当前位置:网站首页>【R】 [density clustering, hierarchical clustering, expectation maximization clustering]
【R】 [density clustering, hierarchical clustering, expectation maximization clustering]
2022-07-03 13:04:00 【Laughing cold faced ghost】
List of articles
Data sets :2 Dimensional datasets —Countries, You can clearly show the clustering effect with a plan . The dataset contains 68 The birth rate of countries and regions (%) And mortality (%).
The experiment purpose : By analyzing the data set , Find the birth rate and mortality rate in different countries and regions , And according to the comparison Prediction and defense of public health .
This experiment uses Density clustering 、 Hierarchical clustering and expectation maximization clustering The above data sets are Clustering analysis , And the three clustering methods are simply compared .
1. Load the dataset 、 Preprocessing set visualization
1.1 Load data set
setwd(" The path where the dataset is stored ")
countries<-read.csv("countries.csv") # Reading data sets
1.2 Data preprocessing
dim(countries)
head(countries)
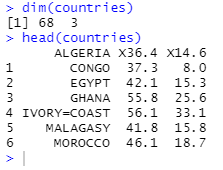
from head() As a result, the data set has no column names , And the row corresponds to a number , Not the corresponding country .
Now we're going to Modify the row and column names :
names(countries)<-c("country","birth","death") # Set three variable names
var<-countries$country # Take variables country The value of is assigned to var
var<-as.character(var) # Change the assigned to character
head(var)
for(i in 1:68) row.names(countries)[i]=var[i]# Put the dataset countries The row name of is named as the response country name
head(countries)
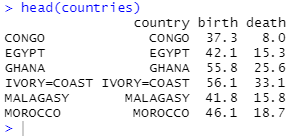
1.3 Visualize the sample points
plot(countries$birth,countries$death) # Draw all 68 A sample points
c<-which(countries$country==" Cluster point 1")
d<-which(countries$country==" Cluster point 2")
e<-which(countries$country==" Cluster point 3")
f<-which(countries$country==" Cluster point 4")
g<-which(countries$country==" Cluster point 5")
h<-which(countries$country==" Cluster point 6")
m<-which.max(countries$birth) # Get the position of the highest birth rate in the data set
points(countries[c(c,d,e,f,g,h,m),-1],pch=16)# Mark the above sample points with solid dots
legend(countries$birth[c],countries$death[c]," Sirius ",bty="n",xjust=0.5,cex=0.8)
# The legend marking the sample points in Sirius area
legend(countries$birth[d],countries$death[d]," Betelgeuse Seven Star area ",bty="n",xjust=0.5,cex=0.8)
legend(countries$birth[e],countries$death[e]," Blue shift area ",bty="n",xjust=0.5,cex=0.8)
legend(countries$birth[f],countries$death[f]," Filipino Star area ",bty="n",xjust=0.5,cex=0.8)
legend(countries$birth[g],countries$death[g]," Cecil sector ",bty="n",xjust=0.5,cex=0.8)
legend(countries$birth[h],countries$death[h]," Arcturus ",bty="n",xjust=0.5,cex=0.8)
legend(countries$birth[m],countries$death[m],countries$country[m],bty="n",xjust=1,cex=0.8)
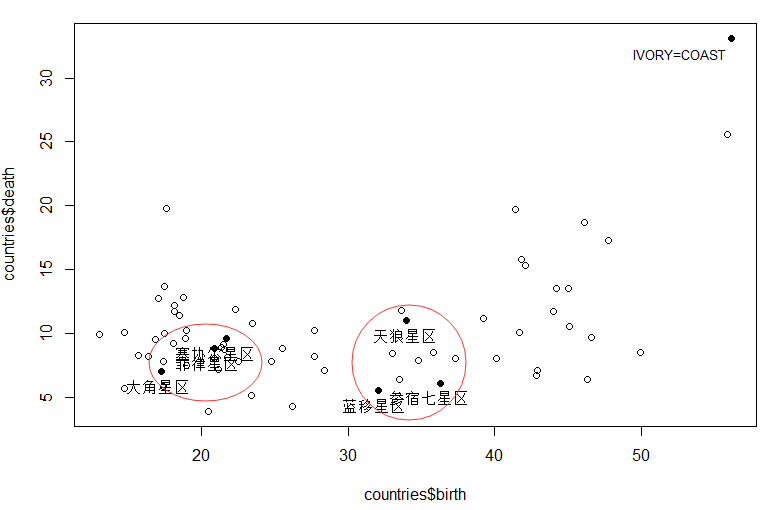
We can probably see from the picture ,( Filipino Star area 、 Cecil sector 、 Arcturus ) Can be grouped into one class ;
9 Sirius 、 Betelgeuse Seven Star area 、 Blue shift area ) For one kind ;
Ivory Coast / Africa (IVORY-COAST) Class I .
also ( Sirius ) And ( Betelgeuse Seven Star area 、 Blue shift area ) The birth rate is similar , The mortality rate is about 5 Percentage .
The above is the data preprocessing part , Let's start clustering the data set density :
2. Density clustering (DBSCAN Algorithm )
2.1 Load package
install.packages("fpc")
library(fpc)
2.2 Set clustering parameter threshold and visualize
# Set parameters of clustering : Radius and density
ds1=dbscan(countries[,-1],eps=1,MinPts=5)# Take the radius parameter eps by 1, Density threshold MinPts by 5
ds2=dbscan(countries[,-1],eps=4,MinPts=5)# Take the radius parameter eps by 4, Density threshold MinPts by 5
ds3=dbscan(countries[,-1],eps=4,MinPts=2)# Take the radius parameter eps by 4, Density threshold MinPts by 2
ds4=dbscan(countries[,-1],eps=8,MinPts=2)# Take the radius parameter eps by 8, Density threshold MinPts by 2
ds1;ds2;ds3;ds4
par(mfcol=c(2,2)) # Set up 4 According to 2 That's ok 2 The blank position of the column
plot(ds1,countries[,-1],main="1:MinPts=5 eps=1")# draw MinPts=5,eps=1 The result of time
plot(ds3,countries[,-1],main="3:MinPts=2 eps=4")# draw MinPts=2,eps=4 The result of time
plot(ds2,countries[,-1],main="2:MinPts=5 eps=4")# draw MinPts=5,eps=4 The result of time
plot(ds4,countries[,-1],main="4:MinPts=2 eps=8")# draw MinPts=2,eps=8 The result of time
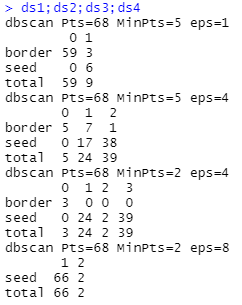
radius 1, threshold 5:DBSCAN The algorithm determines most samples as noise points only 9 Sample points with very similar density are determined as effective clusters .
radius 4, threshold 5: have only 5 Samples are judged as noise points , The remaining samples are classified into the corresponding category clusters .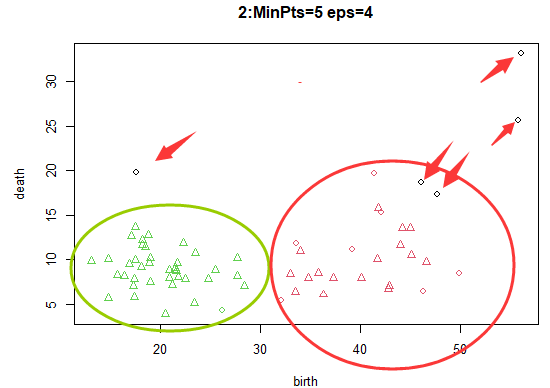
radius 4, threshold 2: More samples are classified into the category of mutually dense samples .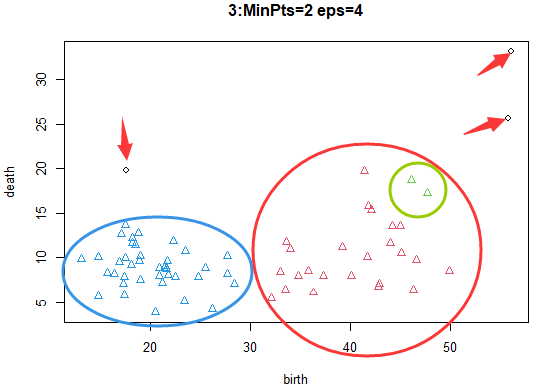
radius 8, threshold 2: Because the core object 、 The determination condition that the density can reach the same height year is relaxed to a great extent , As one can imagine , A large number of sample points will be classified into the same category .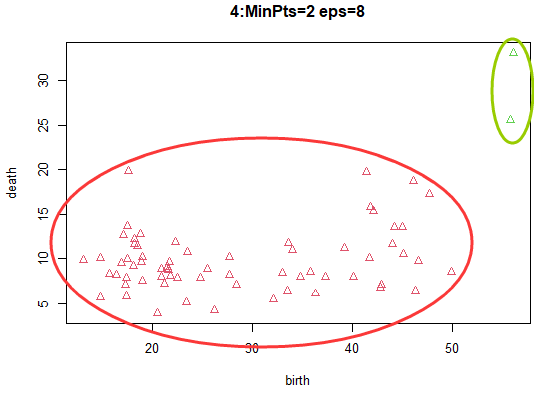
By visualization , obtain DBSCAN The parameter value rule of the algorithm :
- Radius parameter (eps) And threshold parameters (MinPts) The larger the value difference of , The smaller the total number of categories ;
- Radius parameter (eps) Relative to the threshold parameter (MinPts) More hours , The more samples are judged as noise points or edge points .
2.3 Density clustering
1) Before density clustering, we need to calculate the distance matrix of the data set :
d=dist(countries[,-1])# Calculate the data set distance matrix d
max(d);min(d) # Check the maximum distance between samples , minimum value

