当前位置:网站首页>11. Synchronized and lock escalation
11. Synchronized and lock escalation
2022-06-11 12:14:00 【Shixiaozan】
1、 Some interview questions
Talk to you about Synchronized The understanding of the
Synchronized Lock upgrade for you to talk about
Synchronized Is the performance necessarily weaker than Lock

2、 This chapter outlines the route
synchronized Background of lock optimization
Data can be locked Security , But it will bring Performance degradation .
Lockless can improve program performance based on thread parallelism , But it will bring Security is down .
Balance ???

synchronized lock : By the Mark Word It is multiplexed according to different lock flag bits and lock escalation strategy
3、Synchronized Performance changes
3.1、java5 before , Only Synchronized, This is a heavyweight operation at the operating system level
Heavyweight lock , If the competition for locks is fierce , Performance degradation
Java5 Before , Switching between user mode and kernel mode

java The thread of is mapped to the native thread of the operating system , If you want to block or wake up a thread, you need the operating system to intervene , You need to switch between user state and core state , This kind of switch will consume a lot of system resources , Because user mode and kernel mode have their own dedicated memory space , Special registers, etc , Switching from user state to kernel state needs to be passed to many variables 、 Parameters to the kernel , The kernel also needs to protect some register values of user state when switching 、 Variable etc. , So as to switch back to user state and continue to work after kernel state call .
stay Java In previous releases , synchronized It's a heavyweight lock , inefficiency , Because the monitor lock (monitor) It depends on the underlying operating system Mutex Lock To achieve , Both the suspended thread and the recovery thread need to be transferred to the kernel state to complete , Block or wake up a Java Threads need operating system switching CPU State to complete , This state switching takes processor time , If the content in the synchronization code block is too simple , This switching may take longer than user code execution ”, The time cost is relatively high , That's why the early synchronized The reason for low efficiency
Java 6 after , In order to reduce the performance consumption of acquiring lock and releasing lock , Introduced lightweight locks and biased locks
3.2、 Why can every object become a lock ????
3.2.1、markOop.hpp

Monitor It can be understood as a synchronization tool , It can also be understood as a synchronization mechanism , Often described as a Java object . Java The object is natural Monitor , every last Java The object has become Monitor The potential to , Because in Java In the design of , every last Java The object came out of her womb with an invisible lock , It's called an internal lock or Monitor lock .
Monitor The essence of is dependent on the underlying operating system Mutex Lock Realization , The operating system needs to switch between threads from user state to kernel state , The cost is very high .
3.2.2、Monitor( Monitor lock )

Mutex Lock
Monitor Is in jvm Implemented at the bottom , The underlying code is c++ . The essence is dependent on the underlying operating system Mutex Lock Realization , The operating system needs to switch between threads from user state to kernel state , State transition takes a lot of processor time and is very expensive . therefore synchronized yes Java A heavyweight operation in language .
Monitor And java Objects and how threads are associated ?
1. If one java Object is locked by a thread , Then java Object's Mark Word Field LockWord Point to monitor From
2.Monitor Of Owner Field holds the thread that owns the lock of the associated object id
Mutex Lock Switch from user state to core state , So state transition takes a lot of processor time .
3.3、java6 Start , Optimize Synchronized
Java 6 after , In order to reduce the performance consumption of acquiring lock and releasing lock , Introduced lightweight locks and biased locks
There needs to be a gradual upgrading process , Don't poke into the heavyweight lock at the beginning
4、synchronized Lock types and upgrade steps
4.1、 Multithreaded access ,3 Kind of
There is only one thread to access , There is and only Only One
Yes 2 Threads A、B To alternate access
Competition is fierce , Multiple threads to access
4.2、 Upgrade process
synchronized The lock used is the existence Java The one in the head Mark Word in
The lock upgrade function mainly depends on MarkWord Middle lock flag and release bias lock flag
64 Look at the bit mark diagram again

4.3、 unlocked
package com.atguigu.juc.test;
import org.openjdk.jol.info.ClassLayout;
/**
* @author shizan
* @Classname MyObject
* @Description TODO
* @Date 2022/6/7 8:40 Afternoon
*/
public class MyObject {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object o = new Object();
System.out.println("10 Base number hash code : " + o.hashCode());
System.out.println("16 Base number hash code : " + Integer.toHexString(o.hashCode()));
System.out.println("2 Base number hash code : " + Integer.toBinaryString(o.hashCode()));
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(o).toPrintable());
}
}Programs don't have lock competition


