当前位置:网站首页>Common loss function of deep learning
Common loss function of deep learning
2022-07-02 00:35:00 【Falling flowers and rain】
List of articles
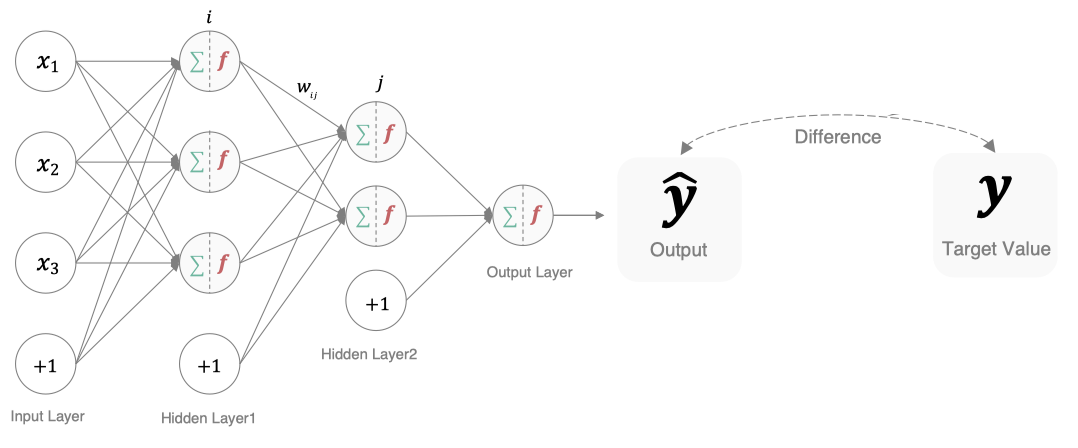
In deep learning , Loss function is a function used to measure the quality of model parameters , The way to measure is to compare the difference between network output and real output , The name of loss function is different in different literatures , There are mainly the following naming methods :

1. Classification task
The cross entropy loss function is most used in the classification task of deep learning , So here we focus on this loss function .
1.1 Multi category tasks
In multi classification tasks, we usually use softmax take logits In the form of probability , Therefore, the cross entropy loss of multi classification is also called softmax Loss , Its calculation method is :
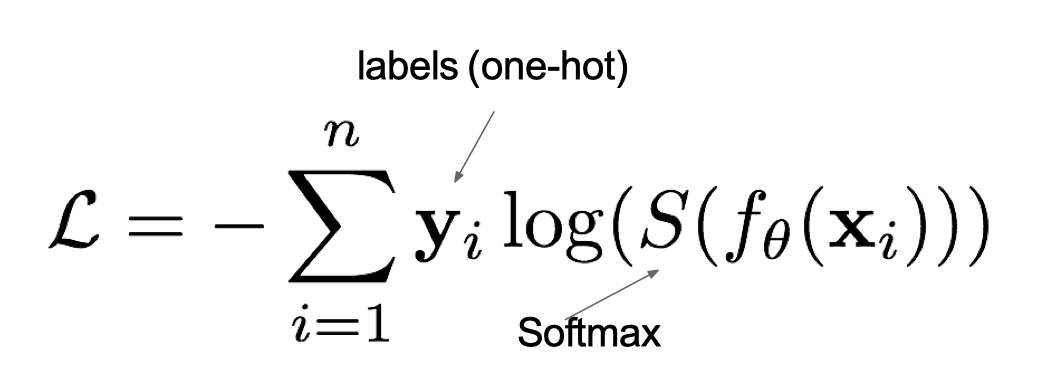
among ,y Is the sample x The true probability of belonging to a category , and f(x) Is the prediction score of the sample belonging to a certain category ,S yes softmax function ,L To measure p,q The difference between the loss results .
Example :

The cross entropy loss in the above figure is :

Understand... From the perspective of probability , Our goal is to minimize the negative value of the logarithm of the prediction probability corresponding to the correct category , As shown in the figure below :

stay tf.keras Use in CategoricalCrossentropy Realization , As shown below :
# Import the corresponding package
import tensorflow as tf
# Set true and predicted values
y_true = [[0, 1, 0], [0, 0, 1]]
y_pred = [[0.05, 0.95, 0], [0.1, 0.8, 0.1]]
# Instantiation cross entropy loss
cce = tf.keras.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy()
# Calculate the loss result
cce(y_true, y_pred).numpy()
The result is :
1.176939
1.2 2. Classified tasks
When processing task 2 , We're not using softmax Activation function , But use sigmoid Activation function , The loss function is adjusted accordingly , Using the cross entropy loss function of binary classification :

