当前位置:网站首页>Unsupervised learning KMeans notes and examples
Unsupervised learning KMeans notes and examples
2022-08-03 12:13:00 【Sheep baa baa baa】
KMeans算法是一种简单的算法,能够快速,Efficiently cluster datasets,Usually it only takes a few iterations.KMeanscan be used as a clustering tool,At the same time, it can also be used as a dimensionality reduction method for feature dimensionality reduction.
KMeans可以通sklearn.cluster.kmeans中进行调用.
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
import numpy as np
blob_centers = np.array(
[[ 0.2, 2.3],
[-1.5 , 2.3],
[-2.8, 1.8],
[-2.8, 2.8],
[-2.8, 1.3]])
blob_std = np.array([0.4, 0.3, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1])
X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=2000, centers=blob_centers,
cluster_std=blob_std, random_state=7)
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
kmeans =KMeans(n_clusters=5)
kmeans.fit(X)
y_pred =kmeans.predict(X)
y_pred
y_pred is kmeans.labels_
kmeans.cluster_centers_##中心位置从中我们可以看出kmeans可以有labels_和cluster_centers_两个函数,kmeans.label_A classified copy of each instance can be displayed,而cluster_centers_Yes shows the classification center.
Predictions can now be made with new samples
x_new = np.array([[0,2],[3,2],[-3,3],[-3,2.5]])
kmeans.predict(x_new)
kmeans.transform(x_new)##Output each instance to5distance from the middle pointkmeans.transform()The distance from the input sample to the center of each category can be displayed.
good_init=np.array([[-3,3],[-3,2],[-3,1],[-1,2],[0,2]])
kmeans =KMeans(n_clusters=5,init =good_init,n_init=1)##initis the initial center point,n_init为迭代次数
kmeans.fit(X)
kmeans.inertia_##Output the within-cluster sum of squares
kmeans.score(X)##Returns negative inertiakmeans的超参数initis the selection method for selecting the center point,n_initis the number of clusters for the center point.
kmeans.inertia_is the sum of the squares of the distances from the sample to the center of the cluster,Call it the inertia of the model,kmeans.scoreis the output with negative inertia.
kmeans++算法:The purpose of its algorithm is to make the initial distribution of the center points wider,The probability of the algorithm converging to a suboptimal solution decreases.可以通过设置参数init为random进行实现.
##实现kmeans++
kmeans_plus = KMeans(n_clusters=5,init='random')
kmeans_plus.fit(X)
kmeans_plus.inertia_加速kmeans:Its algorithm makes use of trigonometric inequalities,Simplified calculation,提升了运行效率,可以通过algorithm=full进行设置.
##实现加速k-means
kmeans_add =KMeans(n_clusters=5,algorithm='full')
kmeans_add.fit(X)
kmeans.inertia_小批量kmeans:The algorithm is able to use mini-batches at each iterationkmeansMove the center point slightly.使用MiniBatchKMeans.
##小批量kmeans
from sklearn.cluster import MiniBatchKMeans
minibatch_kmeans =MiniBatchKMeans(n_clusters=5)
minibatch_kmeans.fit(X)
minibatch_kmeans.inertia_To determine whether a classification is reasonable can be calculated by calculating the silhouette score of the data,其范围在【-1,1】之间,当其=1是,It indicates that the instance classification is very close to the center,and away from other centers.
from sklearn.metrics import silhouette_score
silhouette_score(X,kmeans.labels_)
kmeans_per_k = [KMeans(n_clusters=k, random_state=42).fit(X)
for k in range(1, 10)]
silhouette_scores = [silhouette_score(X, model.labels_)
for model in kmeans_per_k[1:]]
inertias = [model.inertia_ for model in kmeans_per_k]
##对于sihouette_score来说,约接近1Indicates that the location is in its own cluster,and far away from other clusters.
##当接近-1When it means that the cluster is basically wrong
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3))
plt.plot(range(2, 10), silhouette_scores, "bo-")
plt.xlabel("$k$", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Silhouette score", fontsize=14)
plt.axis([1.8, 8.5, 0.55, 0.7])
plt.show()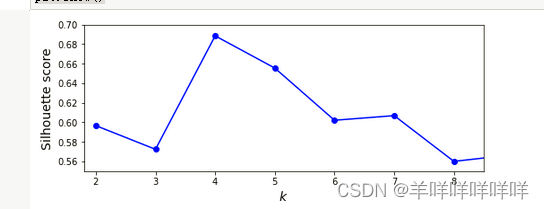
This picture illustrates the differencekThe contour score of the value of .
实例:使用kmeans进行图像分割
##Image segmentation using clustering
# Download the ladybug image
import os
import urllib
PROJECT_ROOT_DIR = "."
