当前位置:网站首页>[array creation in numpy]
[array creation in numpy]
2022-07-26 00:39:00 【In my opinion】
Catalog
Two 、 utilize array Create array
3、 ... and 、 utilize arange Create array
Four 、 Random number creation array
5、 ... and 、ndarray object
6、 ... and 、 Other ways to create arrays
7、 ... and 、 Slicing and indexing of arrays
One 、NumPy What is it? ?
1.NumPy It is the basic library of Scientific Computing , Provide a large number of scientific computing related functions , Such as data statistics , Random number generation , Its core type is multidimensional array (ndarray), Support a large number of dimension arrays and matrix operations , Support vector processing ndarray object , Improve the operation speed of the program .
2.NumPy install
pip install numpy
Two 、 utilize array Create array
1.numpy Module array Function can generate multidimensional arrays , If you generate a two-dimensional array , You need to array Function passes a list type parameter , Each list element is one-dimensional ndarray Type array , As rows of a two-dimensional array ,numpy in shape[n] attribute , You can get the number of elements in each dimension ,n from 0 Start
# The import module
import numpy as np
# Use array Function to create a one-dimensional array
a=np.array[1,2,3,4]
print(a)
# Use array Function to create a two-dimensional array
b=np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]])
print(b)
# Use array Function to create a three-dimensional array
c=np.array([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]])
print(c)
#array Function dtype Use , Specify the type of the element
d=np.array([1,2,3],dtype=float)
print(d)
#array in ndmin Use , Specify the dimension of the array
m=np.array([1,2,3],dtype=float,ndmin=3)
print(m)3、 ... and 、 utilize arange Create array
Use arange Function to create a numeric range and return ndarray object , Format :
numpy.arange(start,end,step)
| Parameters | explain |
| start | Starting value ( The default is 0) |
| end | Termination value ( It doesn't contain ) |
| step | step , The default is 1 |
| dtype | return ndarray Data type of |
# Import numpy
import numpy as np
# review range Use (start,end,step) [start,end)
a=list(range(1,10)) # Step length is 1
print(a)
b=list(range(10))
print(b)
c=list(range(1,10,3))
print(c)
#arange Create array (start,end,step)
m=np.arange(1,11)
print(m)
# Set step size
n=np,arange(1,11,2)
print(n)
# Set up dtype
e=np.arange(10,20,2,dtype=float)
print(e)[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
[1, 4, 7]
[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10][1 3 5 7 9]
[10. 12. 14. 16. 18.]
Four 、 Random number creation array
numpy.random.random(size=None)
This method returns [0.0~1.0) Between random floating-point numbers
# The import module
import numpy as np
# Use random Create a one-dimensional array
a=np.random.random(size=10)
# Create a 2D array
b=np.random.random(size=(2,3)) #2 That's ok 3 Array of columns
# Create a three-dimensional array
c=np.random.random(size=(2,3,4)) # Two 3 That's ok 4 Column Create random integer method :
numpy.random.randint(low,high,size)
This method returns a random integer , If only low, The return range is [0,low), If there is high, The return range is [low,high)
# The import module
import numpy as np
# establish 0~10 One dimensional random integer
a=np.random.randint(11,size=10)
# establish 0~10 Two dimensional random integer
b=np.random.randint(11,size=(2,3)) #2 That's ok 3 Column
# establish 5~10 Three dimensional random integer
c=np.random.ramdint(5,11,size=(2,3,4)) #2 individual 3 That's ok 4 Column Create a standard normal distribution ( The expectation is 0, The variance of 1):
numpy.random.randn(d0,d1...dn):dn Represents each dimension
# The import module
import numpy as np
# Create one dimension
a=np.random.randn(3)
# Create 2D
b=np.random.randn(2,3)
# Create 3D
c=np.random.randn(2,3,4)Creates a normal distribution of specified expectations and variances :
numpy.random.normal(loc,scale,size)
loc: expect ,scale: variance
5、 ... and 、ndarray object
1.ndarray object , Is a collection of data of the same type , By subscript 0 Start indexing the elements in the collection
2.ndarray Object properties of
| attribute | explain |
| .ndim | Rank , Number of axes or dimensions |
| .shape | Dimension of array , For matrices (n,m) |
| .size | The total number of array elements |
| .dtype | Element type |
| .itemsize | The size of each element , Bytes are units |
| .flags | Object's memory information |
| .real | ndarray The real part of the element |
| .imag | ndarray The imaginary part of the element |
6、 ... and 、 Other ways to create arrays
1.zeros establish , Element use 0.0 fill :
numpy.zeros((5,),dtype=int) #5 individual 0 Array of elements
numpy.zeros((2,3)) #2 That's ok 3 Column 0.0 Array of elements
2.ones establish , Element use 1.0 fill
3.empty Create the specified shape 、 Uninitialized array of data types , The value of the element is the value of the previous memory
4.linspace Create a sequence of equal differences
numpy.linspace(5,20,5,endpoint=False) # barring 20
[5. 8. 11. 14. 17.]
5.logspace Create an equal ratio sequence
numpy.logspace(start,stop,num,endpoint,base,dtype)
among , Sequence start value base**start, Termination value base**stop, Generate num individual
7、 ... and 、 Slicing and indexing of arrays
One dimensional array :
1. Indexes :x=numpy.arange(10)
Forward index :x[0]~x[9]
Reverse index :x[-9]~x[-1]
2. section :[start,end,step]
Forward operation in slice :
x[:] : From start to end
x[start:] : from start From the beginning to the end
x[:end] : From the beginning to end-1
x[start:end] : from start Start to end-1
x[start:end:step] : from start Start to end-1, In steps of step
Negative operation in slice :
x[::-1]: Reverse output
x[-5:-2]: Last but not least 5 individual ~ Last but not least 3 individual
Two dimensional array :
1. Indexes :
x=numpy.arange(1,13)
a=x.reshape((4,3)
# Index the second row and the third column
print(a[1,2]) perhaps print(a[1][2])
# Get the second row, the third column, and the third row, the first column
print(a[1,2],a[2,0]) perhaps print(a[(1,2),(2,0)]
2. section :[ Slice rows , Slice columns ] [start:end:step,start:end:step]
x=numpy.arange(1,13)
a=x.reshape((4,3)
print(a(:,:)) # Get all rows and columns
print(a[:,1])# The second column of all rows
print(a[1,:]) # Second row of all columns
print(a[::2,:]) # All odd rows
边栏推荐
- TID-MOP:面向数据交易所场景下的安全管控综合框架
- Data driven DDT for automated testing
- Nodejs starts mqtt service with an error schemaerror: expected 'schema' to be an object or Boolean problem solving
- 【IJCAI 2022】参数高效的大模型稀疏训练方法,大幅减少稀疏训练所需资源
- 力扣记录:剑指offer(2)——JZ13-22
- How to open the Internet and ask friends to play together?
- sql语句练习
- 【oops-framework】界面管理
- HCIP第十三天
- Are you still counting the time complexity?
猜你喜欢
![[redis] ② redis general command; Why is redis so fast?; Redis data type](/img/72/aaa90d5411b8b20b15a7f87b98bd27.png)
[redis] ② redis general command; Why is redis so fast?; Redis data type

