当前位置:网站首页>Multithreading basic part2
Multithreading basic part2
2022-06-27 05:55:00 【Gold content of Xiaobai】
Catalog
Three features to ensure thread safety
synchronized keyword : On the thread " lock ", Keep it safe
The process by which a thread acquires an object lock
How to ensure thread safety in locking operation
synchronized Code block flushes memory
synchronized Different ways of using
1. Decorate member methods in a class , The object of the lock is the current member class object
3. Decorated code block , Identify which object is being
Java Thread safe classes in the standard library
1. It can guarantee the visibility of shared variables
2. Use volatile Decorated variables are equivalent to a memory barrier
Thread safety
Java Memory model (JMM)
JMM It describes the working memory of a thread ( Concept , It doesn't really exist , It's a series CPU Register or cache of ) And main memory ( It's real RAM) The relationship between .
The working memory
Each thread has its own working memory , When accessing shared variables ( Member variables in class , Constant , Static variables ), First, a copy of the shared variable value in the main memory will be put into the thread's own working memory , After that, the read operation of this shared variable is carried out in the current working memory .
Why are threads unsafe
When two processes access the same shared variable at the same time , There will be all kinds of problems , Because each thread actually loads the shared variables into its own working memory for various operations , And that leads to this , Working memory between threads can go wrong , It is possible that the data is updated after the main memory , The working memory of a thread still holds data that has not been updated before , And use this data to operate and write it back to the main memory . May also be , Other threads haven't loaded the shared variables yet , At this time, the newly modified value may not be read from the main memory .( Dirty reading )
Three features to ensure thread safety
visibility
The modification of shared variables by one thread can be immediately perceived and visible by other threads (synchronized- locked ,volatile keyword ,final Keywords also guarantee visibility )
Atomicity
An operation is in progress , The inability to be interrupted and disturbed is called atomicity , for example :
int i = 10; This line of code is atomic , Because it happens at the right time , No chance to be interrupted .
i++ ; It's not atomic , Because it may be read by other threads when it is added .
Prevent command rearrangement
To put it simply , In one way , The code sequence that does not affect the final result is arbitrary , This phenomenon is called instruction rearrangement , However, there will be various problems in multithreading , Take this picture :

