当前位置:网站首页>Seven sorting details
Seven sorting details
2022-07-27 06:26:00 【Envy only mandarin ducks, not immortals】
Catalog
3、 Internal sort and external sort
Two 、 Test methods for major sorting
3、 Bidirectional selection sorting
1、 The finger of the sword Offer 51. Reverse pairs in arrays
One 、 Explanation of sorting
1、 Sort
Sort , Is to make a string of records , According to the size of one or some of the keywords , An operation arranged in ascending or descending order . In the usual context , If it comes to sorting , It's usually in ascending order ( Non descending order ). Sort in the usual sense , They all mean sort in place (in place sort).
2、 Stability of sequencing
In the sequence to be sorted , There are elements with the same value , After sorting , The sorting algorithm whose order of values is equal and does not change is called a stable algorithm . It's in the picture below 5a and 5b The order of has not changed .

3、 Internal sort and external sort
(1) Internal sorting
The data to be sorted is placed in memory
(2) External sorting
Data is stored on the hard disk , Each sorting needs to read part of the contents from the hard disk to the memory , Sort this part of data before writing it to the hard disk . For example, bucket sorting , Radix sorting , Odd sort , These methods can only be used in special situations , Limited .
Two 、 Test methods for major sorting
package Seven_sorts;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
/**
* Test seven sorts
*/
public class SortTest {
// A class that generates random numbers
private static final ThreadLocalRandom random=ThreadLocalRandom.current();
/**
* Produce a size of n Array of random integers , The value range of the array is [l...r]
* @param n The number of elements in the array
* @param l The minimum value of the array
* @param r The maximum value of the array
* @return
*/
public static int[] generaRabdomArrary(int n,int l,int r){
int[] data=new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i <n ; i++) {
// It generates a [l...r) The random number of is placed in the array
data[i]= random.nextInt(l,r);
}
return data;
}
/**
* Generate a size of n An almost ordered array of
* @param n Element number
* @param swaptinmes The number of exchanges , The more times , The more unordered the array
* @return
*/
public static int[] generateSortArrary(int n,int swaptinmes){
// Sir into an ordered array
int[] data =new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
data[i]=i;
}
// Exchange some elements of an ordered array
for (int i = 0; i <swaptinmes; i++) {
int a= random.nextInt(n);
int b= random.nextInt(n);
int temp=data[a];
data[a]=data[b];
data[b]=temp;
}
return data;
}
/**
* Deep copy array
* @param arr
* @return
*/
public static int[] arraryCopy(int[] arr){
return Arrays.copyOf(arr,arr.length);
}
/**
* In the specified array arr The name of the last test is sortName Sorting time of
* @param arr
* @param sortName
*/
public static void testSort(int[] arr,String sortName){
Class<SevenSort> cla=SevenSort.class;
try {
// Get the algorithm according to the name of the tactics
Method method= cla.getDeclaredMethod(sortName,int[].class);
// timing
long start=System.nanoTime();
method.invoke(null,arr);
long end=System.nanoTime();
if (isSorted(arr)){
System.out.println(sortName+" Sort complete , Total time consuming :"+(end-start)/1000000.0+"ms");
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Check whether the current array is a non descending array
* @param arr
* @return
*/
private static boolean isSorted(int[] arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length-1; i++) {
if (arr[i]>arr[i+1]){
System.out.println(" The sorting algorithm is wrong !");
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
3、 ... and 、 Selection sort
1、 Direct selection sorting
Each time, the largest... Is selected from the unordered interval ( Or the smallest ) An element of , At the end of the unordered interval ( Or first ), Until all the data elements to be sorted are finished .

