当前位置:网站首页>[Yugong series] go teaching course 005 variables in July 2022
[Yugong series] go teaching course 005 variables in July 2022
2022-07-07 04:53:00 【InfoQ】
One 、 Variable
1. Definition of variables
2. Role of variables

3. Variable declaration and initialization
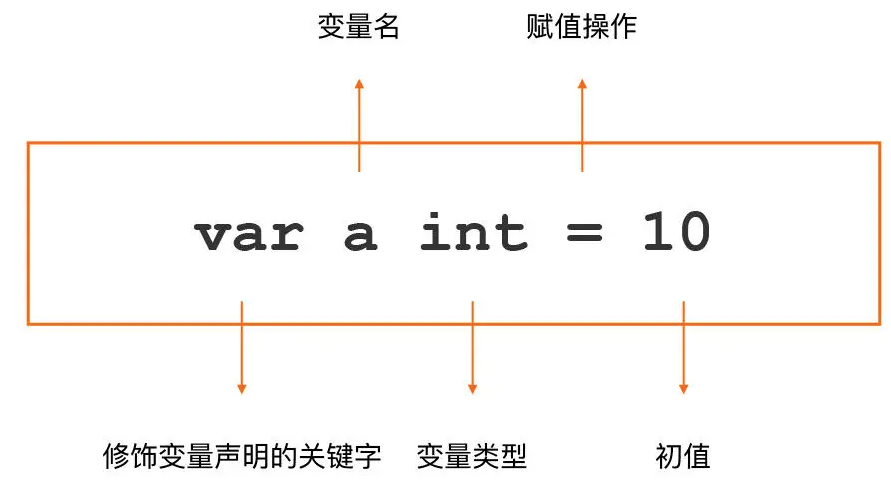
3.1 Declaration of variables
fmt.Println(a)
3.2 Initialization of a variable
var age int=10
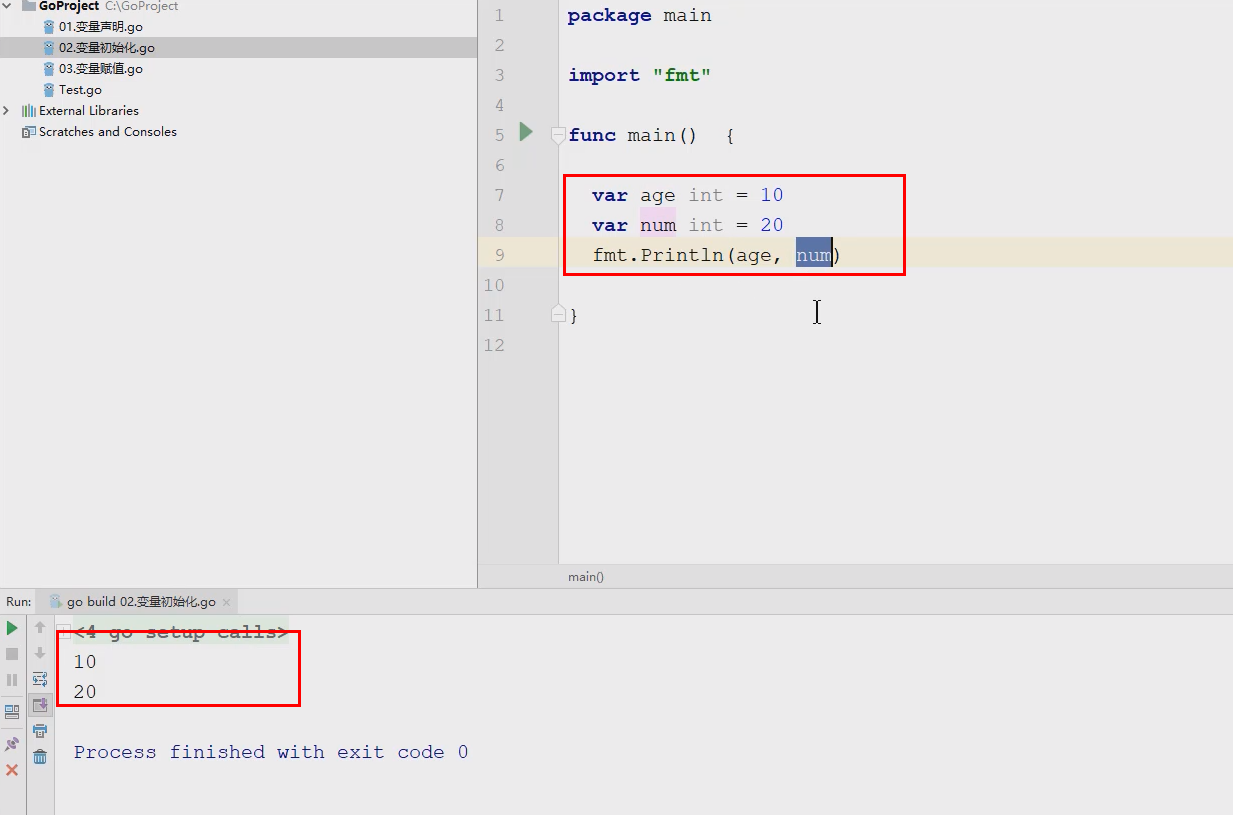
3.3 The assignment of a variable
var age,num int
age=10
num=20
fmt.Println(age,num) //10,20
var age int =10
var num int
num=age
fmt.Println(num) //10
3.4 Case study : Exchange the values of two variables
package main
import "fmt"
func main(){
a := 1
b := 5
var t int
t = a
a = b
b = t
fmt.Println("a = ", a, "b = ", b )
}
package main
import "fmt"
func main(){
a := 1
b := 5
a = a + b
b = a - b
a = a - b
fmt.Println("a = ", a, "b = ", b )
}
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
a := []int{1, 2}
b := []int{3, 4, 5}
a, b = b, a
fmt.Println(`a:`, a)
fmt.Println(`b:`, b)
}
summary
- Variable declarations :var Variable name variable type
- Declare multiple variables :var Variable name 1, Variable name .... type
- Declare an integer variable , The default value is 0
- Output statements can use only one Println function , The middle part is separated by English half width commas !
- You can set the value of a variable , Assign to another variable , And the old value in the variable is overwritten by the new value .
边栏推荐
- What work items do programmers hate most in their daily work?
- [hand torn STL] list
- Vscode 如何使用内置浏览器?
- If you ask me about R code debugging, I will tell you head, STR, help
- 为什么很多人对技术债务产生误解
- [digital analog] source code of MATLAB allcycles() function (not available before 2021a)
- sscanf,sscanf_s及其相关使用方法「建议收藏」
- 广告归因:买量如何做价值衡量?
- JDBC link Oracle reference code
- Station B boss used my world to create convolutional neural network, Lecun forwarding! Burst the liver for 6 months, playing more than one million
猜你喜欢

