当前位置:网站首页>【GAN】SAGAN ICML‘19
【GAN】SAGAN ICML‘19
2022-06-22 06:56:00 【chad_ lee】
《Self-Attention Generative Adversarial Networks》ICML’19,Goodfellow A signature .
The deep convolution network can improve GANs Details of generating high resolution pictures . This article aims to solve the problem of generating large-scale correlation (Long-range dependency) The picture area of ,CNN The influence of local receptive field , So in DCGAN On the basis of the introduction of Self-attention.
What problem to solve
When generating, for example, face images , Details are very important , Like left and right eyes , As long as there is a little asymmetry between the left and right eyes , The generated face will be especially unreal , So the area of the left and right eyes is “ Large scale correlation ”(Long-range dependency) Of . There is Long-range dependency There are a lot of , But because of CNN Limitation of local receptive field ( Convolution kernel is difficult to cover a large area ), It's hard to capture global information , For example, the influence of the left eye on the right eye cannot be seen when convoluting the right eye area , The left and right eyes of the generated face image may not be related .
Want to see the overall information , There are several ways :1、 Increase the size of convolution kernel 、 Expand the feeling field —— Increase the amount of parameters and calculation , And unless the convolution kernel is as large as the picture , Otherwise, there is still a blind spot in the field of vision ;2、 Deepen the convolution layer —— Increase the amount of calculation ;3、 Use the full connection layer to obtain global information —— lose a great deal through trying to save a little .
So the self- attention Introduction is a simple and efficient method .
How do you do it? ——SAGAN Model
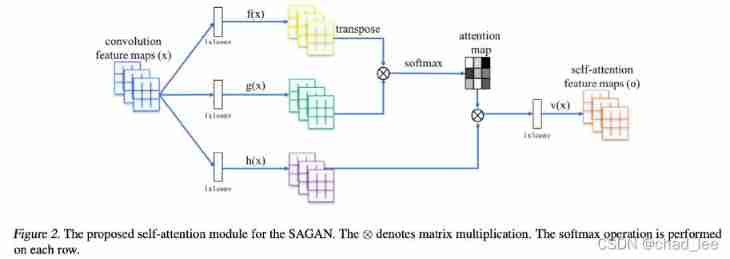
Let's start by introducing :
After convolution operation feature map x x x, x ∈ R C × N \boldsymbol{x} \in \mathbb{R}^{C \times N} x∈RC×N. f ( x ) , g ( x ) , h ( x ) f(x), g(x),h(x) f(x),g(x),h(x) All are 1 × 1 1 \times1 1×1 Convolution of , take f ( x ) f(x) f(x) Transpose and... Of output g ( x ) g(x) g(x) Multiply the output of , after softmax Normalize to get a attention map; What will be obtained attention map and h ( x ) h(x) h(x) Point by point multiplication , obtain self-attention Characteristic graph .
Concrete realization : f ( x ) = W f x , g ( x ) = W g x , h ( x ) = W h x \boldsymbol{f}(\boldsymbol{x})=\boldsymbol{W}_{\boldsymbol{f}} \boldsymbol{x}, \boldsymbol{g}(\boldsymbol{x})= \boldsymbol{W}_{\boldsymbol{g}} \boldsymbol{x}, \boldsymbol{h}(\boldsymbol{x})=\boldsymbol{W}_{\boldsymbol{h}} \boldsymbol{x} f(x)=Wfx,g(x)=Wgx,h(x)=Whx,$W_{g} \in R^{\bar{C} \times C}, W f ∈ R c ˉ × C , W_{f} \in R^{\bar{c} \times C}, Wf∈Rcˉ×C,W_{h} \in R^{C \times C}$ Is the weight matrix of learning , adopt 1 × 1 1\times1 1×1 The realization of convolution , C C C Number of channels , Used in experiments C ˉ = C / 8 \bar{C}=\mathrm{C} / 8 Cˉ=C/8.
use β j , i \beta_{j,i} βj,i Indicates that in the synthesis of j j j When the model is divided into regions, it is right for the i i i The degree of influence of each location , Yes :
β j , i = exp ( s i j ) ∑ i = 1 N exp ( s i j ) , where s i j = f ( x i ) T g ( x j ) \beta_{j, i}=\frac{\exp \left(s_{i j}\right)}{\sum_{i=1}^{N} \exp \left(s_{i j}\right)}, \text { where } s_{i j}=\boldsymbol{f}\left(\boldsymbol{x}_{\boldsymbol{i}}\right)^{T} \boldsymbol{g}\left(\boldsymbol{x}_{\boldsymbol{j}}\right) βj,i=∑i=1Nexp(sij)exp(sij), where sij=f(xi)Tg(xj)