among ,y Is the sample x The true probability of belonging to a category , and y^ Is the prediction probability that the sample belongs to a certain category ,L The loss result used to measure the difference between the real value and the predicted value .
stay tf.keras When implemented in BinaryCrossentropy(), As shown below :
# Import the corresponding package
import tensorflow as tf
# Set true and predicted values
y_true = [[0], [1]]
y_pred = [[0.4], [0.6]]
# Cross entropy loss of instantiated binary classification
bce = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy()
# Calculate the loss result
bce(y_true, y_pred).numpy()
The result is :
0.5108254
2. Return to the task
The loss functions commonly used in regression tasks are as follows :
2.1 MAE Loss
Mean absolute loss(MAE) Also known as L1 Loss, It takes the absolute error as the distance :
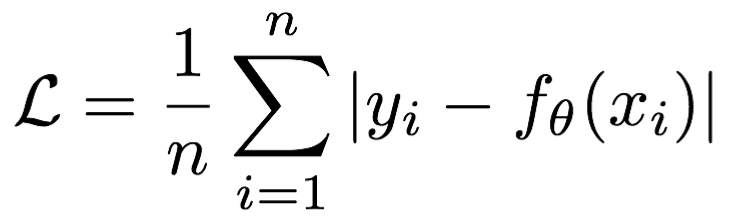
The curve is shown in the figure below :
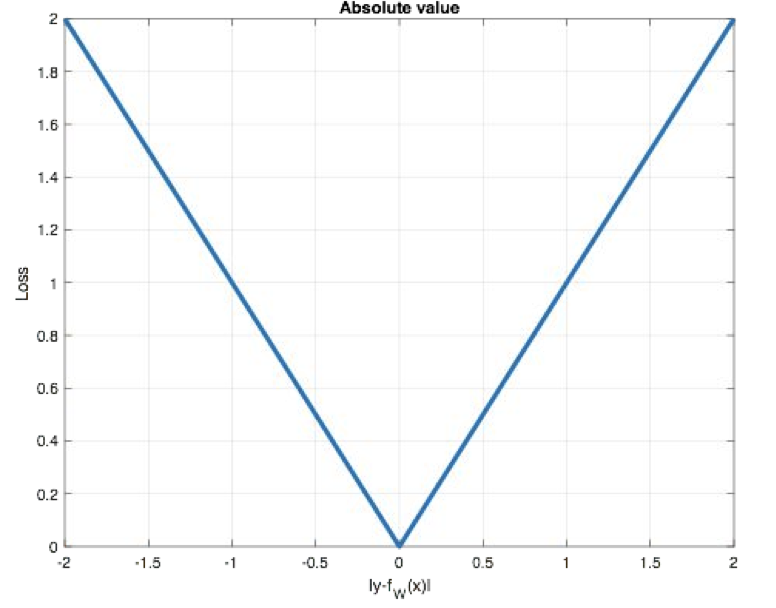
Characteristic is : because L1 loss Have sparsity , To punish larger values , Therefore, it is often added as a regular item to other loss As a constraint .L1 loss The biggest problem is that the gradient is not smooth at zero , Causes the minimum to be skipped .
stay tf.keras Use in MeanAbsoluteError Realization , As shown below :
# Import the corresponding package
import tensorflow as tf
# Set true and predicted values
y_true = [[0.], [0.]]
y_pred = [[1.], [1.]]
# Instantiation MAE Loss
mae = tf.keras.losses.MeanAbsoluteError()
# Calculate the loss result
mae(y_true, y_pred).numpy()
The result is :
1.0
2.2 MSE Loss
Mean Squared Loss/ Quadratic Loss(MSE loss) Also known as L2 loss, Or Euclidean distance , It takes the sum of the squares of the errors as the distance :

The curve is shown in the figure below :

Characteristic is :L2 loss It is also often used as a regular term . When the predicted value is very different from the target value , Gradients explode easily .
stay tf.keras Pass through MeanSquaredError Realization :
# Import the corresponding package
import tensorflow as tf
# Set true and predicted values
y_true = [[0.], [1.]]
y_pred = [[1.], [1.]]
# Instantiation MSE Loss
mse = tf.keras.losses.MeanSquaredError()
# Calculate the loss result
mse(y_true, y_pred).numpy()
The result is :
0.5
2.3 smooth L1 Loss
Smooth L1 The loss function is as follows :

among : 𝑥 = f ( x ) − y 𝑥=f(x)−y x=f(x)−y Is the difference between the real value and the predicted value .

