当前位置:网站首页>Calibration, correction and world coordinate calculation of binocular stereo vision camera (openCV)
Calibration, correction and world coordinate calculation of binocular stereo vision camera (openCV)
2022-06-29 20:51:00 【HNU_ Liu Yuan】
Use opencv Calibrate and correct the binocular stereo vision camera
Camera calibration preparation
Use the binocular camera to take pictures of the plane pasted with checkerboard , Take multiple sets of pictures , Ensure that both the left and right cameras can capture the complete square . And measure the actual size of the checkerboard .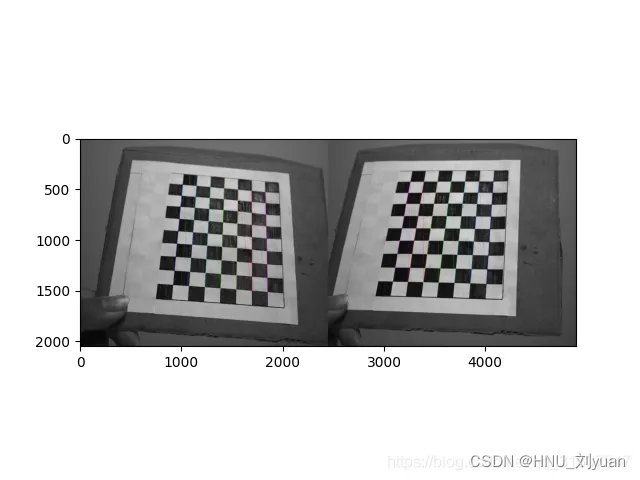

