当前位置:网站首页>[transfer] two-way merging and sorting of C language
[transfer] two-way merging and sorting of C language
2022-06-11 07:52:00 【zljun8210】
In learning the introduction to data structures , There are two ways to merge and sort in the exam ( Merge sort (MERGE-SORT) It is an effective sorting algorithm based on merge operation , The algorithm is a divide-and-conquer method (Divide and Conquer) A very typical application . Merges ordered subsequences , You get a perfectly ordered sequence ; So let's make each subsequence in order , Then make the subsequence segments in order . If two ordered tables are merged into one ordered table , It is called the second way Merger .), The conversion algorithm is as follows :
/*
============================================================================
Name : MergeSort.c
Author : zlj
Version :
Copyright : soft.rz
Description : Hello World in C, Ansi-style
============================================================================
*/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int k=1;
void Merge(int sourceArr[],int tempArr[], int startIndex, int midIndex, int endIndex)
{
int i = startIndex, j=midIndex+1, k = startIndex;
while(i!=midIndex+1 && j!=endIndex+1)
{
if(sourceArr[i] > sourceArr[j])
tempArr[k++] = sourceArr[j++];
else
tempArr[k++] = sourceArr[i++];
}
while(i != midIndex+1)
tempArr[k++] = sourceArr[i++];
while(j != endIndex+1)
tempArr[k++] = sourceArr[j++];
for(i=startIndex; i<=endIndex; i++)
sourceArr[i] = tempArr[i];
for (i=startIndex; i<=endIndex; i++)
printf("%d ", sourceArr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
// Recursion is used internally
void MergeSort(int sourceArr[], int tempArr[], int startIndex, int endIndex)
{
int midIndex;
if(startIndex < endIndex)
{
midIndex = (startIndex + endIndex) / 2;
MergeSort(sourceArr, tempArr, startIndex, midIndex);
MergeSort(sourceArr, tempArr, midIndex+1, endIndex);
Merge(sourceArr, tempArr, startIndex, midIndex, endIndex);
}
printf("\nThe %d Times\n", k);
k++;
}
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
int a[15] = {50, 10, 20, 30, 70, 40, 80, 60, 45, 66, 38, 29, 51,74, 13};
int i, b[15];
printf(" Raw data : \n");
for(i=0; i<15; i++)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
MergeSort(a, b, 0, 14);
printf("\n\n Sorted data : \n");
for(i=0; i<14; i++)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
return 0;
}
The results are as follows :
Raw data :
50 10 20 30 70 40 80 60 45 66 38 29 51 74 13
The 1 Times
The 2 Times
10 50
The 3 Times
The 4 Times
The 5 Times
20 30
The 6 Times
10 20 30 50
The 7 Times
The 8 Times
The 9 Times
40 70
The 10 Times
The 11 Times
The 12 Times
60 80
The 13 Times
40 60 70 80
The 14 Times
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
The 15 Times
The 16 Times
The 17 Times
45 66
The 18 Times
The 19 Times
The 20 Times
29 38
The 21 Times
29 38 45 66
The 22 Times
The 23 Times
The 24 Times
51 74
The 25 Times
The 26 Times
13 51 74
The 27 Times
13 29 38 45 51 66 74
The 28 Times
10 13 20 29 30 38 40 45 50 51 60 66 70 74 80
The 29 Times
Sorted data :
10 13 20 29 30 38 40 45 50 51 60 66 70 74
边栏推荐
- 【案例解读】医疗单据OCR识别助力健康险智能理赔
- 【 史上最全的ENSP【安装图解】!】
- Summary of evaluation index knowledge points in target detection: summary of IOU cross overlap unit and map/ap/tp/fp/np
- 【AtCoder2304】Cleaning
- Sort - Swap sort
- 2021-11-05 definition of cache
- 2022.6.6 extra long growth simulation
- String Simulation Implementation
- pmp到底是什么?
- Database connection pool and bdutils tool
猜你喜欢
![[codeforces1019e] raining season](/img/8e/4a96954ee7dae5f81eaae05b5a075b.png)
[codeforces1019e] raining season
![[untitled] Weng_ C lesson 1](/img/4e/41876093ef6b6a38909832f89e1495.jpg)
[untitled] Weng_ C lesson 1

如何准备PMP新版大纲考试?