4.4、 Partial lock
4.4.1、 The main role
When a piece of synchronous code has been accessed by the same thread multiple times ,
Since there is only one thread, the thread will automatically obtain the lock on subsequent access
The same old customer came to visit , It's convenient to follow the old rules directly
Look at multithreaded ticket selling , Experience the same thread
Hotspot The author of the study found that , Most of the time :
In the case of multithreading , Locks don't just have multithreaded competition , There are also locks Multiple times obtained by the same thread ,
Biased lock is in this case , It was invented to solve Improve performance only when a thread performs synchronization .

adopt CAS Way to modify markword Thread in ID
4.4.2、 Biased lock holding
Theory landing :
In the process of practical application, it is found that , “ Locks are always held by the same thread , Competition is rare ” , in other words The lock is always owned by the first thread that occupies it , This thread is the biased thread of the lock .
Then only when the lock is owned for the first time , Record the bias thread ID . In this way, the thread always holds the lock ( Later, when the thread enters and exits the code block with synchronization lock , No need to lock and release the lock again . It directly compares whether there is a biased lock pointing to the current thread in the object header ) .
If equal Indicates that the bias lock is biased to the current thread , You don't have to try to get the lock again , The lock is not released until competition occurs . After each synchronization , Check the bias thread of the lock ID With the current thread ID Is it consistent , If consistent, go directly to synchronization . There is no need to lock and unlock every time CAS Update object header . If there is only one thread that uses locks from beginning to end , It's clear that biased locks have little overhead , Extremely high performance .
If inconsistency means competition , Locks are not always biased to the same thread anymore , At this time, you may need to upgrade to a lightweight lock , To ensure fair competition between threads . Biased locks only encounter when other threads try to compete for biased locks , The thread holding the biased lock will release the lock , Threads do not actively release biased locks .
Technical realization :
One synchronized Method is locked by a thread , Then the object where this method is located will be in its Mark Word Change the bias lock to the status bit , There will also be pre occupancy 54 Bit to store the thread pointer as an identifier . If the thread accesses the same... Again synchronized When the method is used , The thread only needs to remove the header of the object Mark Word To determine whether there is a bias lock pointing to itself ID , There is no need to enter again Monitor To compete with .
Refine the case Account Object examples
The operation of bias lock does not need to poke directly into the operating system , Don't involve User to kernel conversion , There is no need to upgrade directly to the highest level , We start with a account Object's “ Object head ” For example ,

Suppose a thread executes to synchronized Block of code ,JVM Use CAS The operation puts the thread pointer ID It was recorded that Mark Word among , And modify the deviation mark , Indicates that the current thread obtains the lock . Lock objects become biased locks ( adopt CAS Modify the lock flag bit in the object header ), Literally means “ Prefer the first thread to get it ” Lock of . After executing the synchronization code block , Threads don't actively release biased locks .

At this time, the thread obtains the lock , You can execute synchronized code blocks . When the thread reaches the synchronization code block for the second time, it will judge whether the thread holding the lock is still itself ( Thread holding lock ID Also in the head of the object ),JVM adopt account Object's Mark Word Judge : Current thread ID still , It means that it still holds the lock of this object , You can continue to work in the critical area . Since the lock was not released before , There is no need to re lock here . If there is only one thread that uses locks from beginning to end , It's clear that biased locks have little overhead , Extremely high performance .
Conclusion :JVM Don't negotiate settings with the operating system Mutex( Fight for the kernel ), It just needs to record the thread ID It indicates that you have obtained the current lock , No operating system access .
The above is the bias lock : When there is no other thread competition , Always bias the current thread , The current thread can always execute .
4.4.3、 Biased locking JVM command
java -XX:+PrintFlagsInitial |grep BiasedLock*

Description of important parameters

* Actually, it's locked in JDK1.6 After that, it is turned on by default , But the start-up time is delayed ,
* So you need to add parameters -XX:BiasedLockingStartupDelay=0 , Let it start immediately when the program starts .
*
* Open the bias lock :
* -XX:+UseBiasedLocking -XX:BiasedLockingStartupDelay=0
*
* Close the deflection lock : After closing, the program will directly enter ---------------->>>>>>>> Lightweight lock state .
* -XX:-UseBiasedLocking
4.4.4、Code demonstration

