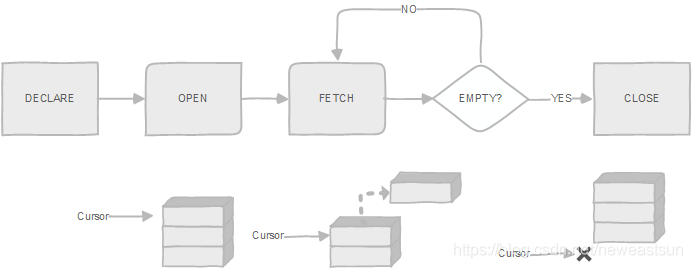
postgresql 游标(cursor)的使用
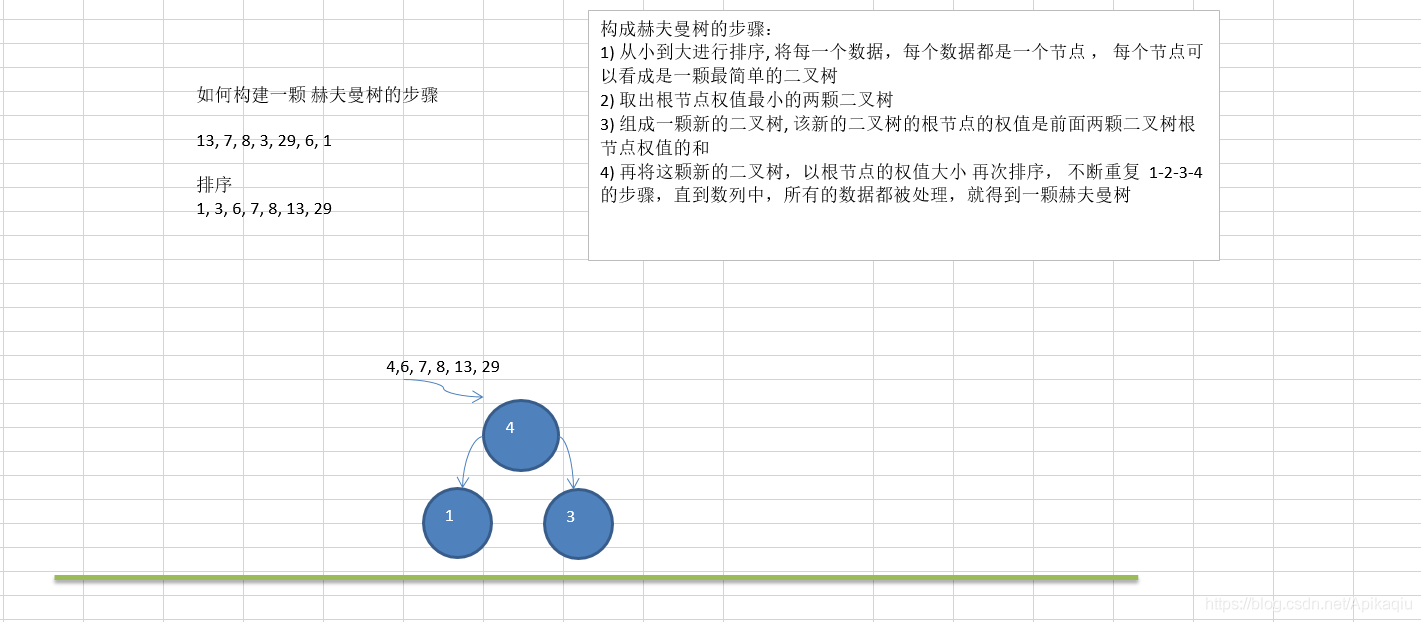
(十二)树--哈夫曼树
超详细MySQL总结
随机推荐
基于C语言的学生信息管理系统_(更新版)_(附源码和安装包)_课程设计_**往事随風**的博客
剑指 Offer 20226/30
iptables防火墙
SQL练习 2022/7/4
bind和function
网络大作业心得笔记
自动化运维工具Ansible(6)Jinja2模板
剑指 Offer 2022/7/9
详解“Node实现数据加密”过程
实际开发中,如何实现复选框的全选和不选
编程Go:学习目录
flink-sql所有语法详解
WARNING: sql version 9.2, server version 11.0.Some psql features might not work.
PostgreSQL模式(Schema)
Kubernetes基础入门(完整版)
k3s-轻量级Kubernetes
数据库根据提纲复习
JS原型链
完美解决keyby造成的数据倾斜导致吞吐量降低的问题
MySql--存储引擎以及索引