2) Segment the distance between samples :
The difference between the maximum value and the minimum value 50 (49.56259-0.2236068) about , Take the number in the middle as 30 And show the data classification results
library(ggplot2)
interval=cut_interval(d,30)
# Segment the distance between samples , The difference between the maximum value and the minimum value 50 about , Take the number in the middle as 30
table(interval) # Show the data classification results
which.max(table(interval)) # Find the interval with the most sample points


3) With different thresholds 、 Density clustering with different radii and visualization
According to the picture above : The distance between sample points is mostly (3.15,5.16] Between , So consider Radius parameter (eps) The values for 3、4、5、 The density threshold parameter is 1-10:
for(i in 3:5) # The radius parameter is 3,4,5
{
for(j in 1:10) # The density threshold parameter is 1 to 10
{
ds=dbscan(countries[,-1],eps=i,MinPts=j) # In the radius of i, The threshold for j when , do dbscan distance
print(ds)
}
}

Some results are shown above
3. Hierarchical clustering (hclust Algorithm )
3.1 Hierarchical clustering
fit_hc=hclust(dist(countries[,-1])) # Yes countries The data set is subject to pedigree clustering
print(fit_hc)
plot(fit_hc)

From the cluster diagram ( No label ) You can see , In the picture Each sample point at the bottom occupies a branch and forms its own class , The more you look up, the more sample points under a branch , Until all the sample points at the bottom are grouped into one class . Measure the height of the tree with the height index on the left side of the graph .
3.2 Adjust the hierarchical clustering parameters and display the results
group_k3=cutree(fit_hc,k=3)
# Using pruning function cutree() Parameters in k control input 3 The result of pedigree clustering of categories
group_k3
table(group_k3)


group_h18=cutree(fit_hc,h=18)
# Using the parameters in the pruning function h Control output Height=18 The result of pedigree clustering
group_h18
table(group_h18)


