当前位置:网站首页>Xgboost Guide
Xgboost Guide
2022-06-23 02:10:00 【Gluttonous competition】
Reprint learning :http://blog.csdn.net/bryan__/article/details/52056112, If there is any infringement , Contact deletion
One .xgboost The advantages of
1. Regularization
xgboost Regular terms are added to the cost function , To control the complexity of the model . The regular term contains the number of leaf nodes in the tree 、 Output on each leaf node score Of L2 The sum of the squared magnitudes . from Bias-variance tradeoff perspective , Regular terms reduce the value of the model variance, Make the model easier to learn , Prevent over fitting , This is also xgboost Is superior to the traditional GBDT A feature of .
2. parallel processing
xgboost Tools support parallelism .boosting Isn't it a serial structure ? How parallel ? Be careful xgboost The parallel of tree Granularity parallelism ,xgboost One iteration is the end of the next iteration ( The first t The cost function of the second iteration contains the preceding t-1 The predicted value of the second iteration ).xgboost The parallelism of is on the feature granularity . We know , One of the most time-consuming steps in learning a decision tree is to sort the values of the features ( Because we want to determine the optimal segmentation point ),xgboost Before training , The data is sorted in advance , And save it as block structure , This structure is used repeatedly in subsequent iterations , Greatly reduced computation . This block Structure also makes parallelism possible , When splitting nodes , You need to calculate the gain for each feature , Finally, the feature with the largest gain is selected to split , Then the gain calculation of each feature can be opened multithreading .
3. flexibility
xgboost Support user-defined objective function and evaluation function , As long as the target function is second derivative .
4. Processing of missing values
There is a missing sample for the value of the feature ,xgboost Can automatically learn its split direction
5. prune
XGBoost Start by building all the subtrees that can be built from the top down , Then prune from bottom to top . Compared with GBM, It is not easy to fall into the local optimal solution
6. Built-in cross validation
xgb.cv() Does it feel convenient
Two .xgboost Parameters of
from http://blog.csdn.net/wzmsltw/article/details/50994481
XGBoost The parameters of can be divided into three types : General parameters 、booster Parameters and learning objective parameters
- General parameters: The parameter control is in lifting (boosting) Which one to use in the process booster, frequently-used booster A tree model (tree) And linear model (linear model).
- Booster parameters: It depends on which one you use booster.
- Learning Task parameters: Control the learning scene , For example, in regression problems, different parameters are used to control the sort .
- In addition to the above parameters, there may be other parameters , Use on the command line
General Parameters
- booster [default=gbtree]
- There are two models to choose from gbtree and gblinear.gbtree A tree-based model is used for lifting calculations ,gblinear The linear model is used for lifting calculation .
The default value is gbtree
- There are two models to choose from gbtree and gblinear.gbtree A tree-based model is used for lifting calculations ,gblinear The linear model is used for lifting calculation .
- silent [default=0]
- take 0 Represents the information printed at the time of shipment , take 1 Time means to operate in silence , Do not print runtime information .
The default value is 0 - It is suggested that 0, The output data in the process is helpful to understand the model and adjust parameters . In addition, I actually set it to 1 It is also often impossible to run silently ..
- take 0 Represents the information printed at the time of shipment , take 1 Time means to operate in silence , Do not print runtime information .
- nthread [default to maximum number of threads available if not set]
- XGBoost Number of threads at run time .
The default value is the maximum number of threads available on the current system - If you want to run at maximum speed , It is not recommended to set this parameter , The model will automatically get the maximum threads
- XGBoost Number of threads at run time .
- num_pbuffer [set automatically by xgboost, no need to be set by user]
- size of prediction buffer, normally set to number of training instances. The buffers are used to save the prediction results of last boosting step.
- num_feature [set automatically by xgboost, no need to be set by user]
- boosting The characteristic dimension used in the process , Set to the number of features .
XGBoost It's automatically set , You don't need to set it manually
- boosting The characteristic dimension used in the process , Set to the number of features .
Booster Parameters
From xgboost-unity, the bst: prefix is no longer needed for booster parameters. Parameter with or without bst: prefix will be equivalent(i.e. both bst:eta and eta will be valid parameter setting) .
Parameter for Tree Booster
- eta [default=0.3]
- To prevent over fitting , The size of the contraction step used in the update process . After each lift calculation , The algorithm gets the weight of the new feature directly . eta By reducing the weight of features, the calculation process of promotion is more conservative .
The default value is 0.3 - The value range is :[0,1]
- Usually last set eta by 0.01~0.2
- To prevent over fitting , The size of the contraction step used in the update process . After each lift calculation , The algorithm gets the weight of the new feature directly . eta By reducing the weight of features, the calculation process of promotion is more conservative .
- gamma [default=0]
- minimum loss reduction required to make a further partition on a leaf node of the tree. the larger, the more conservative the algorithm will be.
- range: [0,∞]
- Models by default , For the partition of a node, only its loss function The result is greater than 0 Only when , and gamma The minimum required is given loss function Value
- gamma The algorithm with a value of is more conservation, And its value depends on loss function , Parameters should be adjusted in the model .
- max_depth [default=6]
- The maximum depth of a number .
The default value is 6 - The value range is :[1,∞]
- Refers to the maximum depth of the tree
- The deeper the tree , The better the fit of the data ( The higher the degree of over fitting ). That is, this parameter is also a control over fitting
- Cross validation is recommended (xgb.cv ) Adjusting parameters
- Usually the value is :3-10
- The maximum depth of a number .
- min_child_weight [default=1]
- The smallest sample weight sum in the child node . If the sample weight sum of a leaf node is less than min_child_weight The split process ends . In the current regression model , This parameter refers to the minimum number of samples required for each model . The more mature the algorithm, the more conservative. That is, increasing this parameter can control over fitting .
- The value range is : [0,∞]
- max_delta_step [default=0]
- Maximum delta step we allow each tree’s weight estimation to be. If the value is set to 0, it means there is no constraint. If it is set to a positive value, it can help making the update step more conservative. Usually this parameter is not needed, but it might help in logistic regression when class is extremely imbalanced. Set it to value of 1-10 might help control the update
- The value range is :[0,∞]
- If the value is 0, That means no limit . If positive , Then bring xgboost The update process is more conservative .
- It is not usually necessary to set this value , But in the use of logistics When returning , If the category is extremely unbalanced , Then adjusting this parameter may have an effect
- subsample [default=1]
- The proportion of subsamples used to train the model to the entire sample set . If set to 0.5 Means that the XGBoost The whole sample set will be randomly washed out 50% Set up a tree model of subsamples , This prevents overfitting .
- The value range is :(0,1]
- colsample_bytree [default=1]
- The proportion of random sampling of features when building the tree .
The default value is 1 - Value range :(0,1]