Camera calibration
For steps 1 Process the photos taken by the left and right cameras , Calculate the parameters of the left and right cameras respectively .
cheese_size = (11, 8) # Checkerboard picture contains the number of grids in the length and width direction
corner_num = cheese_size[0] * cheese_size[1]
unit = 20 # The actual grid spacing here is 20mm
objp = np.zeros((corner_num, 3), np.float32)
objp[:, :2] = np.mgrid[0:cheese_size[0], 0:cheese_size[1]].T.reshape(-1, 2)
objp *= unit
print("objp:", objp.shape)
stereo_right_images = []
stereo_left_images = []
objpoints = []
save = True
for fn in fns:
print(fn)
left_img = cv2.imread(fn)
stereo_left_images.append(left_img) # opencv Read video
right_img = cv2.imread(fn.replace('left', 'right'))
stereo_right_images.append(right_img)
objpoints.append(objp)
print(len(stereo_left_images), len(stereo_right_images))
# Monocular calibration
x, stereo_right_corners = calibrate(
stereo_right_images, objpoints, cheese_size=cheese_size, show_img=True, fnames=fns)
stereo_right_ret, stereo_right_mtx, stereo_right_dist, stereo_right_rvecs, stereo_right_tvecs = x
# stereo_nir_dist = np.zeros_like(stereo_nir_dist)
print('right cali done...')
x, stereo_left_corners = calibrate(
stereo_left_images, objpoints, cheese_size=cheese_size, show_img=True, fnames=fns)
stereo_left_ret, stereo_left_mtx, stereo_left_dist, stereo_left_rvecs, stereo_left_tvecs = x
print('left cali done...')
if _DIST_:
print('--------------------------------------------------------------------')
stereo_right_dist = np.zeros_like(stereo_right_dist)
stereo_left_dist = np.zeros_like(stereo_left_dist)
# Binocular calibration
retval, stereo_left_mtx, stereo_left_dist, stereo_right_mtx, stereo_right_dist, R_left2right, T_left2right, E_left2right, F_left2right= \
cv2.stereoCalibrate(np.array(objpoints), np.squeeze(np.array(stereo_left_corners)),
np.squeeze(np.array(stereo_right_corners)
), stereo_left_mtx, stereo_left_dist,
stereo_right_mtx, stereo_right_dist, (stereo_left_images[0].shape[0],
stereo_left_images[0].shape[1])
# flags=cv2.CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL
) # python3 transfer stereo_left -> stereo_righ tflags=cv2.CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL
h, w, c = stereo_right_images[0].shape
print('stereo cali done...')
if _DIST_:
stereo_right_dist = np.zeros_like(stereo_right_dist)
stereo_left_dist = np.zeros_like(stereo_left_dist)
Among them calibrate Function is :
def calibrate(images, objpoints, cheese_size, show_img=False, fnames=[]):
# termination criteria
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER, 50, 0.001) # Terminate iteration criteria , The maximum number of iterations or the precision reached
imgpoints = []
num = 0
for img in images:
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(gray, cheese_size, None)# Check whether the input picture contains a checkerboard picture
# If found, add object points, image points (after refining them)
if ret == True:
cv2.cornerSubPix(gray, corners, (5, 5), (-1, -1), criteria) # Sub pixel corner detection
# print(corners)
imgpoints.append(corners)
if show_img:
# Draw and display the corners
img = np.copy(img)
cv2.drawChessboardCorners(img, cheese_size, corners, ret) # Checkerboard corner drawing
cv2.imshow('img' , img)
cv2.imwrite("right.jpg", img)
cv2.waitKey(3)
num = num + 1
if show_img:
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# input(' Go back to the next step ')
return cv2.calibrateCamera(objpoints, imgpoints, gray.shape[::-1], None, None), imgpoints # Find out external parameters of the each view with the internal parameters
This process can automatically detect the checkerboard picture in the picture for parameter calculation , Get the internal and external parameter matrix of the two cameras , And the positional relationship between the two cameras .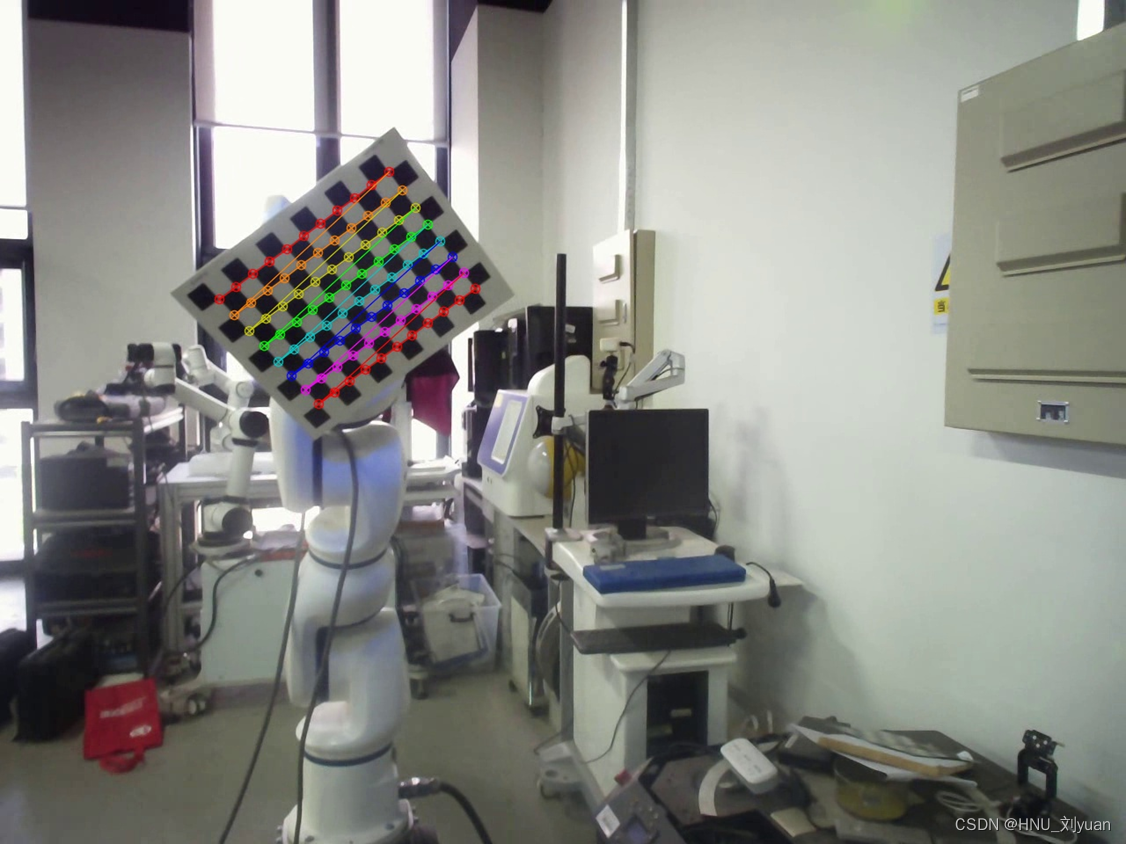
Camera correction
At this time, the parameters of each camera can be obtained , But in reality, it is not an ideal binocular vision model ,Bouguet Stereo correction algorithm , Its core principle is through pixel plane perspective transformation , Minimize the re projection error of left and right images , Make the binocular system closest to the ideal state . That is, stereoscopic correction .
# Binocular correction
R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, validPixROI1, validPixROI2 = cv2.stereoRectify(
stereo_left_mtx, stereo_left_dist, stereo_right_mtx, stereo_right_dist, (w, h), R_left2right, T_left2right, alpha=0)
R1[0, :] *= -1
R2[0, :] *= -1
print('stereo rectify done...')
# Get the mapping transformation
stereo_left_mapx, stereo_left_mapy = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(
