当前位置:网站首页>Dynamic programming knapsack problem 01 knapsack explanation
Dynamic programming knapsack problem 01 knapsack explanation
2022-07-23 16:31:00 【Round to two meters high Xiaochen】
List of articles
One 、 Problem introduction
1. What is dynamic programming ?
Dynamic programming ( English :Dynamic programming, abbreviation DP), It's kind of in math 、 management science 、 Computer science 、 Used in economics and bioinformatics , A method of solving complex problems by decomposing the original problem into relatively simple subproblems . Dynamic programming is often applied to problems with overlapping subproblems and optimal substructure properties
The core idea : By dividing the problem into small problems , Record past results , Reduce repetition
Small example :
A : "1+1+1+1+1+1+1+1 =?"
A : " What is the value of the above equation "
B : Calculation "8"
A : Write... On the left side of the equation above "1+" Well ?
A : " What is the value of the equation "
B : It's a quick answer "9"
A : " How can you know the answer so quickly "
A : " As long as 8 On the basis of 1 That's it "
A : " So you don't have to recalculate , Because you remember that the value of the first equation is 8! Dynamic programming algorithm can also be said to be ' Remember to save time by asking for solutions '"
2. What is the knapsack problem ?
knapsack problem (Knapsack problem) It's a kind of combinatorial optimization NP Problem completely . The problem can be described as : Given a set of items , Each item has its own weight and price , Within the total weight limit , How do we choose , To maximize the total price of the item . The name of the problem comes from how to choose the most suitable item to put in a given backpack . Similar problems often arise in business 、 Combinatorial mathematics , Computational complexity theory 、 In the fields of cryptography and applied mathematics . The knapsack problem can also be described as a decisive problem , That is, the total weight does not exceed W Under the premise of , Whether the total value can reach V? It's in 1978 Year by year Merkle and Hellman Proposed .
Common categories :
- 01 knapsack
- Completely backpack
- Multiple backpack
- Pack in groups
3. What is? 01 knapsack ?
01 Knapsack is the simplest problem in knapsack problem .01 The constraint of knapsack is to give several items , Each item has and only one , And there are two attributes: weight and volume . stay 01 In the knapsack problem , Because there is only one of each kind , For each item, you only need to consider the selection and non selection . If you don't choose to put it in your backpack , There is no need to deal with . If you choose to put it in your backpack , Because I don't know how much space the previously placed items occupy , You need to enumerate all the situations that may occupy the backpack space after putting this item into the backpack .
4. How to solve the knapsack problem ?
It can be roughly divided into these steps :
- State means / Determine the state variable ( function )
- State calculation / Set partitioning / Determine the state transfer equation ( Recurrence equation )
- Determine the boundary conditions
Two 、 Example explanation
1. subject :

2. analysis
2.1 First step : State means
The greatest value is Quantity of articles i and Backpack Capacity j Function of .
Let's set the function f[i][j] Express front i Item Put in Capacity of j The backpack Maximum value of .
The ultimate maximum value is the number of items i from 0 Growth to n, Backpack Capacity j from 0 Growth to m At the time of the f[n][m] value .
2.2 The second step : Determine the state transfer equation
State variables :f[i][j] Before presentation i The capacity of items is j The biggest value of our backpack
The current capacity is j, We have to consider the second i Item Can you put in ? Whether to put in ?
- If the current Backpack Capacity j<v[i], Can't put , be f[i][j]=f[i-1][j]
- If the current Backpack Capacity j>=v[i], It can be put in, but the cost should be compared
2.1 If the first i Items are not put into the backpack , be f[i][j]=f[i-1][j]
2.2 If the first i Put this item into your backpack , be f[i][j]=f[i-1][j-v[i]]+w[i]
If the first i Put this item into your backpack , Then the backpack capacity is left j-v[i], So take the front i-1 Items are put into the remaining capacity of the backpack j-v[i] The maximum value obtained f[i-1][j-v[i]].
State transition equation :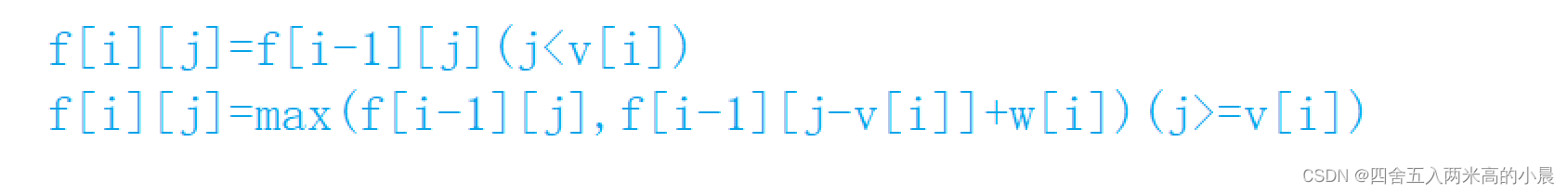
It can be illustrated as :
2.3 The boundary conditions
about 01 For backpacks, the boundary is f[i][j]=0, When i=0 perhaps j=0 when f[i][j] The value of is 0.
i=0 when , It means that there is no item in the backpack , At this time, the maximum value of backpacks is impossible , So for 0;
j=0 when , Indicates that the capacity of the backpack is 0, Then you can't put items at this time , So the maximum value is 0;
3. The process represents
3.1 Core code