- The proportion of random sampling of features when building the tree .
- colsample_bylevel[default=1]
- Determine the proportion of sub samples for each node partition
- Usually do not use , because subsample and colsample_bytree Can already play the same role
- scale_pos_weight[default=0]
- A value greater than 0 can be used in case of high class imbalance as it helps in faster convergence.
- Greater than 0 The value of can handle the situation of category imbalance . Help the model converge faster
Parameter for Linear Booster
- lambda [default=0]
- L2 Regular penalty coefficient
- Used for processing XGBoost The regularization part of . Usually do not use , But it can be used to reduce over fitting
- alpha [default=0]
- L1 Regular penalty coefficient
- When the data dimension is very high, you can use , Make the algorithm run faster .
- lambda_bias
- On the bias L2 Regular .
The default value is 0( stay L1 The regularity of no offset terms on , because L1 Time offset is not important )
- On the bias L2 Regular .
Task Parameters
- objective [ default=reg:linear ]
- Define learning tasks and corresponding learning objectives , The optional objective functions are as follows :
- “reg:linear” – Linear regression .
- “reg:logistic” – Logical regression .
- “binary:logistic” – Logistic regression of dichotomies , The output is probability .
- “binary:logitraw” – Logistic regression of dichotomies , The output result is wTx.
- “count:poisson” – Counting problem poisson Return to , The output is poisson Distribution .
- stay poisson In the regression ,max_delta_step The default value is 0.7.(used to safeguard optimization)
- “multi:softmax” – Give Way XGBoost use softmax The objective function deals with multiple classification problems , You also need to set the parameters num_class( The number of categories )
- “multi:softprob” – and softmax equally , But the output is ndata * nclass Vector , I can take that vector reshape become ndata That's ok nclass Columns of the matrix . No row represents the probability that the sample belongs to each category .
- “rank:pairwise” –set XGBoost to do ranking task by minimizing the pairwise loss
- base_score [ default=0.5 ]
- the initial prediction score of all instances, global bias
- eval_metric [ default according to objective ]
- The evaluation index needed to verify the data , Different target functions will have default evaluation metrics (rmse for regression, and error for classification, mean average precision for ranking)
- Users can add a variety of evaluation indicators , about Python The user to list Pass parameter pairs to the program , instead of map Parameters list Parameter does not override ’eval_metric’
- The choices are listed below:
- “rmse”: root mean square error
- “logloss”: negative log-likelihood
- “error”: Binary classification error rate. It is calculated as #(wrong cases)/#(all cases). For the predictions, the evaluation will regard the instances with prediction value larger than 0.5 as positive instances, and the others as negative instances.
- “merror”: Multiclass classification error rate. It is calculated as #(wrong cases)/#(all cases).
- “mlogloss”: Multiclass logloss
- “auc”: Area under the curve for ranking evaluation.
- “ndcg”:Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain
- “map”:Mean average precision
- “[email protected]”,”[email protected]”: n can be assigned as an integer to cut off the top positions in the lists for evaluation.
- “ndcg-“,”map-“,”[email protected]“,”[email protected]“: In XGBoost, NDCG and MAP will evaluate the score of a list without any positive samples as 1. By adding “-” in the evaluation metric XGBoost will evaluate these score as 0 to be consistent under some conditions.
training repeatively
- seed [ default=0 ]
- Seed of random Numbers .
The default value is 0 - Can be used to produce repeatable results ( Take the same... Every time seed The same random partition can be obtained )
- Seed of random Numbers .
▲ Tradition GBDT With CART As a base classifier ,xgboost It also supports linear classifiers , This is the time xgboost It's equivalent to taking L1 and L2 Logistic regression of regularized terms ( Classification problem ) Or linear regression ( The return question ).
▲ Tradition GBDT We only use the first derivative information when we optimize ,xgboost Second order Taylor expansion of the cost function is carried out , First and second derivatives are used at the same time . By the way ,xgboost The tool supports custom cost functions , As long as the function can be derived first and second order .
▲xgboost Regular terms are added to the cost function , To control the complexity of the model . The regular term contains the number of leaf nodes in the tree 、 Output on each leaf node score Of L2 The sum of the squared magnitudes . from Bias-variance tradeoff perspective , Regular terms reduce the value of the model variance, Make the model easier to learn , Prevent over fitting , This is also xgboost Is superior to the traditional GBDT A feature of .
▲Shrinkage( cut ), It's equivalent to learning speed (xgboost Medium eta).xgboost After an iteration , The weight of the leaf node is multiplied by the coefficient , Mainly to weaken the influence of each tree , Let's have more learning space behind . Practical application , Generally put eta Set it down a little bit , Then set the number of iterations a little bit higher .( Add : Tradition GBDT There is also a learning rate in the implementation of )
▲ Column sampling (column subsampling):xgboost We learn from random forest , Support column sampling , Not only can over fitting be reduced , It also reduces computation , This is also xgboost Different from tradition gbdt A feature of .
▲ Dealing with missing values : There is a missing sample for the value of the feature ,xgboost Can automatically learn its split direction .
▲xgboost Tools support parallelism :boosting Isn't it a serial structure ? How parallel ? Be careful xgboost The parallel of tree Granularity parallelism ,xgboost One iteration is the end of the next iteration ( The first t The cost function of the second iteration contains the preceding t-1 The predicted value of the second iteration ).xgboost The parallelism of is on the feature granularity . We know , One of the most time-consuming steps in learning a decision tree is to sort the values of the features ( Because we want to determine the optimal segmentation point ),xgboost Before training , The data is sorted in advance , And save it as block structure , This structure is used repeatedly in subsequent iterations , Greatly reduced computation . This block Structure also makes parallelism possible , When splitting nodes , You need to calculate the gain for each feature , Finally, the feature with the largest gain is selected to split , Then the gain calculation of each feature can be opened multithreading .
▲ Parallelizable approximate histogram algorithm : When the tree node is splitting , We need to calculate the gain of each segmentation point for each feature , That is to enumerate all possible segmentation points by greedy method . When data cannot be loaded into memory at one time or in a distributed situation , Greedy algorithms become inefficient , therefore xgboost A parallel approximate histogram algorithm is also proposed , For efficient generation of candidate segmentation points .
reply @ Xiao Yan's questions in his comments , Because some formulas are better placed in the text . The main idea of the question discussed in the comments is “xgboost Add a regular term to the cost function , Is it better than cart The pruning of ”. In fact, Chen Tianqi's great God slides It is also mentioned , I worked as a porter .
The learning process of decision tree is to find the optimal decision tree , However, finding the optimal decision tree from all the decision trees in the function space is NP-C problem , So we often use heuristic (Heuristic) Methods , Such as CART Optimization inside GINI Index 、 prune 、 Control the depth of the tree . These heuristic methods often imply an objective function , This is what most people often overlook .xgboost The objective function of is as follows :
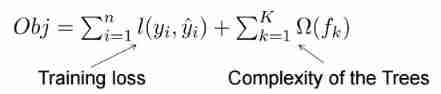
The canonical term controls the complexity of the model , Including the number of leaf nodes T and leaf score Of L2 The square of a module :