stereo_left_mtx, stereo_left_dist, R1, P1, (w, h), 5)
stereo_right_mapx, stereo_right_mapy = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(
stereo_right_mtx, stereo_right_dist, R2, P2, (w, h), 5)
print('initUndistortRectifyMap done...')
And the key parameters can be saved .
if save:
np.save('P1', P1)
np.save('P2', P2)
np.save('stereo_right_mtx', stereo_right_mtx)
np.save('stereo_right_dist', stereo_right_dist)
np.save('stereo_left_mtx', stereo_left_mtx)
np.save('stereo_left_dist', stereo_left_dist)
np.save('R_left2right', R_left2right)
np.save('T_left2right', T_left2right)
Visually verify whether it is :
# Visual verification , See if the grid is aligned
def drawLine(img, num=16):
h, w, *_ = img.shape
for i in range(0, h, h // num):
cv2.line(img, (0, i), (w, i), (0, 255, 0), 1, 8)
return img
for fn in fns:
left_img = cv2.imread(fn)
right_img = cv2.imread(fn.replace('left', 'right'))
frame0 = cv2.remap(right_img, stereo_right_mapx,
stereo_right_mapy, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
frame1 = cv2.remap(left_img, stereo_left_mapx,
stereo_left_mapy, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
img = np.concatenate((frame0, frame1), axis=1).copy()
img = drawLine(img, 32)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
ret = cv2.waitKey(3)
The checkerboard of the corrected picture should be aligned , At the same height .
At this point, the calibration and correction of the camera are completed .
World coordinate calculation
After getting the parameters of the camera , If you know the position of the same point in the left and right video , Can calculate its three-dimensional coordinate position .
Use tracking or other algorithms to get the pixel coordinates of a fixed point on the left and right cameras , Save as txt file , Use left_path and right_path Represents its path .
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
import math
# [K1,K2,P1,P2,k3]
def read_point(left_path,right_path):
point_r=[]
point_l=[]
with open(left_path,"r") as f:
line = f.readline().strip('\n')
while line:
temp=line.split(' ')
point=[int(temp[0]), int(temp[1])]
point_l.append(point)
line=f.readline().strip('\n')
with open(right_path, "r") as f:
line = f.readline().strip('\n')
while line:
temp = line.split(' ')
point = [int(temp[0]), int(temp[1])] #1280
point_r.append(point)
line = f.readline().strip('\n')
point_r = np.array(point_r)
point_l = np.array(point_l)
return point_l,point_r
def computexyz(point_l, point_r, M_l,M_r):
# compute XYZ
ul = point_l[0]
vl = point_l[1]
ur = point_r[0]
vr = point_r[1]
# A = np.zeros((4,3))
A = np.array([[ul * M_l[2][0] - M_l[0][0], ul * M_l[2][1] - M_l[0][1], ul * M_l[2][2] - M_l[0][2]],
[vl * M_l[2][0] - M_l[1][0], vl * M_l[2][1] - M_l[1][1], vl * M_l[2][2] - M_l[1][2]],
[ur * M_r[2][0] - M_r[0][0], ur * M_r[2][1] - M_r[0][1], ur * M_r[2][2] - M_r[0][2]],
[vr * M_r[2][0] - M_r[1][0], vr * M_r[2][1] - M_r[1][1], vr * M_r[2][2] - M_r[1][2]]])
b = np.array([M_l[0][3] - ul * M_l[2][3], M_l[1][3] - vl * M_l[2][3], M_r[0][3] - ur * M_r[2][3],
M_r[1][3] - vr * M_r[2][3]])
temp1 = np.linalg.inv(np.matmul(A.T, A))
temp2 = np.matmul(A.T, b)
point_xyz = np.matmul(temp1, temp2)
return point_xyz
left_path = "data/point_left_c.txt"
right_path = "data/point_right_c.txt"
point_l,point_r = read_point(left_path,right_path)
distRight=np.load("stereo_right_dist.npy").squeeze()
distLeft=np.load("stereo_left_dist.npy").squeeze()
print(distLeft)
print(distRight)
m,n=point_r.shape
K_r = np.load("stereo_right_mtx.npy")
R_r = np.load("R_left2right.npy")
t_r = np.load("T_left2right.npy").squeeze()
R_l = np.eye(3)
t_l = np.array([0,0,0])
P_r = np.zeros((3,4))
P_r[:, 0:3] = R_r
P_r[:, 3] = t_r
M_r=np.matmul(K_r,P_r)
K_l = np.load("stereo_left_mtx.npy")
P_l = np.zeros((3,4))
P_l[:, 0:3] = R_l
P_l[:, 3] = t_l
M_l=np.matmul(K_l,P_l)
Point = []
for i in range(len(point_l)):
Pointxyz = computexyz(point_l[i],point_r[i],M_l,M_r)
Point.append(Pointxyz)
Point = np.array(Point)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.scatter(Point[:,0], Point[:,1], Point[:,2])
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
ax.set_zlabel('z')
plt.show()
You can get the following three-dimensional trajectory diagram .
For specific principles, please refer to other blogs , Everything is very good .
边栏推荐
- Set up your own website (12)
- [compilation principle] syntax analysis
- 如何审核 Active Directory 用户账户更改?
- 习近平在湖北武汉考察时强调 把科技的命脉牢牢掌握在自己手中 不断提升我国发展独立性自主性安全性
- annotation
- [compilation principle] semantic analysis
- Tag based augmented reality using OpenCV
- Gstreamer应用开发实战指南(五)
- Navigation exercises [microcomputer principles] [exercises]
- 2021 CCPC Harbin E. power and modulo (thinking questions)
猜你喜欢