JS also exports Excel

计数排序基础思路

九章云极DataCanvas公司摘获「第五届数字金融创新大赛」最高荣誉!
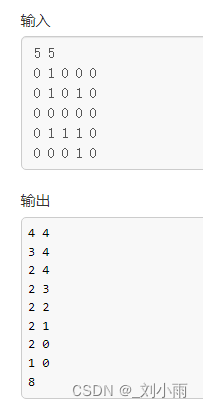
DFS和BFS概念及实践+acwing 842 排列数字(dfs) +acwing 844. 走迷宫(bfs)
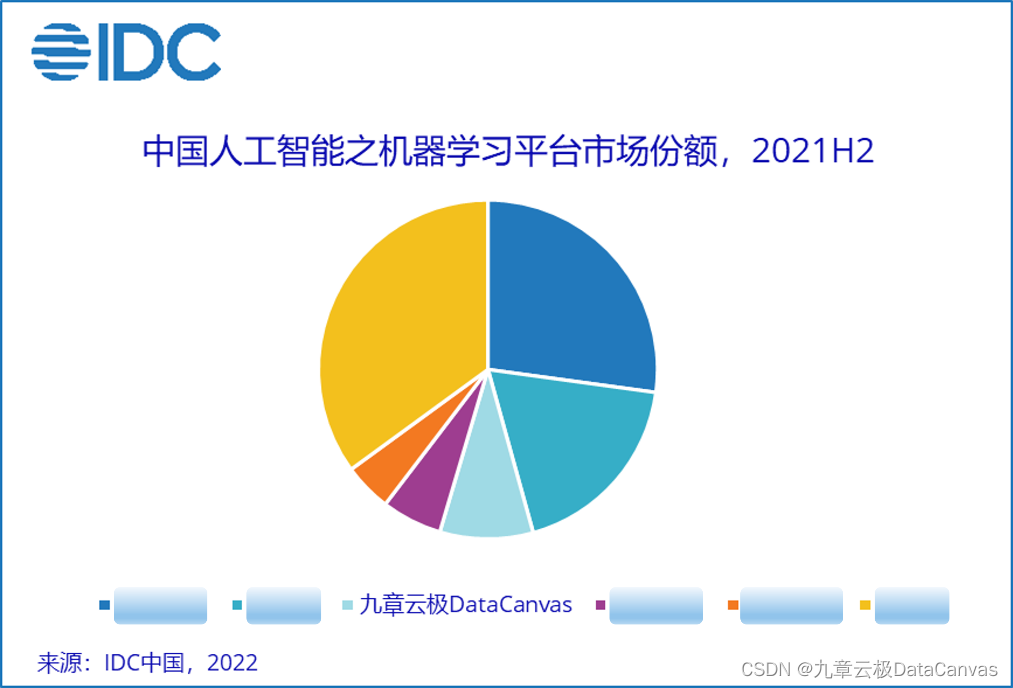
Chapter 9 Yunji datacanvas company has been ranked top 3 in China's machine learning platform market
![[hand torn STL] list](/img/aa/7060ab20b41936419041067cf9daed.jpg)
[hand torn STL] list
程序员上班摸鱼,这么玩才高端!
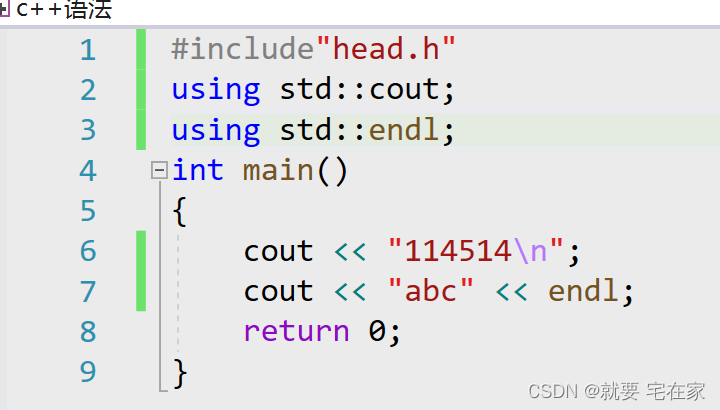
namespace基础介绍

窗口可不是什么便宜的东西

Common methods of list and map
随机推荐
leetcode 53. Maximum subarray maximum subarray sum (medium)
[line segment tree practice] recent requests + area and retrieval - array modifiable + my schedule I / III
Intel David tuhy: the reason for the success of Intel aoten Technology
Comment les tests de logiciels sont - ils effectués sur le site Web? Testez la stratégie!
史上最全学习率调整策略lr_scheduler
Unit test asp Net MVC 4 Application - unit testing asp Net MVC 4 apps thoroughly
Case reward: Intel brings many partners to promote the innovation and development of multi domain AI industry
Section 1: (3) logic chip process substrate selection
一图看懂!为什么学校教了你Coding但还是不会的原因...
Acl2022 | decomposed meta learning small sample named entity recognition
JS variable case
JDBC link Oracle reference code
Thesis landing strategy | how to get started quickly in academic thesis writing
leetcode 53. Maximum Subarray 最大子数组和(中等)
Vscode 如何使用内置浏览器?
Terms used in the Web3 community
JS also exports Excel
acwing 843. N-queen problem
Master the secrets of software security testing methods, and pinch the security test report with your hands
This "advanced" technology design 15 years ago makes CPU shine in AI reasoning