Everything defaults
Demo has no effect

Because the parameter system is enabled by default

-XX:+UseBiasedLocking Open the bias lock ( Default )
-XX:-UseBiasedLocking Close the deflection lock
-XX:BiasedLockingStartupDelay=0 Close the delay ( When demonstrating the deflection lock, it needs to be opened )
Parameter description :
Bias locked in JDK1.6 The above is on by default , The program will not be activated until a few seconds after it is started , have access to JVM Parameter to turn off delay -XX:BiasedLockingStartupDelay=0
If it is determined that the lock is usually in a competitive state You can go through JVM Parameters -XX:-UseBiasedLocking Close the deflection lock , The default is to enter the lightweight lock
Turn off the delay parameter , Enable this feature -XX:BiasedLockingStartupDelay=0

The good days will come to an end ......o(╥﹏╥)o There began to be a second 2 A thread came to grab
4.4.5、 Partial lock revocation
When another thread gradually competes for the lock , You can no longer use the deflection lock , To upgrade to a lightweight lock
Competing threads try CAS Failed to update object header , Will wait until the global security point ( No code will be executed at this time ) Undo the bias lock .
revoke
Partial lock revocation
The bias lock uses a type of lock The mechanism of releasing locks only after competition , Only when other threads compete for locks , The original thread holding the bias lock will be revoked .
Undo needs to wait for the global security point ( There is no bytecode executing at this point in time ) , At the same time, check whether the thread holding the bias lock is still executing :
① The first thread is executing synchronized Method ( In sync block ) , It's not finished yet , Other threads to grab , The deflection lock will be cancelled and Lock escalation .
At this time, the lightweight lock is held by the thread that originally held the biased lock , Continue to execute its synchronization code , And the competing thread will enter the spin wait to get the lightweight lock .
② The execution of the first thread is complete synchronized Method ( Exit sync block ) , Set the object header to the unlocked state and cancel the bias lock , Re bias .

4.5、 Light lock
4.5.1、 The main role
There are threads competing for locks , But the collision time of acquiring locks is very short
The essence is spin lock
4.5.2、 Lightweight lock acquisition
Lightweight locks are designed to work on threads Almost alternating Improve performance when executing synchronization blocks .
Main purpose : Without multithreading competition , adopt CAS Reduce the performance cost of using OS mutexes for heavyweight locks , To put it bluntly, spin first and then block .
Upgrade time : When the biased lock function is turned off or multiple threads compete for the biased lock, the biased lock will be upgraded to a lightweight lock
If a thread A I've got the lock , When a thread B Grab the lock of the object again , Because the lock of the object has been locked by the thread A Get , At present, the lock is biased .
And threads B Find the object's head when competing Mark Word Thread in ID It's not a thread B Own thread ID( It's threads A) , That thread B It will CAS The operator wants to get the lock .
The thread B There are two situations in operation :
If the lock is obtained successfully , Direct replacement Mark Word Thread in ID by B Their own ID(A → B) , Re favor other threads ( About to give the biased lock to other threads , Equivalent to the current thread " By " Lock released ) , The lock will remain biased to lock , A Threads Over , B Thread up ;

If the lock acquisition fails , The preference lock is upgraded to lightweight lock , At this time, the lightweight lock is held by the thread that originally held the biased lock , Continue to execute its synchronization code , And the competing threads B Will enter spin waiting to get the lightweight lock .

4.5.3、Code demonstration

If the deflection lock is closed , You can directly enter the lightweight lock -XX:-UseBiasedLocking
4.5.4、 Spin to a certain number and degree
java6 Before
Enabled by default , By default, the number of spins is 10 Time -XX:PreBlockSpin=10 To modify the
Or the number of spin threads exceeds cpu Half the number of cores
The above understanding is enough , Don't use .
Java6 after
The adaptive
Adaptive means that the number of spins is not fixed
But according to : The time of one spin on the same lock . The state of the thread that owns the lock determines .
4.5.5、 The difference between light weight lock and deflection lock
When the competition for lightweight lock fails , Spin attempts to preempt lock
The lightweight lock needs to be released every time it exits the synchronization block , The biased lock is released when the competition occurs
4.6、 Re lock
There are a large number of threads competing for locks , High conflict
Lock flag position
![]()
Code demonstration