3.2 Manual calculation

The green line indicates that every time you put i About items , And it shows its source
3.3 Code validation

3.4 Complete code
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=1010;
int n,m;
int v[N],w[N];//v Array storage volume ,w Array storage value
int f[N][N];
int main ()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>v[i]>>w[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<=m;j++)
{
f[i][j]=f[i-1][j];// Will not be placed in the i The condition of an item is combined with the condition that it can be put but not put
if(j>=v[i]) f[i][j]=max(f[i][j],f[i-1][j-v[i]]+w[i]);
}
cout<<f[n][m]<<endl;
return 0;
}
3、 ... and 、 Optimize
1. Optimization purpose :
Optimize the two-dimensional representation into one-dimensional , Reduce the use of space , Use a one-dimensional array f[j] Only one line of data is recorded , Give Way j Value sequence loop , Sequential update f[j]
2. Optimized code < Not necessarily right >

3. Program validation

The answer is clearly wrong , Why? ???
4. Error point analysis
If j Is a sequential update , that f[j-v[i]] Will precede f[j] to update , When comparing , In fact, it is comparing with the updated value , This leads to the wrong answer , So here's the solution j Reverse cycle . When j When it is in reverse order ,f[j] Will precede f[j-v[i]] to update , That is to say, use the old value f[j-v[i]] To update f[j], Equivalent to using the previous line f[j-v[i]] Go to more f[j], So the answer is correct .
5. Improved code

There is another small mistake at this time , That's it j The scope is not >=1, because j If it is less than v[i] Will lead to f[j-v[i]] The subscript in becomes negative , So make improvements , The final code is :
边栏推荐
- MySQL multi table query_ Inner connection_ Show internal connections
- Flutter | 给 ListView 添加表头表尾最简单的方式
- VMware platform STS certificate expired
- 博客表情大全
- 阿里二面:MySQL 啥时候用表锁,啥时候用行锁?
- SOC的第一个Hello_World实验
- (已解决)idea编译Gradle项目提示 错误找不到符号
- Cloud native (11) | kubernetes chapter kubernetes principle and installation
- 牛客-TOP101-BM36
- vulnstack红日-4
猜你喜欢

Ali Er Mian: when does MySQL use table locks and row locks?

Bean Validation起源篇----01

ICML 2022 | sparse double decline: can network pruning also aggravate model overfitting?

阿里二面:MySQL 啥时候用表锁,啥时候用行锁?

Flutter 组件的生命周期、State 管理及局部重绘 | 开发者说·DTalk

千万别让富坚义博看到这个

7月HCIP Datacom认证考试通过
自定义一个对象

Mysql客户端到服务端字符集的转换

将.calss文件转为.jar-idea篇
随机推荐
[suctf 2018]multisql (MySQL precompiled)
知道为什么PCBA电路板会板翘吗?
ICML 2022 | sparse double decline: can network pruning also aggravate model overfitting?
JS filter / replace sensitive characters
Cover - computer knowledge guide
CloudCompare&PCL 法向量空间采样(NSS)
激光共聚焦如何选择荧光染料
vulnstack红日-4
Flutter | 指定页面回传值的类型
VMware platform STS certificate expired
7月HCIP Datacom认证考试通过
基于USB数据采集卡(DAQ)与IO模块的热电阻温度采集「建议收藏」
距7月30日PMP考试不足10天,应该做点什么?
Redis key has no expiration time set. Why was it actively deleted
STM32F103+RFID-RC522模块 实现简单读卡写卡demo「建议收藏」
Flutter 组件的生命周期、State 管理及局部重绘 | 开发者说·DTalk
fastadmin,非超级管理员,已赋予批量更新权限,仍显示无权限
【Taro】小程序picker动态获取数据
PgSQL mistakenly deletes PG_ Wal file, service startup failed
大端模式和小端模式的记忆方法