synchronized keyword : On the thread " lock ", Keep it safe
synchronized- Monitor lock monitor lock
What is a lock ?
Let me give you an example which is not very appropriate , We can compare each thread to a person , Compare a locked code block to a toilet , If these threads need to go to the same toilet , So let's say you go to a thread first , Once inside, the thread will lock the toilet , During this period, other threads can't get in if they want to , This is the mutual exclusion between threads , Only when this thread comes out can it go in .
If threads do not need to grab the same toilet , Then it can be said that there is no mutual exclusion problem , Because a thread enters a different lock on a toilet .
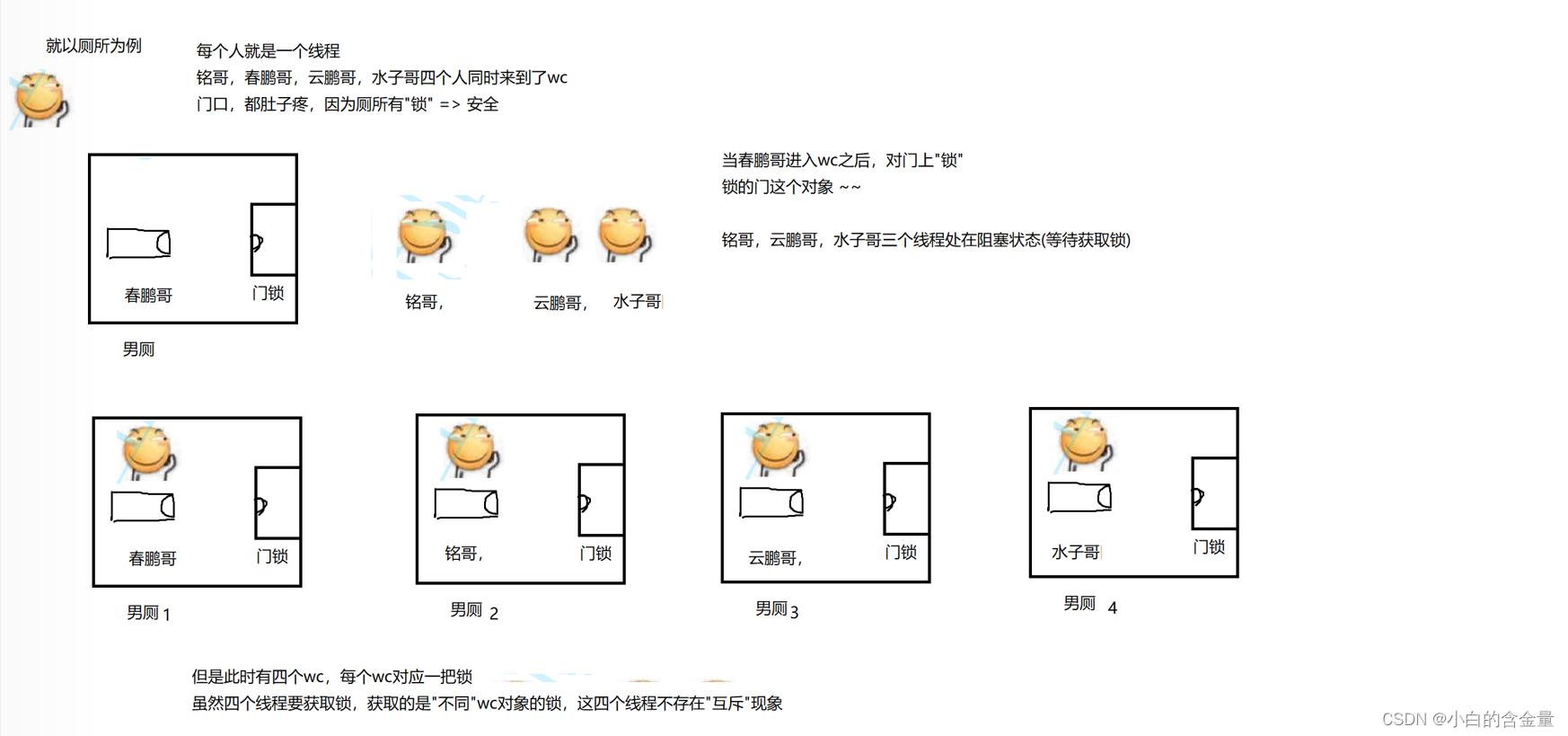
Mutual exclusion
When a thread needs to acquire the lock of an object , If other threads also want to obtain the lock of the same thread , It will be blocked .
Be sure to pay attention to , Mutex only occurs when a thread operates on the same object , There is no mutual exclusion between different objects .
The process by which a thread acquires an object lock

Each thread enters synchronized Code block , Will try to perform the locking operation .
When exiting a code block , Is to release the lock .

How to ensure thread safety in locking operation
synchronized Code block flushes memory
Threads execute synchronized The flow of code blocks
a. Get object lock
b. Copy variable values from main memory to working memory
c. Execute code
d. Write the changed value back to main memory
e. Release object lock
Because at the same time , Only one thread can enter the locked code , Guarantee mutual exclusion , At this point, the code block is a single threaded operation , It does not involve thread insecurity . Therefore, the locking operation is also the embodiment of natural atomicity and visibility .

synchronized Different ways of using
1. Decorate member methods in a class , The object of the lock is the current member class object

2. Modified static method , The lock is the current class object ( Globally unique , It is equivalent to locking the class )

At this point, just call this kind of object , Only one thread can execute at a time increase2 Method
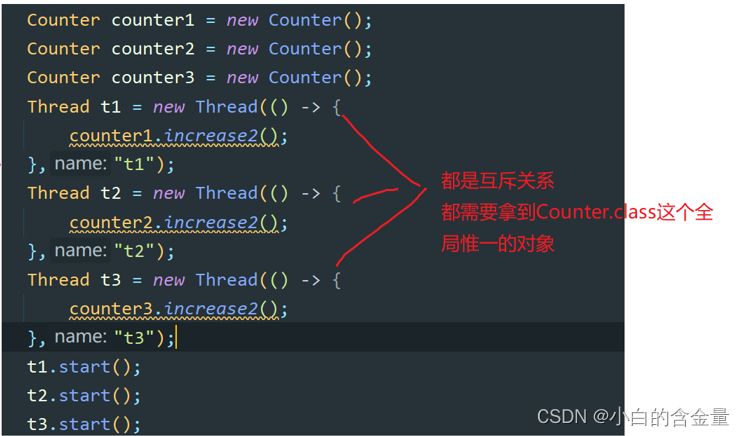
3. Decorated code block , Identify which object is being
The granularity of the lock is finer , Most used , Just add... To some code that needs to be locked synchronzied Key words can be used
We can go through this Lock every object

