当前位置:网站首页>(p21-p24) unified data initialization method: List initialization, initializing objects of non aggregate type with initialization list, initializer_ Use of Lisy template class
(p21-p24) unified data initialization method: List initialization, initializing objects of non aggregate type with initialization list, initializer_ Use of Lisy template class
2022-06-12 08:27:00 【Ordinary people who like playing basketball】
List of articles
1. Unified initialization : List initialization
stay C++98/03 in , Corresponding to ordinary arrays and can be directly copied in memory (memcpy ()) The object of can be used List initialization To initialize the data
// Initialization of an array
int array[] = {
1,3,5,7,9 };
double array1[3] = {
1.2, 1.3, 1.4 };
// Object initialization
struct Person
{
int id;
double salary;
}zhang3{
1, 3000 };
stay C++11 in , List initialization has become more flexible , Let's take a look at the following code for initializing class objects
- eg:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
public:
Test(int) {
}
private:
Test(const Test &);
};
int main(void)
{
//t1: The most regular initialization method , Initialize the object through the provided structure with parameters
Test t1(520);
/* Grammar mistakes , Because the copy constructor provided is private . If the copy constructor is public ,520 Will be converted by implicit type conversion Test(int) Construct an anonymous object , Then, the anonymous object is copied and constructed t2 The mistake is VS It doesn't show up in , stay Linux Use in g++ The compiler will prompt the error described , The screenshot is as follows ps:vs It is useless to define the copy construct and the equal sign operator as private in , Unless used explicit */
Test t2 = 520;
/* t3 and t4: Used C++11 To initialize objects , Effect and t1 In the same way . In the beginning ,{} Whether the preceding equal sign is written or not has no effect on the initialization behavior . t3 Although the equal sign is used , But it is still list initialization , So private copy constructs have no effect on it . */
Test t3 = {
520 };
Test t4{
520 };
//t1、arr1 and t2、arr2: These two are the list initialization methods of basic data types , You can see , And object initialization methods are unified .
int a1 = {
1314 };
/* t4、a2、arr2 Writing , yes C++11 New syntax format added in , In this way, you can directly follow the initialization list after the variable name , To initialize variables or objects . */
int a2{
1314 };
int arr1[] = {
1, 2, 3 };
int arr2[]{
1, 2, 3 };
// Use list initialization to new Operator creates a new object for initialization
/* The pointer p Points to a new The memory returned by the operator , Initialize the memory data to... Through list initialization 520 Variable b After using the initial list for anonymous objects , And then copy initialization . Array array A block of memory is dynamically allocated on the heap , The initialization of multiple elements is directly completed through list initialization . */
int * p = new int{
520};
double b = double{
52.134};
int * array = new int[3]{
1,2,3};
return 0;
}
- test :

besides , List initialization can also be used directly on the return value of the function :
- eg:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(int id, string name)
{
cout << "id: " << id << ", name: " << name << endl;
}
};
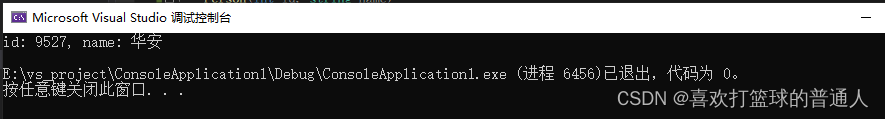
Person func()
{
// In code return { 9527, " Hua an " }; Equivalent to return (9527, " Hua an " );, An anonymous object is returned directly
return {
9527, " Hua an " };
}
int main(void)
{
Person p = func();
return 0;
}
- test :
2. List initialization details
Polymer
- stay C++11 in , The use of list initialization has been greatly enhanced , But some vague concepts also follow , As you can see from the previous example , List initialization can be used to initialize custom types , But for a custom type , List initialization may have two execution results
- eg:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct T1
{
int x;
int y;
}a = {
123, 321 };
struct T2
{
int x;
int y;
T2(int, int) : x(10), y(20) {
}
}b = {
123, 321 };
int main(void)
{
cout << "a.x: " << a.x << ", a.y: " << a.y << endl;
cout << "b.x: " << b.x << ", b.y: " << b.y << endl;
return 0;
}
- test :