The above figure shows the use of Parameters in pruning function h Control output Height=3 and 18 Clustering results when .
sapply(unique(group_k3),function(g)countries$country[group_k3==g])
# See above K=3 The clustering results of each category of samples
plot(fit_hc)
rect.hclust(fit_hc,k=4,border="blue")
# Frame with a blue rectangle 4 Clustering results of classification
rect.hclust(fit_hc,k=3,border="red")
# Frame... With a red rectangle 3 Clustering results of classification
rect.hclust(fit_hc,k=7,which=c(2,6),border="green")
# Frame with a green rectangle 7 The number of categories 2 Class and 6 Clustering results of classes
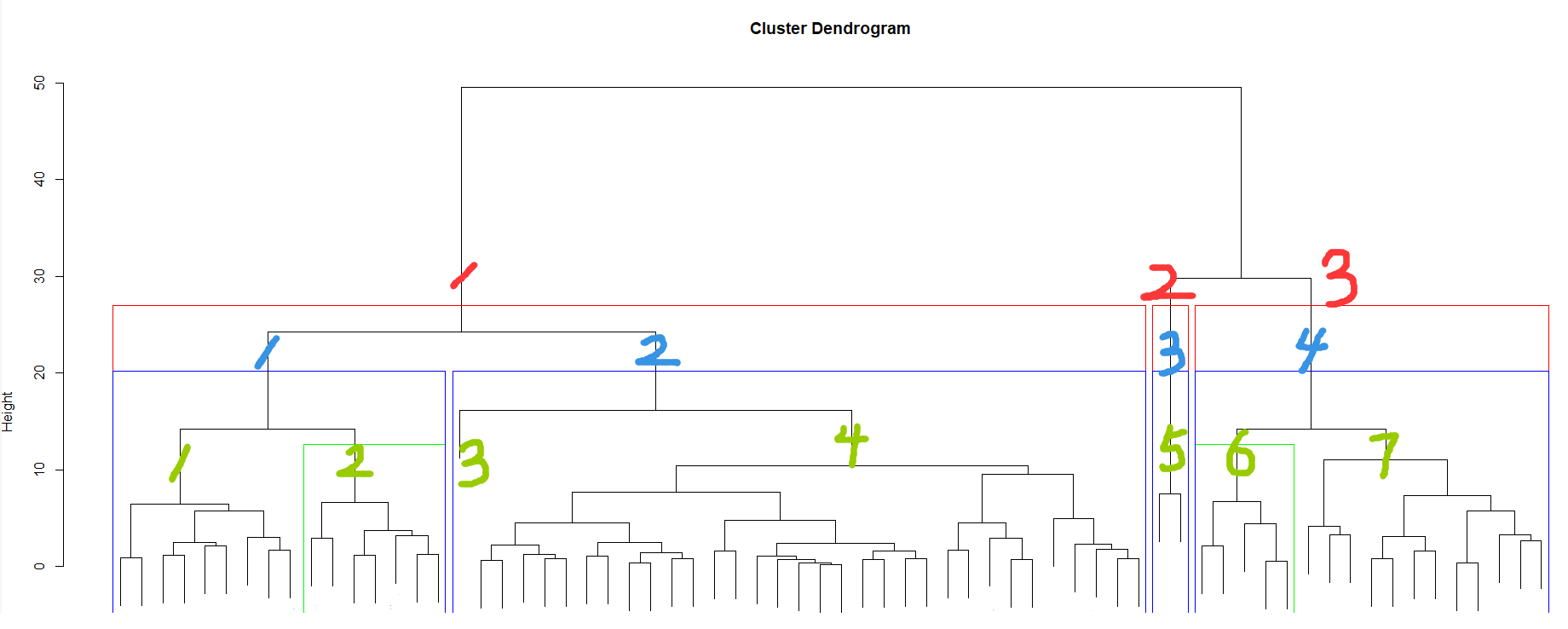
The clustering effect of setting the number of categories is shown in the above figure
4. Expectation maximization clustering (Mclust Algorithm )
4.1 Expect to maximize clustering and obtain relevant information
1) Load related packages
library(mclust)
2) Perform expectation maximization clustering and obtain relevant information
fit_EM=Mclust(countries[,-1]) # Yes countries The dataset goes on EM clustering
summary(fit_EM)# obtain EM Information summary of clustering results
summary(fit_EM,parameters=TRUE) # obtain EM Details of clustering results