4.7、 A small summary
Advantages and disadvantages of various locks 、synchronized Lock upgrade and implementation principle

synchronized Lock upgrade process summary : In a word , Spin first , No more blocking .
It's actually locking the previous pessimism ( Heavyweight lock ) Turn to using bias locks under certain conditions and using lightweight ( spinlocks CAS) In the form of
synchronized There are great differences between the modification method and the implementation of code block on bytecode , But the internal implementation is still based on the object header MarkWord To achieve .
JDK1.6 Before synchronized Using a heavyweight lock , JDK1.6 After that, we optimized , With no lock -> Biased locking -> Lightweight lock -> Upgrade process of heavyweight lock , Instead of using heavyweight locks in any case .
Biased locking : Suitable for single threaded situations , Enter the synchronization method when there is no lock competition / Code blocks use biased locks .
Lightweight lock : Suitable for less competitive situations ( This is similar to the scope of use of optimistic locks ), Upgrade to lightweight lock when there is competition , The lightweight lock adopts spin lock , If the synchronization method / If the code block execution time is very short , The use of lightweight locks will occupy cpu Resources, but it is relatively more efficient than using heavyweight locks .
Heavyweight lock : Suitable for highly competitive situations , If the synchronization method / Code blocks take a long time to execute , Then the performance cost of using lightweight lock spin is more serious than using heavyweight lock , At this time, it needs to be upgraded to heavyweight lock .
5、JIT Compiler optimization of locks
JIT: Just In Time Compiler, It is generally translated into real-time compiler
5.1、 Lock elimination
package com.atguigu.juc.lockupgrade;
/**
* @auther zzyy
* @create 2021-03-27 15:17
* Lock elimination
* from JIT From an angle, it's equivalent to ignoring it ,synchronized (o) Does not exist. , This lock object is not shared and spread to other threads ,
* In the extreme, there is no underlying machine code of the lock object at all , Eliminates the use of locks
*/
public class LockClearUPDemo {
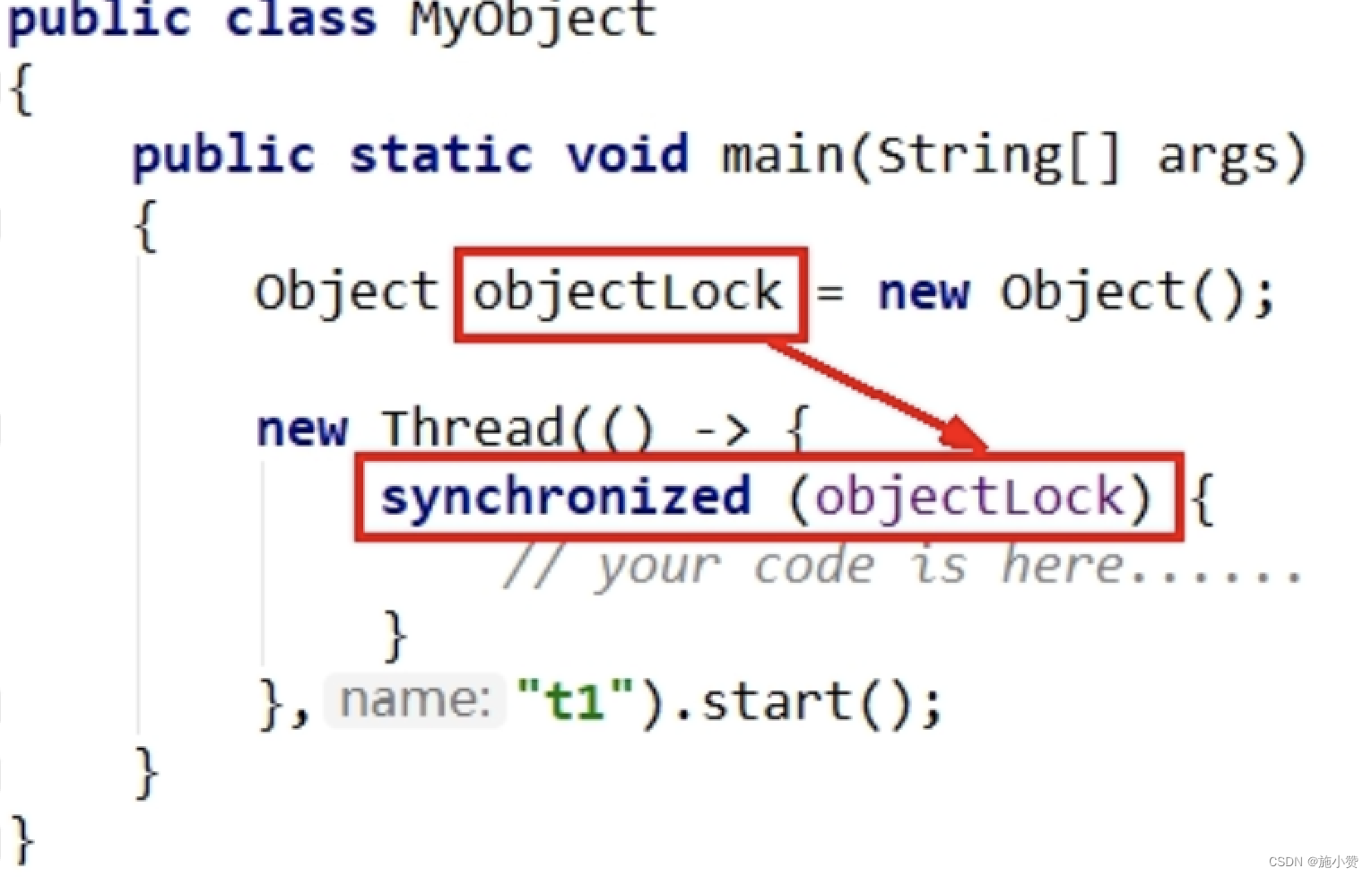
static Object objectLock = new Object();// natural , There is only one lock
public void m1() {
// Lock elimination ,JIT Will ignore it , synchronized( Object lock ) Does not exist. . Abnormal
Object objectLock = new Object();// Lock elimination
synchronized (objectLock) {
System.out.println("----hello lock");
}
}
}5.2、 Lock coarsening
package com.atguigu.juc.lockupgrade;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @auther zzyy
* @create 2021-03-27 15:19
* Lock coarsening
* If the method is connected end to end , The front and rear adjacent objects are the same lock object , that JIT The compiler will put these synchronized The blocks are combined into a large block ,
* Bold to enlarge the scope , You can apply for the lock once , Avoid repeated applications and release locks , Improved performance
*/
public class LockBigDemo {
static Object objectLock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (objectLock) {
System.out.println("11111");
}
synchronized (objectLock) {
System.out.println("22222");
}
synchronized (objectLock) {
System.out.println("33333");
}
}, "a").start();
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (objectLock) {
System.out.println("44444");
}
synchronized (objectLock) {
System.out.println("55555");
}
synchronized (objectLock) {
System.out.println("66666");
}
}, "b").start();
}
}边栏推荐
- Let you understand selection sorting (C language)
- 进度条加载
- When I saw the sudden death of a 28 year old employee, I wanted to moisten
- 采用快慢指针法来解决有关数组的问题(C语言)
- JMeter learning experience
- SQLServer连接数据库(中文表)部分数据乱码问题解决
- Is reflection really time-consuming? How long does it take to reflect 100000 times.
- POJ 3278 catch the cow (width first search, queue implementation)
- 纯数据业务的机器打电话进来时回落到了2G/3G
- Golang uses XOR ^ to exchange two variables and encrypt / decrypt them
猜你喜欢