9,2,5a,7,5b,4,3,6
For this set of data , At the beginning of sorting ,
Sorted array ( Disordered interval ) by [i...n), Sorted array ( Ordered interval ) by []
After the first sorting ,2,9,5a,7,5b,4,3,6
Sorted array ( Disordered interval ) by [i...n)-1, Sorted array ( Ordered interval ) by []+1
/**
* Direct selection sorting
* @param arr
*/
public static void selsctionSort(int[] arr){
// The initial unordered interval [i...n), The ordered interval is []
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// Minimum element index subscript
int min=i;
for (int j = i+1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[j]<arr[min]){
min=j;
}
}
// here min Is the index of the minimum value , Exchange operations
swap(arr,i,min);
}
}2、 Heap sort
CSDN https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/124864506
https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/124864506
3、 Bidirectional selection sorting
Optimize direct selection sorting , Select the maximum and minimum values at the same time
/**
* Bidirectional selection sorting
* @param arr
*/
public static void selectionSortOP(int[] arr){
int low=0;
int high= arr.length-1;
// Cycle termination conditions , When low==high when , The unordered interval leaves only the last element , At this point, the array has been ordered
while (low<high){
int min=low;
int max=low;
for (int i = low+1; i <=high; i++) {
if (arr[i]<arr[min]){
min=i;
}
if (arr[i]>arr[max]){
max=i;
}
}
// here min Corresponds to the minimum index , Swap to the front of the unordered interval
swap(arr,min,low);
// Pay attention to consider when low==max The situation of
if (low==max){
max=min;
}
swap(arr,max,high);
low++;
high--;
}
}Four 、 Exchange sort
(1) Bubble sort
CSDN https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/124098197
https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/124098197
/**
* Bubble sort
* @param arr
*/
public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length-1 ; i++) {
boolean isSSwapped=false;
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length-i-1 ; j++) {
if (arr[j]>arr[j+1]){
swap(arr,j,j+1);
isSSwapped=true;
}
}
if (!isSSwapped){
break;
}
}
}2、 Quick sort
Quick sort ,20 One of the greatest algorithms of the th century , The core idea is zoning
Select a value in the unordered interval as the dividing point pivot, Start scanning collection , All in the array are less than pivot The element of is placed on the left side of the dividing point , Will be greater than or equal to pivot The element of is placed on the right side of the dividing point , After this round of exchange ,pivot In the final position , Then repeat the above process in two sub intervals , Until the whole combination is in order .
(1) Partition method 1

When arrays are nearly ordered , The performance degradation of quick sort is very serious , In extreme cases , Suppose the array is almost ordered , When partitioning according to the leftmost element , It will cause extreme imbalance between the two recursive subtrees in the recursive process , It will even degenerate into a linked list . The solution is to select any element in the array as the partition point for each recursion .
/**
* Quick sort
* @param arr
*/
public static void quickSort(int[] arr){
quickSortInternal(arr,0,arr.length-1);
}
private static void quickSortInternal(int[] arr, int l, int r) {
// // Optimize 2
// if (r-l<=15){
// insertionSort(arr,l,r);
// return;
// }
if (l>=r){
return;
}
int p=partion(arr,l,r);
// Continue to sort quickly in two subintervals
// Less than v The elements of
quickSortInternal(arr,l,p-1);
// Greater than v The elements of
quickSortInternal(arr,p+1,r);
}
/**
* Partition method
* @param arr
* @param l
* @param r
* @return
*/
private static int partion(int[] arr, int l, int r) {
// // Optimize 1
// int randomIndex=random.nextInt(l,r);
// swap(arr,l,randomIndex);
int v=arr[l];
//arr[l+1...j] Time is less than v The range of , At first, this interval has no elements
int j=l;
//arr[j+1...i] Time greater than v The range of , At first, this interval also has no elements
for (int i = l+1; i <=r ; i++) {
if (arr[i]<v){
swap(arr,i,j+1);
j++;
}
}
// This element j It's the last one <v The elements of , Just put v Exchange to j The location of
swap(arr,l,j);
return j;
}
(2) Partition method 2

/**
* Quick sort digging
* @param arr
*/
public static void quickSortHoare(int[] arr){
quickSortHoareInternal(arr,0,arr.length-1);
}
private static void quickSortHoareInternal(int[] arr, int l, int r) {
// // Optimize 2
// if (r-l<=15){
// insertionSort(arr,l,r);
// return;
// }
if (l>=r){
return;
}
int p=partitionHoare(arr,l,r);
// Continue to sort quickly in two subintervals
// Less than v The elements of
quickSortHoareInternal(arr,l,p-1);
// Greater than v The elements of
quickSortHoareInternal(arr,p+1,r);
}
/**
* Zoning method II excavation method
* @param arr
* @param l
* @param r
* @return
*/
private static int partitionHoare(int[] arr, int l, int r) {
int randomIndex=random.nextInt(l,r);
swap(arr,l,randomIndex);
int pivot=arr[l];
int i=l;
int j=r;
while (i<j){
// First, let j Go forward from the back to the first one less than v The element of stops
while(i<j&&arr[j]>=pivot){
j--;
}
arr[i]=arr[j];
// Then let's i Walk from front to back to the first greater than v The elements of
while (i<j&&arr[i]<=pivot){
i++;
}
arr[j]=arr[i];
}
arr[i]=pivot;
return i;
}5、 ... and 、 Insertion sort
1、 Direct insert sort
Select the first element of the unordered interval each time , Insert at the right position in the ordered interval