It can also be done through .class Lock the entire class directly

You can even pass parameters yourself , Customize the mutex relationship between threads

Java Thread safe classes in the standard library
The collection classes we learned earlier are unsafe in multithreading

So to ensure thread safety , We can use the following types :

These classes are all from java.util.concurrent class (Java Concurrent toolkit )

These classes guarantee thread safety , for example :
ConcurrentHashMap class : Lock all the methods

volatile keyword
1. It can guarantee the visibility of shared variables
volatile Keyword can force the thread to read and write the variable value of main memory
Equivalent to common shared variables , This keyword guarantees the visibility of shared variables

a. When the thread reads the content decorated by this keyword , The thread reads the value directly from main memory to working memory , Whether or not the current working memory is controlled by this value
b. When the thread writes this keyword variable , Refresh the current modified variable value from the working memory to the main memory immediately , also During this process, other threads will wait ( Not blocking ), Until the operation of writing back to main memory is completed , Ensure that the value read must be the refreshed value
For the same volatile Variable , His write operation must have occurred before the read operation , Make sure you read the data after the main memory is refreshed .
volatile Only visibility is guaranteed , Atomicity is not guaranteed , So if the thread is not atomic, the operation is still unsafe .
2. Use volatile Decorated variables are equivalent to a memory barrier
volatile Decorated code can prevent instruction rearrangement , That is, it must be after the execution of the previous code , The following code is executed before execution , No matter what CPU Which way do you think is better ,volatile The modified code execution position is fixed .

边栏推荐
- 1317. 将整数转换为两个无零整数的和
- [622. design cycle queue]
- Nlp-d62-nlp competition d31 & question brushing D15
- Go log -uber open source library zap use
- QListWidgetItem上附加widget
- 【Cocos Creator 3.5.1】坐标的加法
- 【FPGA】基于bt1120时序设计实现棋盘格横纵向灰阶图数据输出
- How to check the frequency of memory and the number of memory slots in CPU-Z?
- 洛谷P4683 [IOI2008] Type Printer 题解
- Some articles about component packaging and my experience
猜你喜欢

双位置继电器JDP-1440/DC110V

Qt使用Valgrind分析内存泄漏

Zener diode zener diode sod123 package positive and negative distinction

Edge loads web pages in IE mode - edge sets ie compatibility

Open the door small example to learn ten use case diagrams

开门小例子学习十种用例图

Gao Xiang slam14 lecture - note 1

多线程基础部分Part 1

Assembly language - Wang Shuang Chapter 13 int instruction - Notes

Discussion on streaming media protocol (MPEG2-TS, RTSP, RTP, RTCP, SDP, RTMP, HLS, HDS, HSS, mpeg-dash)
随机推荐
[nips 2017] pointnet++: deep feature learning of point set in metric space
【QT小作】使用结构体数据生成读写配置文件代码
表单校验 v-model 绑定的变量,校验失效的解决方案
1317. 将整数转换为两个无零整数的和
Qt使用Valgrind分析内存泄漏
导航【机器学习】
leetcode298周赛记录
Acwing's 57th weekly match -- BC question is very good
OpenCV的轮廓检测和阈值处理综合运用
Spark 之 WholeStageCodegen
Codeforces Round #802 (Div. 2)
IP网络通信的单播、组播和广播
项目-h5列表跳转详情,实现后退不刷新,修改数据则刷新的功能(记录滚动条)
汇编语言-王爽 第11章 标志寄存器-笔记
【Cocos Creator 3.5.1】input. Use of on
Unity point light disappears
What is BFC? What's the usage?
Go日志-Uber开源库zap使用
WebRTC系列-网络传输之7-ICE补充之提名(nomination)与ICE_Model
Some articles about component packaging and my experience