CHAPTER_ID = "unsupervised_learning"
IMAGES_PATH = os.path.join(PROJECT_ROOT_DIR, "images", CHAPTER_ID)
os.makedirs(IMAGES_PATH, exist_ok=True)
images_path = os.path.join(PROJECT_ROOT_DIR, "images", "unsupervised_learning")
os.makedirs(images_path, exist_ok=True)
DOWNLOAD_ROOT = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ageron/handson-ml2/master/"
filename = "ladybug.png"
print("Downloading", filename)
url = DOWNLOAD_ROOT + "images/unsupervised_learning/" + filename
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, os.path.join(images_path, filename))
from matplotlib.image import imread
image = imread(os.path.join(images_path, filename))
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=8).fit(X)
segmented_img = kmeans.cluster_centers_[kmeans.labels_]##Make adjustments to the instance samples,变成kmeansclustered class
segmented_img =segmented_img.reshape(image.shape)
segmented_imgs = []
n_colors = (10, 8, 6, 4, 2)
for n_clusters in n_colors:
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=n_clusters, random_state=42).fit(X)
segmented_img = kmeans.cluster_centers_[kmeans.labels_]
segmented_imgs.append(segmented_img.reshape(image.shape))
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.05, hspace=0.1)
plt.subplot(231)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.title("Original image")
plt.axis('off')
for idx, n_clusters in enumerate(n_colors):
plt.subplot(232 + idx)
plt.imshow(segmented_imgs[idx])
plt.title("{} colors".format(n_clusters))
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()Download the data here,然后通过kmeans进行聚类,Then by changing the number of clusters,画出图像.

实例2:利用kmeansPerform dimensionality reduction and preprocessing
这里通过MNISTThe image in the dimensionality reduction process
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
X_digits,y_digits =load_digits(return_X_y=True)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X_digits,y_digits)
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
log_reg =LogisticRegression()
log_reg.fit(x_train,y_train)
log_reg.score(x_test,y_test)
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
log_kmeans = Pipeline([
('kmeans',KMeans(n_clusters=50)),
('log_reg',LogisticRegression())
])
log_kmeans.fit(x_train,y_train)
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
param_grid = dict(kmeans__n_clusters=range(2, 100))
grid_clf = GridSearchCV(log_kmeans,param_grid,cv=3,verbose=2)
grid_clf.fit(x_train,y_train)
grid_clf.best_params_
grid_clf.score(x_test,y_test)
Logistic regression is used here for classification,查看没有使用kmeans时和使用kmeanswhen compared with the negative inertia,found the effect to be better.
实例三:使用kmeans进行半监督学习
##Semi-supervised learning using clustering
k =50
kmeans =KMeans(n_clusters=k)
x_digist_dist = kmeans.fit_transform(x_train)
representative_digit_idx =np.argmin(x_digist_dist,axis=0)##找到50the image closest to the center
x_representative_digists=x_train[representative_digit_idx]
x=x_representative_digists
log_reg =LogisticRegression(multi_class="ovr", solver="lbfgs", max_iter=5000, random_state=42)
log_reg.fit(x,y)
log_reg.score(x_test,y_test)
##Propagating tag instances by tag
y_train_propagated =np.empty(len(x_train),dtype=np.int32)
print(y_train_propagated)
for i in range(k):
y_train_propagated[kmeans.labels_==i]=y[i]
log_reg =LogisticRegression(multi_class="ovr", solver="lbfgs", max_iter=5000, random_state=42)
log_reg.fit(x_train,y_train_propagated)
log_reg.score(x_test,y_test)上面是通过给50samples were manually annotated,进行训练后,Propagate the labeled labels to all samples to all instances that agree on the cluster,Examples of cluster boundaries are included here,but will result in a false flag.
percentile_cloest=20
x_cluster_dist =x_digist_dist[np.arange(len(x_train)),kmeans.labels_]
x_cluster_dist
for i in range(k):
in_cluster =(kmeans.labels_==i)
cluster_dist = x_cluster_dist[in_cluster]
cutoff_distance=np.percentile(cluster_dist,percentile_cloest)
above_cutoff = (x_cluster_dist>cutoff_distance)
x_cluster_dist[in_cluster&above_cutoff]=-1
partially_propagated =(x_cluster_dist !=-1)
x_train_partially=x_train[partially_propagated]
y_train_partially =y_train[partially_propagated]
log_reg =LogisticRegression(multi_class="ovr", solver="lbfgs", max_iter=5000, random_state=42)
log_reg.fit(x_train_partially,y_train_partially)
log_reg.score(x_test,y_test)The above is filtered close to the center20%data are marked,然后进行训练.