/**
* Direct insert sort
* @param arr
*/
public static void insertionSort(int[] arr){
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length ; i++) {
// Ordered interval [0..1) By default, the first element is ordered , The interval to be sorted [i...n)
// Select the first element of the first interval of the unordered interval , Keep looking forward, choose a position to put
// for (int j = i; j >=1&&arr[j]<arr[j-1]; j--) {
// swap(arr,j,j-1);
// }
for (int j = i; j >=1; j--) {
if (arr[j]>arr[j-1]){
//arr[i] It happens to be the last element of the ordered interval , The first element of an unordered interval
break;
}else {
swap(arr,j,j-1);
}
}
}
}
2、 Binary Insertion Sort
The principle of half insertion sort algorithm is the same as that of direct insertion sort algorithm . It's just , When inserting data into sorted data , Use to half find ( Two points search ). Take the middle element of the sorted sequence first , Compare with the data to be inserted , If the value of the intermediate element is greater than the data to be inserted , Then the data to be inserted belongs to the first half of the array , Otherwise, it belongs to the second half . By analogy , Keep narrowing down , Determine where to insert .
/**
* Binary Insertion Sort
* @param arr
*/
public static void insertionSortBS(int[] arr){
// Ordered interval [0...i) Disordered interval [i...n)
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int val=arr[i];
// Ordered interval [left...right]
int left=0;
int right=i;
while (left<right){
int mid=(left+right)/2;
if (val<arr[mid]){
right=mid;
}else {
left=mid+1;
}
}
// Move [left...i) The elements of
for (int j = i; j >left; j--) {
arr[j]=arr[j-1];
}
//left Is the position to be inserted
arr[left]=val;
}
}
3、 Shell Sort
When the array is close to order , The efficiency of insertion sorting is very high , Hill sorting is constantly adjusting the small array in order , Until the whole large array is close to order , At this time, use insert sorting again , Efficiency will be greatly improved .
① Choose an integer first gap, Divide the array to be sorted into gap Group , All distances are gap Is the same group ,, First, insert and sort each small array .
② Give Way gap=gap/2(3), Repeat the first step
③ When gap=1 when , At this point, it shows that the entire array has been adjusted to be almost orderly , You only need to insert and sort again , In this way, the efficiency will be improved a lot .