Output of the final attention layer o = ( o 1 , o 2 , … , o j , … , o N ) ∈ R C × N \boldsymbol{o}=\left(\boldsymbol{o}_{\boldsymbol{1}}, \boldsymbol{o}_{\mathbf{2}}, \ldots, \boldsymbol{o}_{\boldsymbol{j}}, \ldots, \boldsymbol{o}_{\boldsymbol{N}}\right) \in \mathbb{R}^{C \times N} o=(o1,o2,…,oj,…,oN)∈RC×N:
o j = v ( ∑ i = 1 N β j , i h ( x i ) ) , h ( x i ) = W h x i , v ( x i ) = W v x i \boldsymbol{o}_{\boldsymbol{j}}=\boldsymbol{v}\left(\sum_{i=1}^{N} \beta_{j, i} \boldsymbol{h}\left(\boldsymbol{x}_{\boldsymbol{i}}\right)\right), \boldsymbol{h}\left(\boldsymbol{x}_{\boldsymbol{i}}\right)=\boldsymbol{W}_{\boldsymbol{h}} \boldsymbol{x}_{\boldsymbol{i}}, \boldsymbol{v}\left(\boldsymbol{x}_{\boldsymbol{i}}\right)=\boldsymbol{W}_{\boldsymbol{v}} \boldsymbol{x}_{\boldsymbol{i}} oj=v(i=1∑Nβj,ih(xi)),h(xi)=Whxi,v(xi)=Wvxi
In addition, residual connection is required :
y i = γ o i + x i \boldsymbol{y}_{\boldsymbol{i}}=\gamma \boldsymbol{o}_{\boldsymbol{i}}+\boldsymbol{x}_{\boldsymbol{i}} yi=γoi+xi
among γ \gamma γ Is a learnable proportional parameter , γ \gamma γ Is initialized to 0, Then gradually learn to assign more weights to nonlocal features . The author believes that the early stage mainly depends on CNN Learn local features , The task ranges from simple to difficult , Gradually add weight to nonlocal features . stay SAGAN There are attention modules in the generator and the discriminator . Cross training D D D and G G G Of loss:
L D = − E ( x , y ) ∼ p d a t a [ min ( 0 , − 1 + D ( x , y ) ) ] − E z ∼ p z , y ∼ p data [ min ( 0 , − 1 − D ( G ( z ) , y ) ) ] L G = − E z ∼ p z , y ∼ p data D ( G ( z ) , y ) \begin{aligned} L_{D}=&-\mathbb{E}_{(x, y) \sim p_{d a t a}}[\min (0,-1+D(x, y))] \\ &-\mathbb{E}_{z \sim p_{z}, y \sim p_{\text {data }}}[\min (0,-1-D(G(z), y))] \\ L_{G}=&-\mathbb{E}_{z \sim p_{z}, y \sim p_{\text {data }}} D(G(z), y) \end{aligned} LD=LG=−E(x,y)∼pdata[min(0,−1+D(x,y))]−Ez∼pz,y∼pdata [min(0,−1−D(G(z),y))]−Ez∼pz,y∼pdata D(G(z),y)
From another perspective —— Stacking model
SAGAN It's all about DCGAN Two layers are added on the basis of self-attention layer , Most of the author's open source code also comes from DCGAN, Other open source SAGAN Just add two layers of attention .
This can also be seen from the model diagram in the paper , f ( x ) f(x) f(x) Namely q u e r y query query, g ( x ) g(x) g(x) Namely k e y key key, h ( x ) h(x) h(x) Namely v a l u e value value. The model diagram is just a description of attention Calculation process :
Stability training GAN The technique of
Spectral Normalization
SAGAN quote SNGAN Spectral norm normalization method , But at the same time D and G Spectral norm normalization is added , Give Way D To satisfy the 1-lipschitz Limit , It also avoids G Too many parameters of lead to abnormal gradient , Make the whole training smooth and efficient .
Normalization of spectral norm is achieved by dividing the gradient by a spectral norm , The spectral norm is derived from the gradient matrix itself .
Two Time- Scale Update Rule(TTUR)
Optimizing G When , We assume by default that our D The discrimination ability is better than the current G The ability to generate is better , such D Talent coaching G Learn for the better . The usual practice is to update D One or more times , Then update G Parameters of ,TTUR A simpler update strategy is proposed , That is to say D and G Set different learning rates , Give Way D Faster convergence . That is, the learning rate of the discriminator is generally set to be greater than that of the generator .
What effect does it bring
In addition to better experimental results , The author also proved that Long-range dependency, Success justifies itself .
visualization attention map:

The arrow represents the dot “query location”, It can be seen that the neural network learns to allocate attention according to the similarity of color and texture , Not just spatial adjacency ( Such as the upper left corner ), So although some query points are very close in space , But their attention maps can be very different .
边栏推荐
- Why did I choose rust
- Dijin introduces digi connectcore voice control software for connectcore system module
- Map of STL knowledge summary
- Which is the best agency mode or decoration mode
- 仙人掌之歌——进军To C直播(2)
- Five common SQL interview questions
- JS中控制对象的访问
- [php]tp6 cli mode to create tp6 and multi application configurations and common problems
- 6. install the SSH connection tool (used to connect the server of our lab)
- How can we effectively alleviate anxiety? See what ape tutor says
猜你喜欢

一个算子在深度学习框架中的旅程
![[out of distribution detection] learning confidence for out of distribution detection in neural networks arXiv '18](/img/07/d5479dde181c355d95c73e2f58c0da.jpg)
[out of distribution detection] learning confidence for out of distribution detection in neural networks arXiv '18

流程引擎解决复杂的业务问题

Introduction to 51 Single Chip Microcomputer -- timer and external interrupt
![[php]tp6 cli mode to create tp6 and multi application configurations and common problems](/img/19/0a3319b04fe6449c90ade6f27fca4a.png)
[php]tp6 cli mode to create tp6 and multi application configurations and common problems
vue连接mysql数据库失败

How can we effectively alleviate anxiety? See what ape tutor says
![[openairinterface5g] RRC NR resolution (I)](/img/04/fec30b5c86f29d82bd7d0b13293494.jpg)
[openairinterface5g] RRC NR resolution (I)

The journey of an operator in the framework of deep learning

Xh_CMS渗透测试文档
随机推荐
Cesium loading 3D tiles model
Rebuild binary tree
Generate string mode
[M32] simple interpretation of MCU code, RO data, RW data and Zi data
-Bash: telnet: command not found solution
Difference between grail layout and twin wing layout
What exactly is the open source office of a large factory like?
C skill tree evaluation - customer first, making excellent products
The song of cactus - marching into to C live broadcast (1)
leetcode:面试题 08.12. 八皇后【dfs + backtrack】
C language - deep understanding of arrays
Which is the best agency mode or decoration mode
Tpflow V6.0.6 正式版发布
College entrance examination is a post station on the journey of life
The tidb community offline exchange meeting was seen by the partners from Tianjin and Shijiazhuang~
Introduction to 51 Single Chip Microcomputer -- minimum system of single chip microcomputer
CNN模型合集 | Resnet变种-WideResnet解读
Five common SQL interview questions
Great progress in code
cookie的介绍和使用