What does this have to do with pruning ?
Skip a series of derivations , Let's go straight to xgboost The formula used to split the nodes in the tree :

This formula formally follows ID3 Algorithm ( use entropy Calculate the gain ) 、CART Algorithm ( use gini Exponentially calculate the gain ) It's consistent , They all use some value after splitting subtract Some value before splitting , Thus, the gain . To limit the growth of trees , We can join the threshold , When the gain is greater than the threshold, the node is split , On the type of gamma That's the threshold , It is the number of leaf nodes in the regular term T The coefficient of , therefore xgboost While optimizing the objective function, it is equivalent to pre pruning . in addition , There is also a coefficient in the above formula lambda, It's in the regular term leaf score Of L2 Modulus squared coefficient , Yes leaf score It's smoothed , It also prevents over fitting , This is a tradition GBDT Features not available in .
xgboost Use experience to sum up
▲ Multi category classification , Category needs to be from 0 Start coding
▲Watchlist It will not affect the model training .
▲ Category characteristics must be coded , because xgboost All features are assumed to be numerical by default
▲ Adjustable parameter :Notes on Parameter Tuning as well as Complete Guide to Parameter Tuning in XGBoost (with codes in Python)
https://github.com/dmlc/xgboost/blob/master/doc/param_tuning.md
http://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2016/03/complete-guide-parameter-tuning-xgboost-with-codes-python/
▲ In training , In order that the results may be reproduced , Remember to seed random numbers .
▲XGBoost How to get the importance of the characteristics ? The importance of a feature (feature score), Equal to the sum of the number of times it was selected as a tree node splitting feature , Like features A In the first iteration ( The first tree ) Was chosen 1 Split the tree nodes for the second time , Selected in the second iteration 2 Time ….. So the final feature A Of feature score Namely 1+2+….
边栏推荐
- //1.8 char character variable assignment integer
- Wechat mobile terminal development - account login authorization
- 2022-1-14
- Uniapp View Horizontal Center
- Operator part
- Initial structure
- Bc110 tic tac toe chess
- On function overloading from several examples
- Exercise analysis summary
- Game (sanziqi & minesweeping)
猜你喜欢