In the above programs, the objects are initialized in the form of list initialization , But the result is different , object b Not initialized by data in initialization list , Why is that ?
- object a Is to initialize a custom aggregate type , It will use the data in the initialization list as a copy to initialize T1 Members of the structure .
- In structure T2 A constructor is customized in , So the actual initialization is done through this constructor .
It is also a custom structure and uses list initialization to initialize objects when creating objects , Why are objects initialized differently within a class ?
- Because if you use list initialization to initialize objects , You also need to determine whether the type corresponding to this object is a polymer , The data in the initialization list will be copied to the object .
Use List initialization when , For what type C++ I think it is a polymer ?
- An ordinary array itself can be seen as an aggregate type
int x[] = {
1,2,3,4,5,6};
double y[3][3] = {
{
1.23, 2.34, 3.45},
{
4.56, 5.67, 6.78},
{
7.89, 8.91, 9.99},
};
char carry[] = {
'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'};
std::string sarry[] = {
"hello", "world", "nihao", "shijie"};
Classes that meet the following conditions (class、struct、union) Can be seen as an aggregation type :
No user-defined constructor .
Unselfish or protected non static data members .
- scene 1: Class has private members , Cannot initialize with list initialization
struct T1
{
int x;
long y;
protected:
int z;
}t{
1, 100, 2}; // error, Class has private members , Cannot initialize with initialization list
- scene 2: Class has non static members that can be initialized through list initialization , But it cannot initialize static member variables .
struct T2
{
int x;
long y;
protected:
// Static variables in the structure z Cannot initialize with list initialization , Its initialization follows the static member initialization method .
static int z;
}t{
1, 100, 2}; // error
No base class .
No virtual function .
Class cannot have use {} and = Directly initialized non static data members ( from c++14 From the beginning ).
- from C++14 Start , Using list initialization can also be used in classes {} and = Initialized non static data members .
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct T2
{
int x;
long y;
protected:
static int z;
}t1{
1, 100 }; // ok
// Initialization of static members
int T2::z = 2;
struct T3
{
int x;
double y = 1.34;
int z[3]{
1,2,3};
};
int main(void)
{
T3 t{
520, 13.14, {
6,7,8}}; // error, c++11 I won't support it , from c++14 From the beginning
return 0;
}
Non polymer
For classes of aggregate type, you can directly use list initialization to initialize objects , It is also possible to use list initialization if the aggregation conditions are not met
- You need to customize a constructor inside the class , Class member variables are initialized in the constructor using the initialization list :
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct T1
{
int x;
double y;
// Initializing class members with an initialization list in the constructor
T1(int a, double b, int c) : x(a), y(b), z(c){
}
virtual void print()
{
cout << "x: " << x << ", y: " << y << ", z: " << z << endl;
}
private:
int z;
};
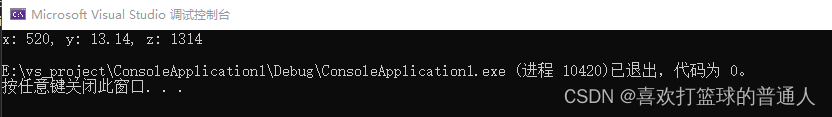
int main(void)
{
T1 t{
520, 13.14, 1314 }; // ok, Class members are initialized using the initialization list based on the constructor
t.print();
return 0;
}
- test :
in addition , It should be noted that the definition of aggregate types is not recursive , That is to say When a non static member of a class is a non aggregate type , This class may also be an aggregate type , For example, the following example :
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct T1
{
int x;
double y;
private:
int z;
};
struct T2
{
/* You can see ,T1 Not an aggregate type , Because it has a Private Non static members of . But even though T2 There is a non static member of non aggregate type t1,T2 Still an aggregate type , You can use list initialization directly . */
T1 t1;
long x1;
double y1;
};
int main(void)
{
/* Just to finish up t2 Object initialization process , For members of non aggregate types t1 When doing initialization , You can write a pair of empty braces directly {}, This is equivalent to calling T1 The parameterless constructor for . */
T2 t2{
{
}, 520, 13.14 };
return 0;
}
For an aggregate type , Using list initialization is equivalent to assigning values to each of the elements , For non aggregate types , You need to customize an appropriate constructor first , At this point, using list initialization will call its corresponding constructor .
3.std::initializer_list
- stay C++ Of STL In the container , You can initialize data of any length , The initialization list can only be used to initialize fixed parameters , If you want to do and STL It also has the ability to initialize with any length , have access to std::initializer_list This lightweight class template is used to implement .
- std::initializer_list Characteristics of class template :
It is a lightweight container type , Internally defined iterators iterator And so on , Iterators obtained during traversal are read-only .
about std::initializer_list for , It can receive initialization lists of any length , But the element must be of the same type T
stay std::initializer_list There are three internal member interfaces :size(), begin(), end().
std::initializer_list Objects can only be initialized or assigned as a whole .
As an ordinary function parameter
- Receive any number of parameters of the same type
- If you want to customize a function and accept any number of parameters ( Argument function ), You only need to specify the function parameter as std::initializer_list, Use initialization list { } You can pass data as an argument .
- eg:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void traversal(std::initializer_list<int> a)
{
for (auto it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main(void)
{
initializer_list<int> list;
cout << "current list size: " << list.size() << endl;
traversal(list);
list = {
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0 };
cout << "current list size: " << list.size() << endl;
traversal(list);
cout << endl;
list = {
1,3,5,7,9 };
cout << "current list size: " << list.size() << endl;
traversal(list);
cout << endl;
// Pass data directly through the initialization list , The initialization list can be viewed as an object //
traversal({
2, 4, 6, 8, 0 });
cout << endl;
traversal({
11,12,13,14,15,16 });
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
- test :