Fastadmin background setting radio button

At least 3 years for learning amplifier?

liunx指令

时钟树综合(CTS)

How to judge the quality of conductive slip ring from its appearance

High energy live broadcast, a gathering of celebrities! We invite you to explore bizdevops.

Mapbox GL development tutorial (12): loading surface layer data
![Navigation experiment [microcomputer principle] [experiment]](/img/79/8311a409113331e72f650a83351b46.png)
Navigation experiment [microcomputer principle] [experiment]
![Navigation [microcomputer principle]](/img/79/8311a409113331e72f650a83351b46.png)
Navigation [microcomputer principle]

In depth good article | yolov5+deepsort multi-target tracking in-depth interpretation and testing (including source code)
随机推荐
At least 3 years for learning amplifier?
量子机器学习的基础和应用:一个简明文献综述
[notes] take notes again -- learn by doing Verilog HDL – 008
High energy live broadcast, a gathering of celebrities! We invite you to explore bizdevops.
Gstreamer应用开发实战指南(五)
如何评价科大讯飞AI翻译笔P20系列,值得买吗?
Selection of materials for space conductive disc slip ring
2021 CCPC Harbin E. power and modulo (thinking questions)
Reinforcement learning weekly (issue 51): integration of PAC, ilql, RRL & model free reinforcement learning into micro grid control: overview and Enlightenment
日本樱桃一颗拍出1980元天价,网友:吃了有上当的感觉
"Xiaodeng" active directory password expiration notification function is available for operation and maintenance
Ovirt database modify delete node
Community interview -- jumpserver open source fortress in the eyes of an it newcomer
[buuctf.reverse] 142_ [SUCTF2019]babyunic
Liunx instruction
liunx指令
[today in history] June 29: SGI and MIPS merged; Microsoft acquires PowerPoint developer; News corporation sells MySpace
Codeforces Global Round 21 C D E
What are the mainstream brands of smart door locks? What characteristics should we pay attention to when purchasing door locks?
导航 习题【微机原理】【习题】