/**
* Shell Sort
* @param arr
*/
public static void shellSort(int[] arr){
int gap= arr.length/2;
// Step one, step two
while (gap>1){
insertionSortGap(arr,gap);
gap=gap/2;
}
// When gap be equal to 1 when , The whole large array is almost orderly , At this point, insert the sort again
insertionSort(arr);
}
/**
* Insert sorted 1 Replace with gap This is the insertion sort here
* @param arr
* @param gap
*/
private static void insertionSortGap(int[] arr, int gap) {
for (int i =gap; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = i; j-gap >=0&&arr[i]<arr[j-gap] ; j--) {
swap(arr,j,j-gap);
}
}
}6、 ... and 、 Merge sort
return : Keep dividing the original array into sub arrays ( Split in two ), Until there is only one element left in each array , The return process is over
and : Continue to combine two adjacent words into a large array , The merging process is to merge the ordered subarray into a large ordered subarray , Until it is merged into the whole array .
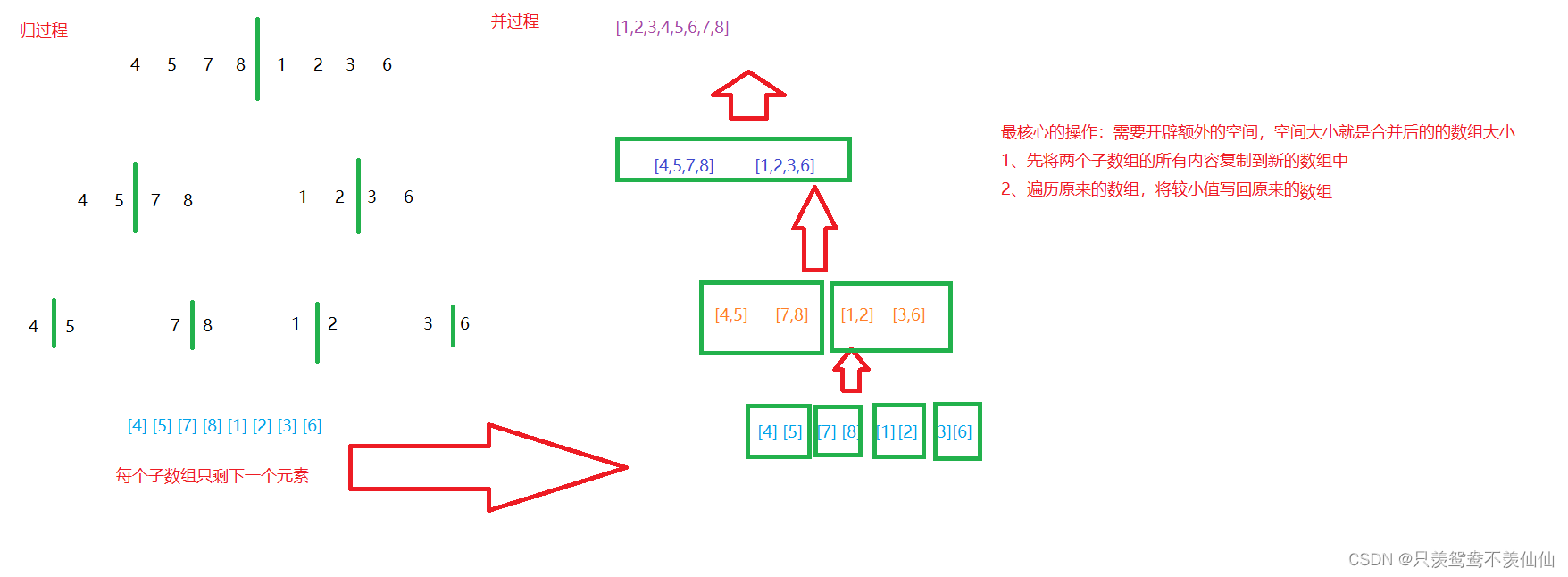
As shown in the figure , Traverse two subarrays , Write the smaller value back to the original array arr in
/**
* Merge sort
* @param arr
*/
public static void mergeSort(int[] arr){
mergSortInternal(arr,0,arr.length-1);
}
/**
* stay arr[l..r) Practice merging and sorting
* @param arr
* @param l
* @param r
*/
private static void mergSortInternal(int[] arr, int l, int r) {
// // Optimize 2
// if (r-l<=15){
// insertionSort(arr,l,r);
// return;
// }
if (l>=r){
// At this point, the array is an ordered array
return;
}
int mid=l+(r-l)/2;
mergSortInternal(arr,l,mid);
mergSortInternal(arr,mid+1,r);
// here arr[l...mid) and [mid+1...r) It's in order , At this point, you only need to merge the two arrays
merge(arr,l,mid,r);
// // Optimize 2
// if (arr[mid]>arr[mid+1]){
// // When the two arrays are out of order , To merge
// merge(arr,l,mid,r);
// }
}
private static void insertionSort(int[] arr, int l, int r) {
for (int i = l+1; i <=r; i++) {
for (int j = i; j >=l+1&&arr[j]<arr[j-1]; j--) {
swap(arr,j,j-1);
}
}
}
/**
* take arr[l...mid) and [mid+1...r) And is a large ordered array [l...r)
* @param arr
* @param l
* @param mid
* @param r
*/
private static void merge(int[] arr, int l, int mid, int r) {
// First create a new array temp, Copy the value of the subarray to the first array
int[] temp=new int[r-l+1];
for (int i = 0; i <temp.length; i++) {
//temp The index subscript of is 0...arr.length-1
//arr The index subscript of is l...r, The poor l An offset of units
temp[i]=arr[i+l];
}
// Array 1 The starting subscript of
int i=l;
// Array 2 The starting subscript of
int j=mid+1;
for (int k = l; k <=r; k++) {
if (i>mid){
// The first array has been traversed
arr[k]=temp[j-l];
j++;
}else if(j>r){
// The second array has been traversed
arr[k]=temp[i-l];
i++;
}else if(temp[i-l]<=temp[j-l]){
// take temp[i-l] Write back to arr[k]
arr[k]=temp[i-l];
i++;
}else{
//arr[i-ll]>temp[j-l], Just write back temp[j-l]
arr[k]=temp[j-l];
j++;
}
}
}
7、 ... and 、 Sort exercises
1、 The finger of the sword Offer 51. Reverse pairs in arrays