As a constructor parameter
- If a custom class wants to receive any number of arguments when constructing an object , The constructor can be specified as std::initializer_list type , The container is also used inside the custom class to store the received multiple arguments .
- eg:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
public:
Test(std::initializer_list<string> list)
{
for (auto it = list.begin(); it != list.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
m_names.push_back(*it);
}
cout << endl;
}
private:
vector<string> m_names;
};
int main(void)
{
Test t({
"jack", "lucy", "tom" });
Test t1({
"hello", "world", "nihao", "shijie" });
return 0;
}
test :

Reference resources : List initialization
边栏推荐
- MES帮助企业智能化改造,提高企业生产透明度
- Bean的作用域
- TMUX common commands
- Vision transformer | arXiv 2205 - TRT vit vision transformer for tensorrt
- visual studio2019的asp.net项目添加日志功能
- What is an extension method- What are Extension Methods?
- MYSQL中的查询
- Py & go programming skills: logic control to avoid if else
- Instructions spéciales pour l'utilisation du mode nat dans les machines virtuelles VM
- Group planning chapter I
猜你喜欢
(p36-p39) right value and right value reference, role and use of right value reference, derivation of undetermined reference type, and transfer of right value reference

FDA reviewers say Moderna covid vaccine is safe and effective for children under 5 years of age

Hands on learning and deep learning -- Realization of linear regression from scratch

JVM学习笔记:三 本地方法接口、执行引擎

JVM学习笔记:垃圾回收机制
KAtex problem of vscade: parseerror: KAtex parse error: can't use function '$' in math mode at position

Why should enterprises implement MES? What are the specific operating procedures?

How to understand the production scheduling of APS system?

(P17-P18)通过using定义基础类型和函数指针别名,使用using和typedef给模板定义别名

(P21-P24)统一的数据初始化方式:列表初始化、使用初始化列表初始化非聚合类型的对象、initializer_lisy模板类的使用
随机推荐
(P19-P20)委托构造函数(代理构造函数)和继承构造函数(使用using)
Regular expressions in JS
工厂的生产效益,MES系统如何提供?
What should be paid attention to when establishing MES system? What benefits can it bring to the enterprise?
Convolutional neural network CNN based cat dog battle picture classification (tf2.1 py3.6)
Vision Transformer | Arxiv 2205 - TRT-ViT 面向 TensorRT 的 Vision Transformer
Face recognition using BP neural network of NNET in R language
牛客网的项目梳理
报错:清除网站内搜索框中的历史记录?
Map the world according to the data of each country (take the global epidemic as an example)
vscode 下载慢解决办法
企业上MES系统的驱动力来自哪里?选型又该注意哪些问题?
FPGA implementation of right and left flipping of 720p image
Calling stored procedures in mysql, definition of variables,
(P36-P39)右值和右值引用、右值引用的作用以及使用、未定引用类型的推导、右值引用的传递
FPGA to flip video up and down (SRAM is61wv102416bll)
What kind of sparks will be generated when the remote sensing satellite meets the Beidou navigation satellite?
call方法和apply方法
安科瑞电动机保护器具有过载反时限、过载定时限、接地、起动超时、漏电、欠载、断相、堵转等功能
Hands on learning and deep learning -- simple implementation of linear regression