It can be seen from the results , The optimal number of categories is 4, And each category contains 12、2、17、37 Samples .
4.2 Graphic display of results
plot(fit_EM)
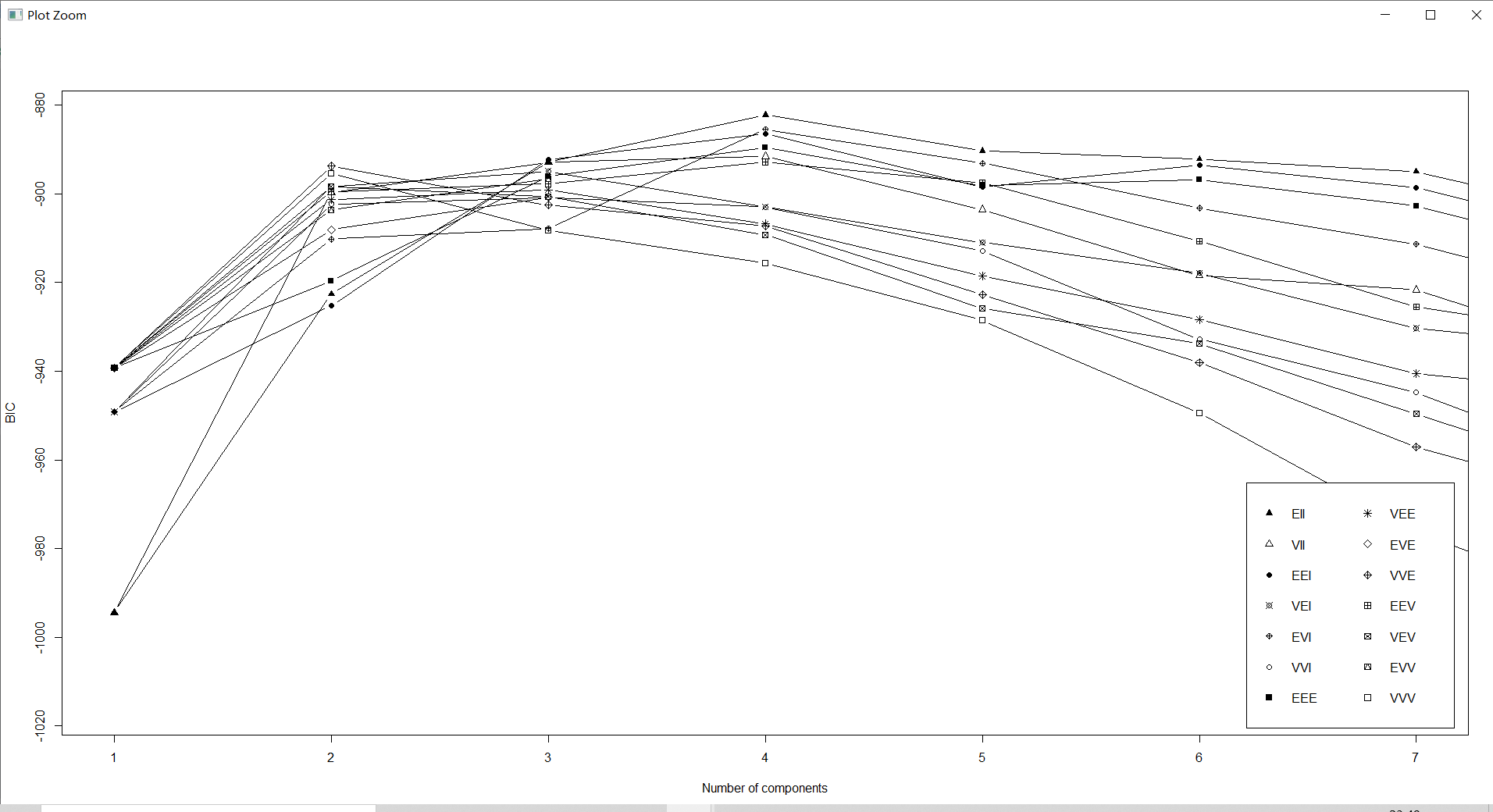
countries_BIC<-mclustBIC(countries[,-1])# Get data set countries Under the number of models and categories BIC value
countries_BICsum=summary(countries_BIC,data=countries[,-1])# Get data set countries Of BIC Value overview
countries_BICsum
countries_BIC
plot(countries_BIC,G=1:7,col="black")
names(countries_BICsum)
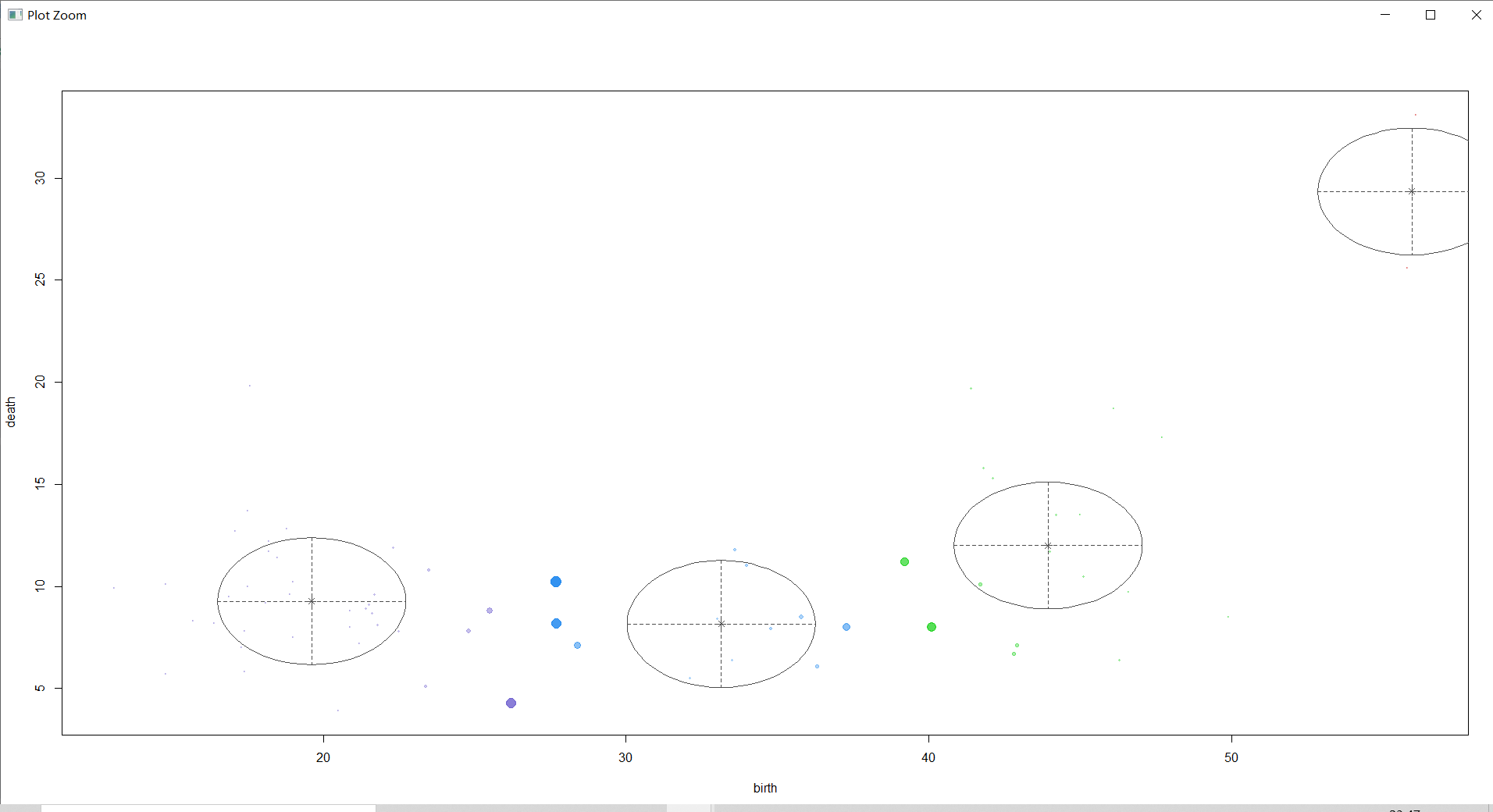
mclust2Dplot(countries[,-1],classification=countries_BICsum$classification,parameters=countries_BICsum$parameters,col="black")
# Draw a classification map
① see BIC:

② see classification:

③ see uncertainty:
④ see density:
countries_BIC<-mclustBIC(countries[,-1])# Get data set countries Under the number of models and categories BIC value
countries_BICsum=summary(countries_BIC,data=countries[,-1])# Get data set countries Of BIC Value overview
countries_BICsum
countries_BIC


plot(countries_BIC,G=1:7,col="black")
names(countries_BICsum)
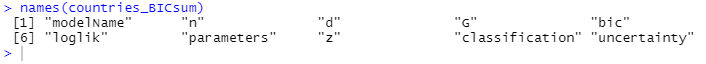
mclust2Dplot(countries[,-1],classification=countries_BICsum$classification,parameters=countries_BICsum$parameters,col="black")
# Draw a classification map
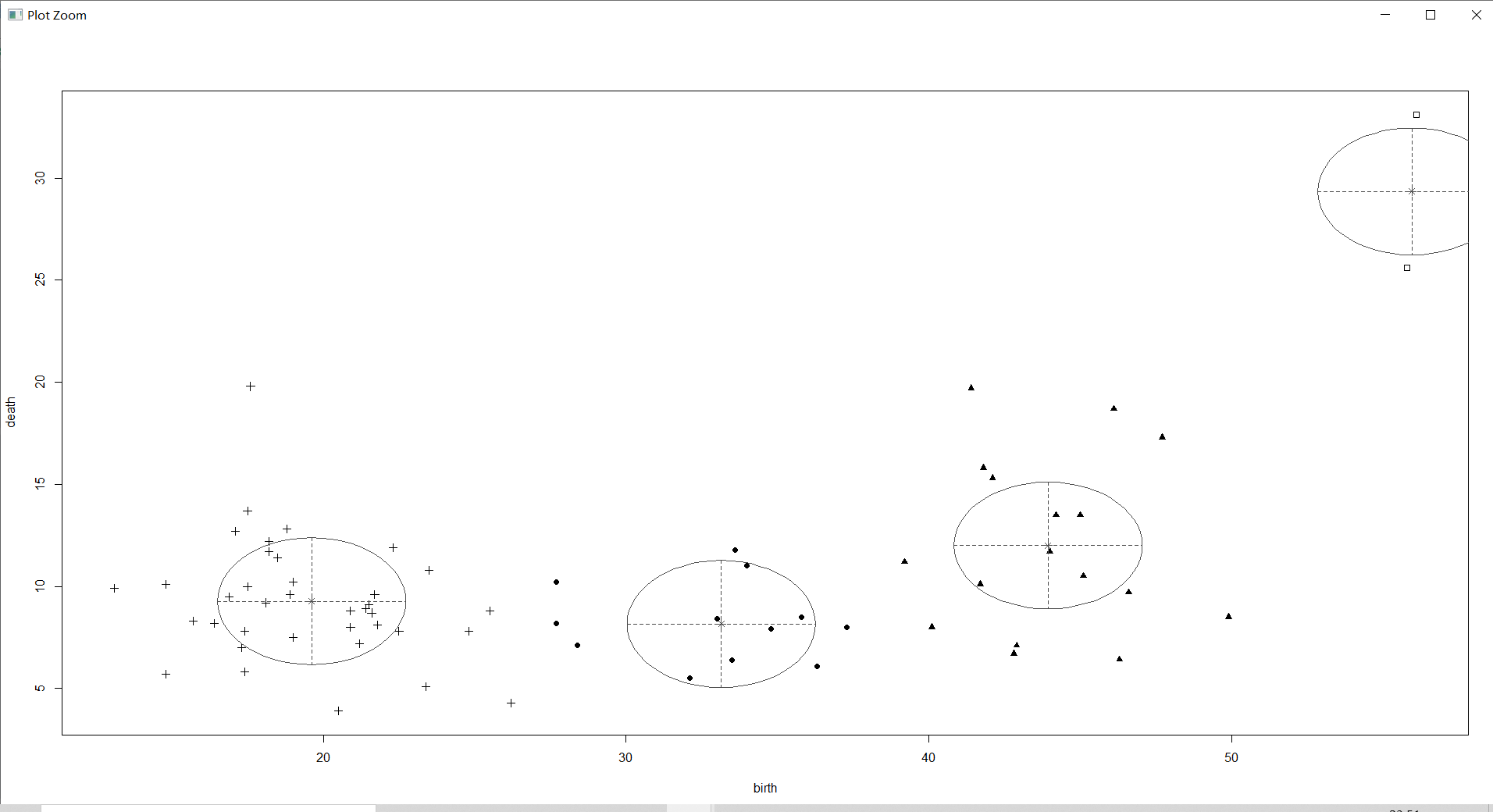