HCIP第十二天
BGP comprehensive experiment

基于MFFMB的电商评论文本分类研究

快速入门顺序表链表

Jmeter之用户自定义变量和抽离公共变量

Verilog grammar basics HDL bits training 06

The way to understand JS: six common inheritance methods of JS
The way of understanding JS: what is prototype chain
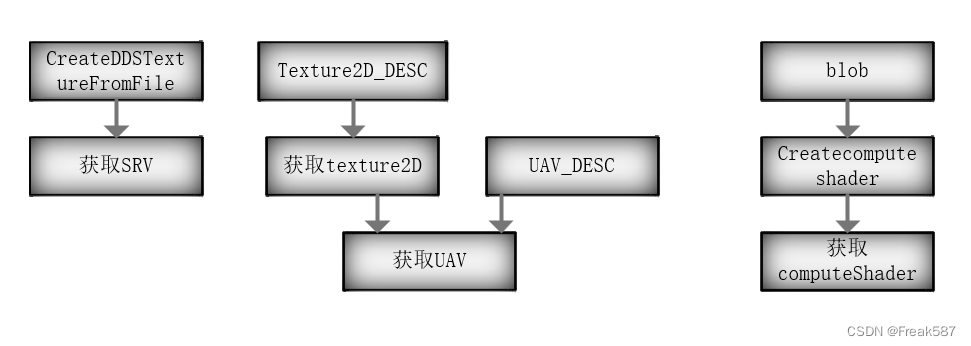
Getting started with D3D calculation shaders
随机推荐
Sorting out the encapsulation classes of control elements in appium
本地电脑架设传奇怎么开外网叫朋友一起玩?
Shardingsphere data slicing
Redis killed twelve questions. How many questions can you carry?
sql语句练习
HNOI2012矿场搭建
SereTOD2022 Track1代码剖析-面向半监督和强化学习的任务型对话系统挑战赛
Data driven DDT for automated testing
sql(基础二)
12. Neural network model
DC-6--vulnhub靶场
C#从入门到精通(三)
【NumPy中数组相关方法】
[GOM引擎]假人配置的脚本设置方法
测试左移和测试右移的概念
快速入门顺序表链表
MPLS experiment
8个小妙招-数据库性能优化,yyds~
LDP related knowledge
分布式事务和Seata的AT模式原理