9、聊聊ThreadLocal

Flink multi stream conversion (side output stream shunting, union, connect) real-time reconciliation of APP payment operations and third-party payment operations

gocron 定时任务管理平台

微信web开发者,如何学习web开发

吊打面试官,涨姿势

C# 将OFD转为PDF

Flink window table valued function
![[JUC supplementary] atomic class, unsafe](/img/24/e51cfed39fe820fb46cca548af1782.jpg)
[JUC supplementary] atomic class, unsafe

Let you understand bubble sorting (C language)
Specflow环境搭建
随机推荐
Gocron scheduled task management platform
Serveur FTP: téléchargement et utilisation de Serv - U
Flick scrolling window, sliding window, session window, global window
Let you understand selection sorting (C language)
Problems encountered in installing mysql8 under centos7.x couldn't open file /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/rpm-gpg-key-mysql-2022
Elk - elastalert largest pit
.net core 抛异常对性能影响的求证之路
记一次 mysql 主从不同步问题排查
Flink spark vs. Flink
Zhejiang University and Microsoft Asia Research Institute released a new method of video recognition, which can recognize video frame by frame without data marking, or can be used for sign language tr
软件项目管理 7.1.项目进度基本概念
The wonderful use of XOR (C language)
让你理解选择排序(C语言)
JMeter learning experience
Live app source code, and the status bar and navigation bar are set to transparent status
flink 窗口表值函数
中间人攻击之ettercap嗅探
Wechat web developers, how to learn web development
When a pure data service machine calls in, it falls back to 2g/3g
Merge two ordered arrays (C language)