The above figure not only circles the main distribution areas of each category of samples with ellipses , The center point of the category is marked , And the probability that the sample belongs to the corresponding category is displayed by the size of the sample point graph .
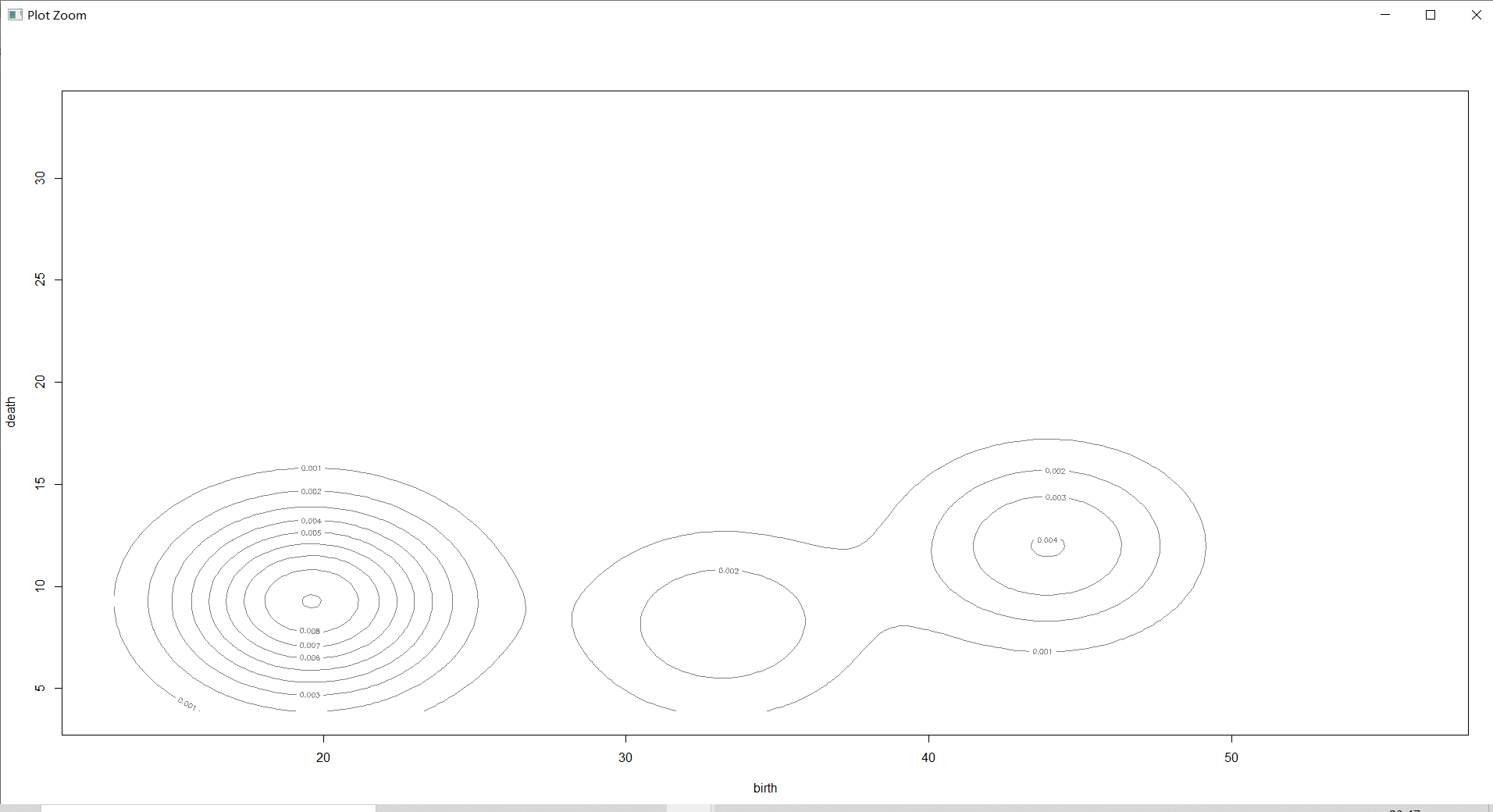
countries_Dens=densityMclust(countries[,-1])# Estimate the density of each sample
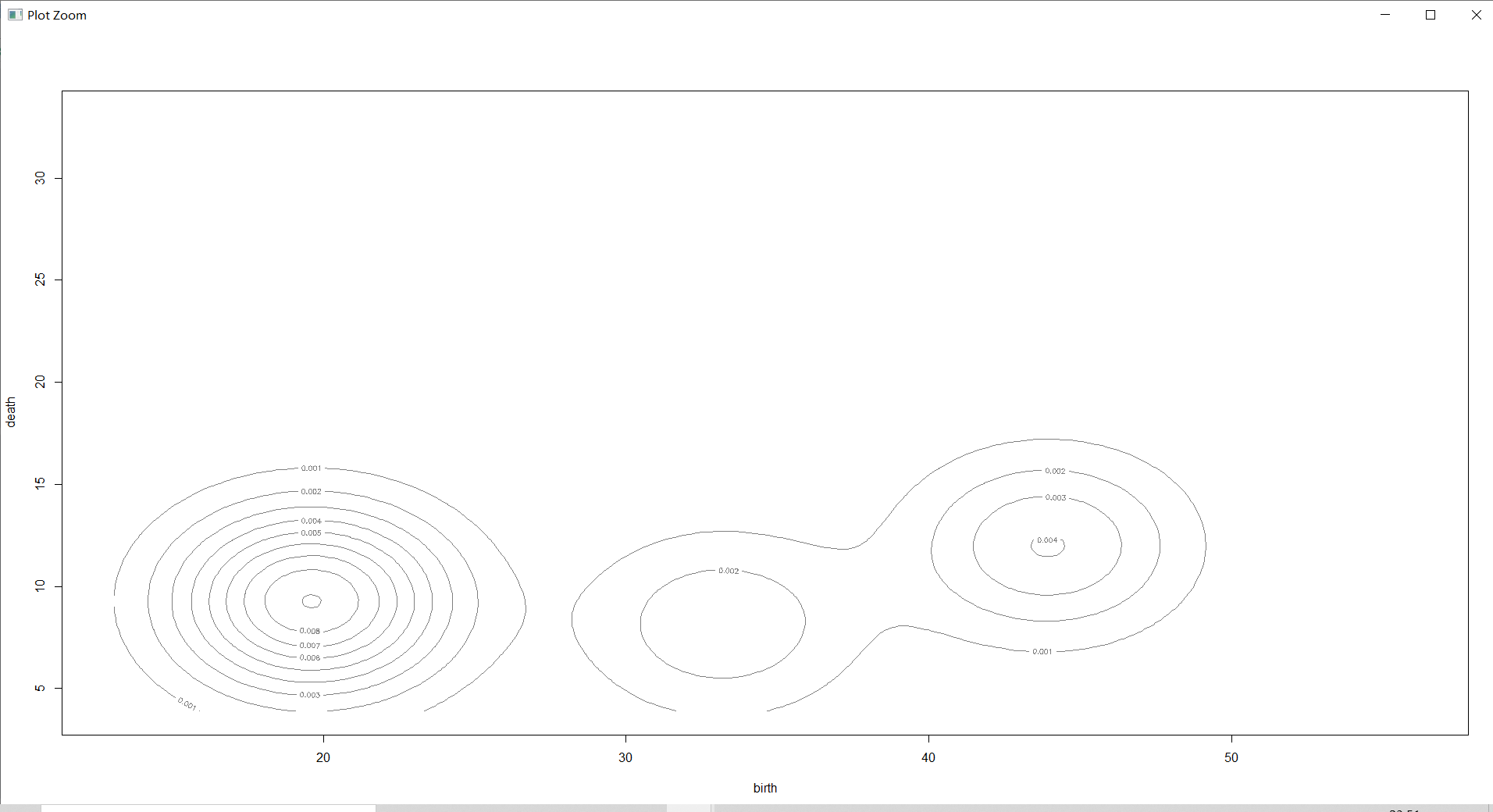
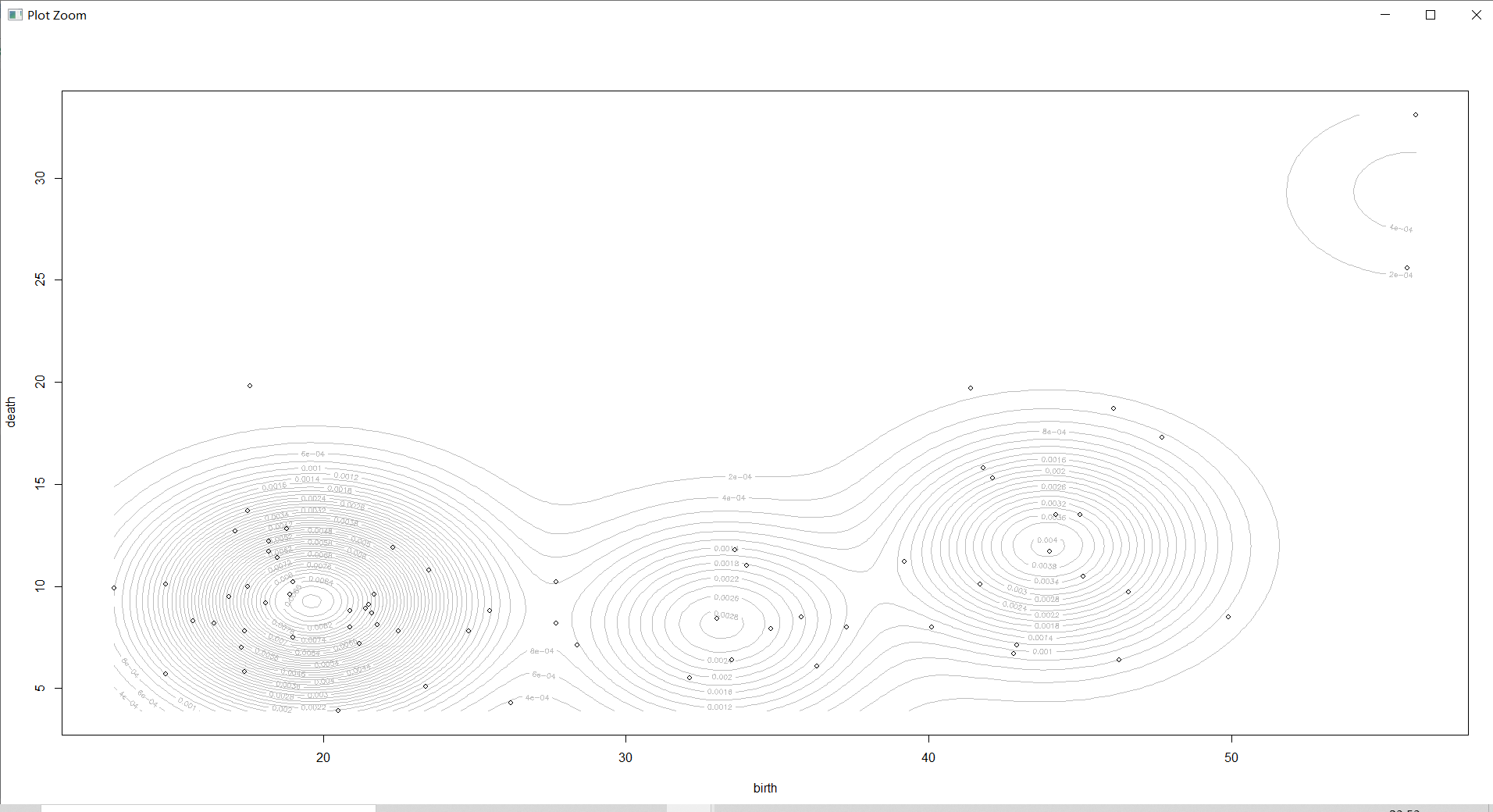
2 Dimensional density diagram
plot(countries_Dens,countries[,-1],col="grey",nlevels=55)# do 2 Dimensional density diagram
① see BIC:

② see density:
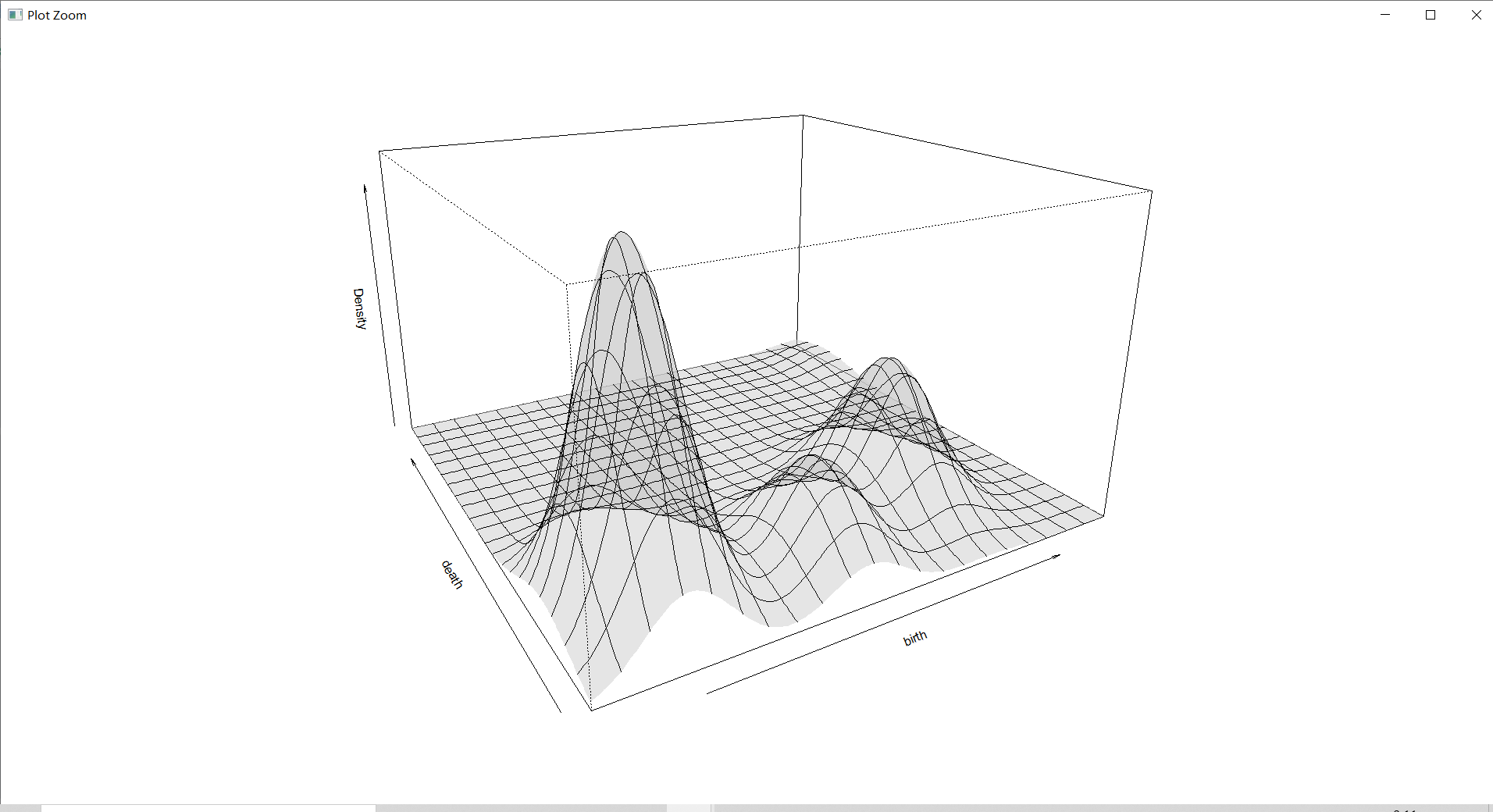
3 Dimensional density diagram
plot(countries_Dens,type="persp",col=grey(0.8)) # do 3 Dimensional density diagram
① see BIC:
② see density:
( Need to load for a while )
Density estimation diagram is a three-dimensional graph , It shows the density area more intuitively , Make a general understanding of the density .
summary
Pedigree clustering ?: From the visualization, we can feel the difference between pedigree clustering and mean clustering and central point clustering in the previous experiment . The visual graph of genealogical clustering is like a genealogy, which is divided into many different branches , The bottom of the branch is the name of all sample points .
Density clustering : The difference from other clusters is You need to set the threshold and radius . Relative to the above mean clustering 、 For central point clustering and pedigree clustering , Its advantage is to make up for the former can only find “ Class round ” The defects of clustering , The density clustering algorithm is based on “ density ” To cluster , Clusters of arbitrary shape can be found in spatial databases with noise .
Expectation maximization clustering : The idea is very clever , When using this algorithm for clustering , it Treat the data set as a probability model with hidden variables , And to achieve model optimization , That is, the purpose is to obtain the clustering method that is most consistent with the nature of the data , adopt “ Repeatedly estimate ” Model parameters to find the optimal solution , At the same time, the corresponding optimal number of categories is given K. therefore , Expect to maximize clustering relative to the previously mentioned clustering More abstract .
Reference
dbscan: Density-based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN)/ writing RDocumentation
hclust: Hierarchical Clustering/ writing RDocumentation
Mclust: Model-Based Clustering/ writing RDocumentation
DBSCAN Algorithm / Wen Jianshu @dreampai
Summary of clustering analysis algorithm / Wen Zhihu @ Shi Xian
be based on EM Clustering algorithm R package mclust/ Wen Jianshu @ Xiaorunze
Experimental data
Data sets &R The language code
Extraction code :1111( Here should be automatically filled )
边栏推荐
- Social community forum app ultra-high appearance UI interface
- [problem exploration and solution of one or more filters or listeners failing to start]
- 剑指 Offer 17. 打印从1到最大的n位数
- Glide 4.6.1 API initial
- Harmonic current detection based on synchronous coordinate transformation
- 高效能人士的七个习惯
- The foreground uses RSA asymmetric security to encrypt user information
- 【数据挖掘复习题】
- Kotlin notes - popular knowledge points asterisk (*)
- Xctf mobile--rememberother problem solving
猜你喜欢