As can be seen from the above figure , This function is actually a piecewise function , stay [-1,1] Between is actually L2 Loss , That's it L1 The problem of unsmooth , stay [-1,1] Outside the range , It's actually L1 Loss , This solves the problem of gradient explosion of outliers . This loss function is usually used in target detection .
stay tf.keras Use in Huber Calculate the loss , As shown below :
# Import the corresponding package
import tensorflow as tf
# Set true and predicted values
y_true = [[0], [1]]
y_pred = [[0.6], [0.4]]
# Instantiation smooth L1 Loss
h = tf.keras.losses.Huber()
# Calculate the loss result
h(y_true, y_pred).numpy()
result :
0.18
summary
Know the loss function of classification task
The cross entropy loss function of multi classification and the cross entropy loss function of two classificationKnow the loss function of the regression task
MAE,MSE,smooth L1 Loss function
边栏推荐
- Slf4j print abnormal stack information
- Review data desensitization system
- To meet the needs of consumers in technological upgrading, Angel water purifier's competitive way of "value war"
- Is it safe and reliable to open an account in Caixue school and make new debts?
- From 20s to 500ms, I used these three methods
- BPR (Bayesian personalized sorting)
- Talents come from afar, and Wangcheng district has consolidated the intellectual base of "strengthening the provincial capital"
- Use es to realize epidemic map or take out order function (including code and data)
- 2023 Lexus ES products have been announced, which makes great progress this time
- Is it safe to choose mobile phone for stock trading account opening in Beijing?
猜你喜欢

Leetcode skimming: stack and queue 04 (delete all adjacent duplicates in the string)

How do Lenovo computers connect Bluetooth headsets?
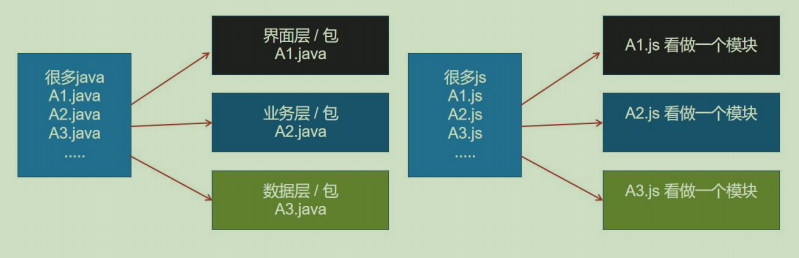
Promise and modular programming
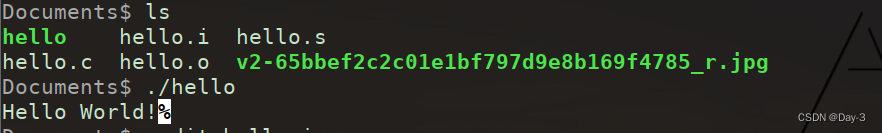
GCC compilation
Leetcode skimming: stack and queue 03 (valid parentheses)
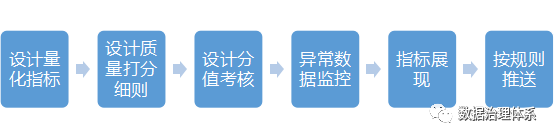
How to improve data quality

Heketi record

Ldr6035 smart Bluetooth audio can continuously charge and discharge mobile devices

Leetcode question brushing: stack and queue 07 (maximum value of sliding window)

Niuke - Practice 101 - reasoning clown
随机推荐
EMC circuit protection device for surge and impulse current protection
Qt5.12.9 migration tutorial based on Quanzhi H3
Niuke - Practice 101 - reasoning clown
RFID makes the inventory of fixed assets faster and more accurate
Weather forecast applet source code weather wechat applet source code
【底部弹出-选择器】uniapp Picker组件——底部弹起的滚动选择器
Example explanation: move graph explorer to jupyterlab
From 20s to 500ms, I used these three methods
【模板】自适应辛普森积分
Leetcode skimming: binary tree 03 (post order traversal of binary tree)
Node -- egg implements the interface of uploading files
449-原码、补码、反码
Leetcode question brushing: stack and queue 07 (maximum value of sliding window)
LeetCode 0241. Design priority for arithmetic expressions - DFS
Leetcode skimming: stack and queue 03 (valid parentheses)
[leetcode] number of maximum consecutive ones
How to open an account for individual stock speculation? Is it safe?
SQL数据分析之子查询的综合用法和案例题【耐心整理】
How to type spaces in latex
二叉搜索树的创建,查找,添加,删除操作