当前位置:网站首页>How to expand the capacity of golang slice slice
How to expand the capacity of golang slice slice
2022-07-03 18:00:00 【Bald cat light King】
Golang Slice How to expand the slice
Golang Easy to learnList of articles
One 、Slice What is the data structure ?
section (slice) yes Golang A special data structure , This data structure makes it easier to use and manage data sets . Slicing is built around the concept of dynamic arrays , Can automatically grow and shrink on demand . section (slice) It can be regarded as an array with variable length .
section (slice) Itself is not a dynamic array or array pointer . Its internal data structure refers to the underlying array through the pointer , Set the relevant properties to limit the data reading and writing operations in the specified area .
section (slice) Is a reference to a contiguous fragment of an array , So slicing is a reference type .
Two 、 Detailed code
1. data structure
slice The structure of is composed of 3 Part of the form ,Pointer Is a pointer to an array ,len Represents the length of the current slice ,cap Is the capacity of the current slice .cap Always greater than or equal to len Of .
Usually we are talking about slice Conduct append When waiting for operation , It may cause slice Automatic expansion of .
The code is as follows ( Example ):
type slice struct {
array unsafe.Pointer
len int
cap int
}
2. Expansion principle
If the capacity of the slice is less than 1024 Elements , So when we expand capacity slice Of cap Multiply by 2; Once the number of elements exceeds 1024 Elements , The growth factor is zero 1.25, That's a quarter of the original capacity at a time .
If after the expansion , We haven't touched the capacity of the original array yet , that , The position of the pointer in the slice , It's still the original array , If after the expansion , Exceeds the capacity of the original array , that ,Go Will open up a new memory , Copy the original value , This does not affect the original array at all .
2. How to understand expansion rule 1
Rule one :
If the capacity of the slice is less than 1024 Elements , So when we expand capacity slice Of cap Multiply by 2; Once the number of elements exceeds 1024 Elements , The growth factor is zero 1.25, That's a quarter of the original capacity at a time .
1. When less than 1024 Element time
The code is as follows ( Example ):
func main() {
// Establish a capacity of 2 Of section
addCap := make([]string, 0, 2)
// Insert a number , Occupy one capacity
addCap = append(addCap, "1")
// Print the address at this time
fmt.Println("addCap 1", addCap, cap(addCap), &addCap[0])
// Insert a number , Occupy one capacity
// Then print the address at this time
addCap = append(addCap, "1")
fmt.Println("addCap 2", addCap, cap(addCap), &addCap[0])
// Insert a number , Occupy one capacity
// Then print the address at this time
addCap = append(addCap, "1")
// At this time, the three numbers have exceeded the capacity , Then the slice capacity will be expanded , At this time, the address will also become a new address
fmt.Println("addCap 3", addCap, cap(addCap), &addCap[0])
}
result ( Example ):
2. When more than 1024 Element time
The code is as follows ( Example ):
func main() {
// Establish a capacity of 1022 Of section
addCap1024 := make([]int, 1022, 1024)
// Insert a number , Occupy one capacity Capacity 1023
addCap1024 = append(addCap1024, 1)
// Print the address at this time
fmt.Println("addCap1024 1", cap(addCap1024), &addCap1024[0])
// Insert a number , Occupy one capacity
// Then print the address at this time
addCap1024 = append(addCap1024, 1)
fmt.Println("addCap1024 2", cap(addCap1024), &addCap1024[0])
// Insert a number , Occupy one capacity
// Then print the address at this time
addCap1024 = append(addCap1024, 1)
// At this time, the three numbers have exceeded the capacity 1024, Then the slice capacity will be expanded , At this time, the address will also become a new address
fmt.Println("addCap1024 3", cap(addCap1024), &addCap1024[0])
}
result ( Example ):
At this time, the capacity Cap Added 1280 - 1024 = 256 , That is to say 1024 Of 25 %
namely The growth factor is zero 1.25, That's a quarter of the original capacity at a time .
2. How to understand expansion rule 2
Rule one :
If after the expansion , We haven't touched the capacity of the original array yet , that , The position of the pointer in the slice , It's still the original array , If after the expansion , Exceeds the capacity of the original array , that ,Go Will open up a new memory , Copy the original value , This does not affect the original array at all .
1. Simply understand memory address replacement
The code is as follows ( Example ):
func main() {
// Establish a capacity of 2 Of section
addCap := make([]string, 0, 2)
// Insert a number , Occupy one capacity
addCap = append(addCap, "1")
// Print the address at this time
fmt.Println("addCap 1", addCap, cap(addCap), &addCap[0])
// Insert a number , Occupy one capacity
// Then print the address at this time
addCap = append(addCap, "1")
fmt.Println("addCap 2", addCap, cap(addCap), &addCap[0])
// take oth The pointer to the slice address
// Then print the address at this time and addCap equally , That is, when the capacity is not touched , Or the original array
oth := addCap[0:1]
fmt.Println("oth 1",oth,cap(oth),&oth[0])
// At this time, modify the original array oth The address pointed to remains unchanged , But the value of the first number has changed 3
addCap[0] = "3"
fmt.Println("oth 2",oth,cap(oth),&oth[0])
// Insert a number , Occupy one capacity
// Then print the address at this time
addCap = append(addCap, "1")
// Modify again at this time It is already the new address after expansion The original array will remain unchanged namely oth The value of the address pointed to remains unchanged
addCap[0] = "4"
// At this time, the three numbers have exceeded the capacity , Then the slice capacity will be expanded , At this time, the address will also become a new address , The first number will also be changed to 4
fmt.Println("addCap 3", addCap, cap(addCap), &addCap[0])
// but oth It still retains the pointer address of the original array , So still 3
fmt.Println("oth 3",oth,cap(oth),&oth[0])
}
result ( Example ):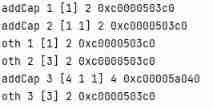
At this time, the capacity Oth Point to the original slice location , The new slice after expansion points to a new location , The changes made will not affect the original slice .
summary
Through the above two examples, you can easily understand in Golang The main form of medium slice expansion . Because the bottom layer of the slice is also allocated in consecutive memory blocks , So slices can also get indexes 、 The benefits of iteration and Optimization for garbage collection , It is very suitable for our in-depth study .
I hope this blog will be beneficial to you . I am the light king , I represent myself. .边栏推荐
- Graduation summary
- A. Odd Selection【BruteForce】
- This diversion
- The second largest gay dating website in the world was exposed, and the status of programmers in 2022
- Detailed explanation of common network attacks
- 圖像24比特深度轉8比特深度
- 【统信UOS】扫描仪设备管理驱动安装
- A. Berland Poker & 1000 [simple mathematical thinking]
- Automata and automatic line of non-standard design
- supervisor监控Gearman任务
猜你喜欢