Gan totem column bridgeless boost PFC (single phase) seven PFC duty cycle feedforward
![[problem exploration and solution of one or more filters or listeners failing to start]](/img/82/e7730d289c4c1c4800b520c58d975a.jpg)
[problem exploration and solution of one or more filters or listeners failing to start]

【数据挖掘复习题】

Node. Js: use of express + MySQL
Xctf mobile--app2 problem solving
Xctf mobile--app1 problem solving

【数据库原理及应用教程(第4版|微课版)陈志泊】【第三章习题】
Xctf mobile--app3 problem solving
The latest version of lottery blind box operation version

【R】【密度聚类、层次聚类、期望最大化聚类】
随机推荐
【習題五】【數據庫原理】
CVPR 2022 图像恢复论文
Detailed explanation of the most complete constraintlayout in history
Sitescms v3.1.0 release, launch wechat applet
2022-02-09 survey of incluxdb cluster
电压环对 PFC 系统性能影响分析
阿里 & 蚂蚁自研 IDE
Analysis of the influence of voltage loop on PFC system performance
2022-01-27 use liquibase to manage MySQL execution version
4. 无线体内纳米网:电磁传播模型和传感器部署要点
[data mining review questions]
The latest version of blind box mall thinkphp+uniapp
Slf4j log facade
The latest version of lottery blind box operation version
Node.js: express + MySQL的使用
Solve system has not been booted with SYSTEMd as init system (PID 1) Can‘t operate.
Dix règles de travail
Application of ncnn Neural Network Computing Framework in Orange Pi 3 Lts Development Board
Method overloading and rewriting
Sword finger offer 14- ii Cut rope II