package Seven_sorts.Leetcode;
/**
* Reverse pairs in arrays
*/
public class jianzhiOffer_reversePairs {
public int reversePairs(int[] nums){
return reversePairsInternal(nums,0,nums.length-1);
}
/**
* stay nums[l...r] Merge and sort on , Returns the sorted reverse pair
* @param nums
* @param l
* @param r
* @return
*/
private int reversePairsInternal(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
// At this time, the array is empty or the array has only one element
if (l>=r){
return 0;
}
int mid=l+(r-l)/2;
// First, find the number of pairs in reverse order of the first sub array
int leftCount=reversePairsInternal(nums,l,mid);
// In finding the number of pairs in reverse order of the second sub array
int rightCount=reversePairsInternal(nums,mid+1,r);
if (nums[mid]>nums[mid+1]){
// At this time, the left and right arrays are in order , But there is still reverse order between these two arrays , Then find the reverse order pair of the merging process
return leftCount+rightCount+merge(nums,l,mid,r);
}
//nums[mid]<nums[mid+1], It shows that the whole array is in order at this time , There is no reverse order pair
return leftCount+rightCount;
}
/**
* Merge two ordered group arrays nums[l...mid] and nums[mid+1], Return the number of pairs in reverse order with the merger
* @param nums
* @param l
* @param mid
* @param r
* @return
*/
private int merge(int[] nums, int l, int mid, int r) {
// The number of reverse pairs generated after merging
int count=0;
int temp[] =new int[r-l+1];
for (int i = l; i <=r; i++) {
temp[i-l]=nums[i];
}
int i=l,j=mid+1;
for (int k = l; k <=r; k++) {
if (i>mid){
// The first array has been processed , Directly splice the second array , At this time, there is no reverse order
nums[k]=temp[j-l];
j++;
} else if (j>r) {
// The second array has been processed , Directly splice the first array , At this time, there is no reverse order
nums[k]=temp[i-l];
i++;
} else if (temp[i-l]<=temp[j-l]) {
nums[k]=temp[i-l];
i++;
}else {
// At this point, the first array element > The second array element , from i Start to mid All elements that end are compared to arr[j] It's all in reverse order
// The number of pairs in reverse order is mid-i+1
count+=mid-i+1;
nums[k]=temp[j-l];
j++;
}
}
return count;
}
}
2、 Sort list


package Seven_sorts.Leetcode;
/**
* Sort list
*/
public class Num148_sortList {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null){
return head;
}
// Find the middle node of the list , Split
ListNode mid=middle(head);
ListNode x=head;
while (x.next!=mid){
x=x.next;
}
x.next=null;
// First sort the left and right sub linked lists
ListNode l1=sortList(head);
ListNode l2=sortList(mid);
// Merge two sublink lists
return merge(l1,l2);
}
/**
* Merge two ordered sub linked lists into a large ordered linked list
* @param l1
* @param l2
* @return
*/
private ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1==null){
return l2;
}
if (l2==null){
return l1;
}
if (l1.val<=l2.val) {
l1.next = merge(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
}else {
l2.next=merge(l1,l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
/**
* Find the middle node of the list
* @param head
* @return
*/
private ListNode middle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fir=head;
ListNode sec=head;
while (fir!=null&&fir.next!=null){
fir=fir.next.next;
sec=sec.next;
}
return sec;
}
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
}
}
8、 ... and 、 Related codes
边栏推荐
- The problem that tqdm cannot display in a single line
- Communication mechanism cases
- Compatibility test knowledge points
- selenium知识点
- bug分类及缺陷和csv文件测试
- The concept of interface testing and the use of postman tools
- wireshark图形界面抓包
- 数据库命令
- C language - program compilation
- Reading and writing of file content - data flow
猜你喜欢

Tangent space and TBN matrix

Learning the operation environment needs to be equipped during software testing

单元集成(接⼝)测试

Navigation related messages

The problem that tqdm cannot display in a single line

iptables防火墙及SNAT和DNAT

内部类的相关知识

Detailed explanation of thread safety problems

PLL of IP core

Related knowledge of internal classes
随机推荐
数据库在终端的基础操作
Brief introduction to unity window interface
selenium知识点
允许或者禁止同时连接到一个non-domain和一个domain网络
Index and transaction of database (emphasis)
Dynamic planning for solving problems (5)
Allow or prohibit connecting to a non domain and a domain network at the same time
Unity hub login no response
Launch file of ROS operation management
Automatic tracking
Unable to start program, access denied?
Programming learning records - Lesson 8 [array and design Gobang, minesweeping game]
How to distinguish an independent server from a VPS host?
如何规范式编写yaml文件
接口测试概念及Postman工具简介使用
Some descriptions and usage of database index
5g's past and present life -- a brief introduction to the development of mobile communication
学习软件测试时需要配备的运行环境需求搭建
Sexy prime number (acwing daily question)
ROS分布式通信