DBSCAN聚类算法:It is a continuous area that defines a high density,It is by receiving parameterseps画一个圆,Count the number of samples within the circle,The minimum sample size is given by min_samples来决定,而且DBSCAN只能用于分类,但不能预测.
##DBSCAN
from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
X,y=make_moons(n_samples=1000,noise=0.05)
dbscan =DBSCAN(eps=0.05,min_samples=5)##min_samplesInclude at least one core instance5个实例,eps=0.05The description area is yes0.05为半径
dbscan.fit(X)
dbscan.labels_
##当数值=-1时,Explains that the algorithm treats the data as anomalies
dbscan.core_sample_indices_##The index of the core instance
dbscan.components_##核心实例本身dbscan.labels_Displays a copy of the instance classification,dbscan.core_sample_indicesDisplays the core instance index of the data.
dbscan.components_Displays the coordinates of the core instance.
实例四:对Olivettiface data for clustering,And determine whether you have the correct number of clusters.
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_olivetti_faces
data =fetch_olivetti_faces()Hierarchical classification of datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedShuffleSplit
sss = StratifiedShuffleSplit(n_splits=1,test_size=40,random_state=42)
train_index,test_index = next(sss.split(data.data,data.target))
x_train=data.data[train_index]
y_train =data.target[train_index]
x_test=data.data[test_index]
y_test=data.target[test_index]
sss_val = StratifiedShuffleSplit(n_splits=1,test_size=80,random_state=42)
train_index,val_index =next(sss_val.split(x_train,y_train))
x_train_new =x_train[train_index]
y_train_new =y_train[train_index]
x_val =x_train[val_index]
y_val =y_train[val_index]Choose the number of clusters with the best effect
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
kmeans =[KMeans(n_clusters=n).fit(x_train) for n in range(1,200,5)]
from sklearn.metrics import silhouette_score
silhouette_score =[silhouette_score(x_train,kmeans[i].labels_) for i in range(2,40)]
silhouette_score
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 20))
plt.plot(range(6,196,5), silhouette_score, "bo-")
plt.xlabel("$k$", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Silhouette score", fontsize=14)
plt.show()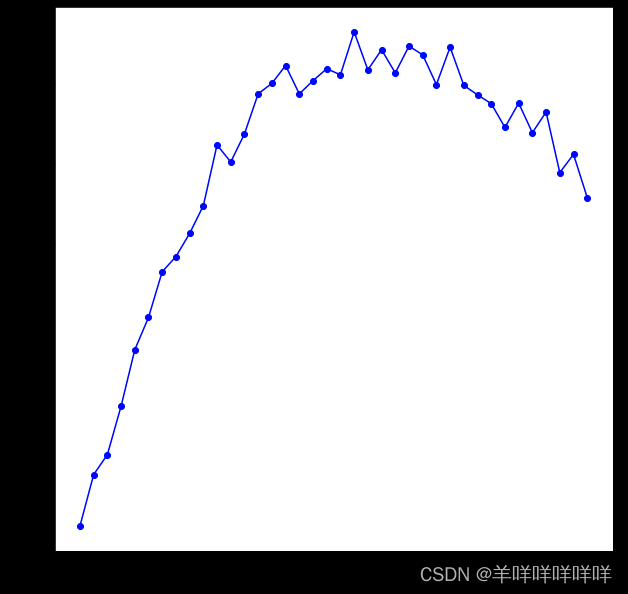
kmeans =KMeans(n_clusters=135)
kmeans.fit(x_train)
kmeans.inertia_显示结果
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
net start mysql 启动报错:发生系统错误5。拒绝访问。
bash case usage
LyScript 实现对内存堆栈扫描
智能日报脚本
Apache APISIX 2.15 版本发布,为插件增加更多灵活性
无监督学习KMeans学习笔记和实例
How to do App Automation Testing?Practical sharing of the whole process of App automation testing
LeetCode-142. 环形链表 II
数据库系统原理与应用教程(075)—— MySQL 练习题:操作题 151-159(十九):综合练习
一个扛住 100 亿次请求的红包系统,写得太好了!!
【倒计时5天】探索音画质量提升背后的秘密,千元大礼等你来拿
信创建设看广州|海泰方圆亮相2022 信创生态融合发展论坛
微信为什么使用 SQLite 保存聊天记录?
小身材有大作用——光模块寿命分析(二)
常用lambda表达式
Go 语言快速入门指南: 介绍及安装
谷歌研究员被群嘲:研究员爆料AI有意识,被勒令休假
bash while循环和until循环
Kubernetes 网络入门
Matlab学习11-图像处理之图像变换