Google account cannot be logged in & external links cannot be opened automatically & words with words cannot be used

Information theory and coding

Ansible practice of Nepal graph
CSDN browser assistant for online translation, calculation, learning and removal of all advertisements

Classical questions of function recursion

Nfv and SDN

9. class and object practice and initialization list

1. Mx6u bare metal program (6) - timer

Common mistakes in C language (sizeof and strlen)

JS prototype and prototype chain Paramecium can understand
随机推荐
On function overloading from several examples
Bc113 small leloding alarm clock
Uint8 serializing and deserializing pits using stringstream
Initial structure
[CodeWars] Convert Decimal Degrees to Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
JS case: support canvas electronic signature function on PC and mobile
JS to realize the rotation chart (riding light). Pictures can be switched left and right. Moving the mouse will stop the rotation
Dynamic address book in C language (add, delete, modify, check (duplicate), delete, sort and export)
Performance testing -- Interpretation and practice of 16 enterprise level project framework
II Data preprocessing
Muduo simple usage
Application and challenge of ten billion level map data in Kwai security intelligence
How to make word notes beautiful
C. Diluc and Kaeya——Codeforces Round #724 (Div. 2)
Third order magic cube formula
Small knowledge points of asset
An interesting example of relaxed memory models
JS advanced part
Nebula operator cloud practice
Primary pointer part