QT learning diary 9 - dialog box
Discussion sur la logique de conception et de mise en oeuvre du processus de paiement

Leetcode Valentine's Day Special - looking for a single dog
Draw some simple graphics with MFC
![AcWing 271. Teacher Yang's photographic arrangement [multidimensional DP]](/img/3d/6d61fefc62063596221f98999a863b.png)
AcWing 271. Teacher Yang's photographic arrangement [multidimensional DP]

Three gradient descent methods and code implementation
![Lesson 13 of the Blue Bridge Cup -- tree array and line segment tree [exercise]](/img/da/0a282b4773fe3909d1e5e9d19f8549.jpg)
Lesson 13 of the Blue Bridge Cup -- tree array and line segment tree [exercise]

Market demand survey and marketing strategy analysis report of global and Chinese pet milk substitutes 2022-2028

Vs2013 has blocked the installer, and ie10 needs to be installed
模块九作业
随机推荐
Image 24 bits de profondeur à 8 bits de profondeur
SQL injection database operation foundation
[tutorial] build your first application on coreos
The difference between i++ and ++i: tell their differences easily
[linux]centos 7 reports an error when installing MySQL "no package MySQL server available" no package ZABBIX server MySQL available
Kotlin的协程:上下文
Three gradient descent methods and code implementation
统计图像中各像素值的数量
解决Zabbix用snmp监控网络流量不准的问题
Basic grammar of interview (Part 2)
PHP MySQL order by keyword
SDNUOJ1015
Global and Chinese pediatric palliative care drug market development research and investment planning recommendations report 2022-2028
STM32 realizes 74HC595 control
How to draw non overlapping bubble chart in MATLAB
[combinatorics] generating function (shift property)
数学公式(测试)
Module 9 operation
[combinatorics] recursive equation (case where the non-homogeneous part is exponential | example where the non-homogeneous part is exponential)
PHP MySQL create database