Black Qunhui dsm7.0.1 physical machine installation tutorial

Collation of basic knowledge of intermediate development of Andrews (for interview)

如何做好空状态设计?来看这份全面总结

【案例解读】医疗单据OCR识别助力健康险智能理赔
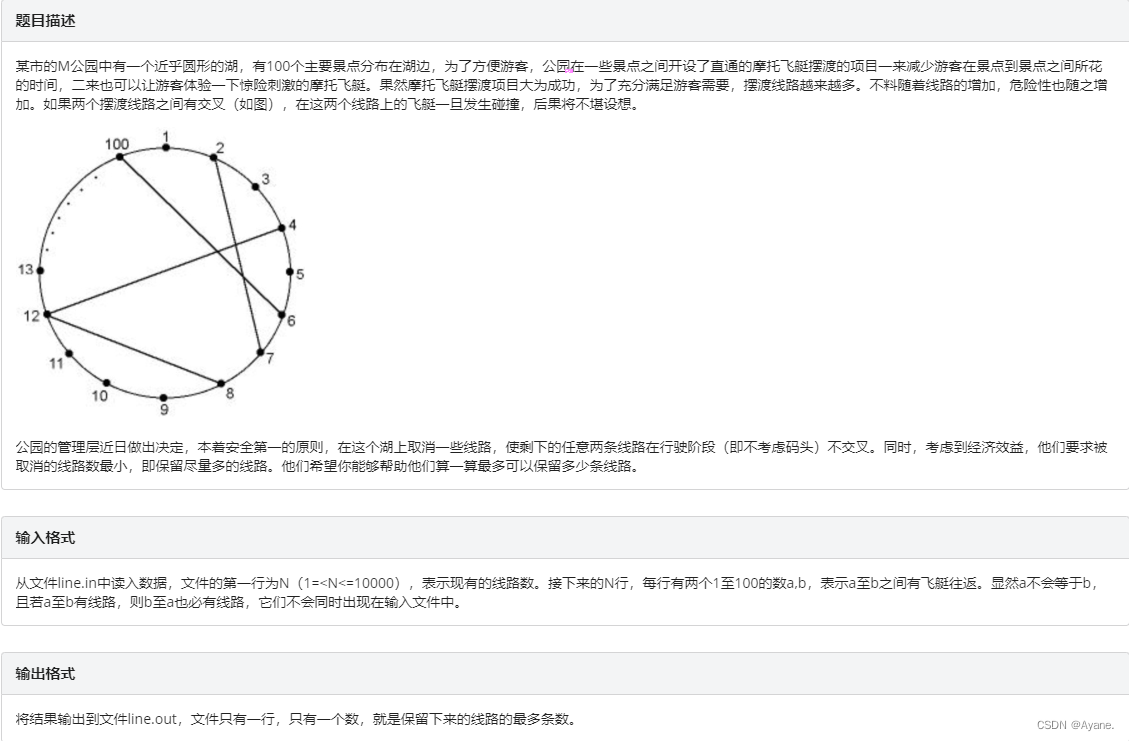
2022.6.7 special student simulation

安卓初中级开发基础知识整理(面试自用)

Storage of floating point in memory
随机推荐
Zero foundation self-study SQL course | outer join external connection
[atcoder2376] black and white tree (game)
Socket [5] - struct linker usage
C language three chess games
How to output the percent sign "%" in printf function in C language
二本毕业,银行外包测试工作 4 个月有余。聊聊一些真实感受 ...
You got 8K in the 3-year function test, but you were actually pretending to work hard
Remote office experience | community essay solicitation
Simple use of string
TiDB Cloud 上線 Google Cloud Marketplace,以全新一棧式實時 HTAP 數據庫賦能全球開發者
Image data enhancement (translation, rotation, brightness transformation, flipping, adding Gaussian noise, scaling, cropping)
2022.6.6 extra long growth simulation
Alchemy experience (model training of deep learning) the necessity of timely adjusting training parameters for some situations (the adjustment of learning rate LR is the primary) summarizes some metho
Tidb cloud launched Google cloud marketplace, empowering global developers with a new stack of real-time HTAP databases
代码设置ConstraintLayout的layout_constraintDimensionRatio
图数据库无缝集成Tushare接口
2022.6.7 特长生模拟
C. Managing history (greedy / hashing / thinking / good questions)
Note: JDBC
After 4 years of naked resignation from the test, the test post of 15K interview was rubbed on the ground, and the result made me collapse and cry