当前位置:网站首页>Information theory and coding
Information theory and coding
2022-06-23 02:01:00 【A new doggerel imitating ancient times】
Information theory studies the measurement of information , The content mainly focuses on Shannon's three theorems , The limit value of information transmission rate without distortion is studied , And the limit value of information rate under the condition that the information source is given and certain distortion is allowed , It also studies how to make the best use of the transmission capacity of the channel when the bit error rate is less than the given value .
Coding is the feasible direction pointed out by Shannon , A discipline developed to seek effective and reliable compilation methods , This paper mainly studies various feasible coding schemes and implementation techniques in noisy channels .
Information theory
- What is the message ?
Information is an increase in certainty , Measurement of information ( entropy ) It is a measure of information uncertainty . - Digital communication system
Digital communication system source 、 Source and channel encoder 、 channel 、 Source and channel decoder 、 Shinjuku consists of five parts ;
The source encoder converts the source symbols into symbols suitable for channel transmission , And compress the redundancy of the source to improve the effectiveness of communication , Also called compression coding ;
The channel encoder improves the reliability of communication by adding redundant error correction symbols , Cooperate with decoding to reduce the error rate to the allowable range .
1. Source
- The mathematical model of the source is a sample space and a probability measure .
- Sources are divided into discrete and continuous 、 Having no memory and having memory . Discrete memoryless single symbol source only outputs one discrete symbol message at a time , Symbols at different times are statistically independent of each other ; The message output from the discrete memoryless extended source is a symbol sequence composed of many symbols sent at different times , Successively issued symbols are statistically independent of each other , The probability of a symbol sequence is the product of the probabilities of each symbol in the sequence ; There is a dependency between messages sent out successively in time by a memory source .
2. channel
- The mathematical model of the channel is described by transition probability .
- Channels are divided into discrete and continuous 、 Having no memory and having memory . Discrete memoryless single symbol channel (DMC) The input and output of are discrete single symbols without memory , Discrete memoryless N The input and output of the dimensional expansion channel are all N The symbol sequence of , The channel transition probability of the sequence corresponds to N Product of symbol channel transition probabilities .
- Four common DMC: Binary symmetric channel , Interference free channel , Binary delete channel , binary Z channel .
3. Measurement of information
Self information
- Self information ( The amount of information ):

- Conditional self information : Received yj After the xi The uncertainty of whether it happens :

q(xi) For a priori probability ,q(xi|yj) It's a posterior probability .
Mutual information
- Mutual information : event x,y The mutual information between them is y What happens is about x The amount of information , be equal to “x The amount of self information ” subtract “y Under the condition of x The amount of self information ”:



- The nature of mutual information
reciprocity : I(x;y)=I(y;x);
Negativity : yj The occurrence of xi The possibility of happening ;
When xi,yj Statistical independence , The mutual information quantity and conditional mutual information quantity are 0;
The mutual information of any two events is not greater than the self information of one event .
Information entropy
Average self information ( entropy , Source entropy ):

Average conditional self information ( Conditional entropy ):
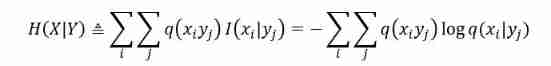
joint probability q(xiyj)=q(yj|xi)q(xi)=q(xi|yj)q(yj); When X and Y Statistical independence ,q(xiyj)=q(xi)q(yj).Joint entropy :H(X) In two dimensions XY On the promotion of

Average mutual information ( Interaction entropy ):

entropy , Conditional entropy , The relation of joint entropy :

When X,Y Statistical independence :
Interaction entropy and source entropy , The relation of conditional entropy :

Properties of entropy function
- Extremum ( Maximum discrete entropy theorem ): For a finite set of discrete random variables , When the events in the set occur with equal probability , Entropy is maximum .

- Conditional entropy is less than or equal to unconditional entropy : H(Y|X) ≤ H(Y);
- The joint entropy is greater than the entropy of the independent event , Less than or equal to the sum of the entropy of two independent events :H(XY)>=H(X),H(XY)>=H(Y),H(XY)<=H(X)+H(Y).
Average mutual information property
- non-negative :I(X;Y)>=0;
- reciprocity :I(X;Y)=I(Y;X);
- extremum :I(X;Y)<=H(X),I(X;Y)<=H(Y);
- Concavity and convexity : Average mutual information I(X;Y) It's the source n Convex function , It's a channel u Type convex function .
4. Source code
Lossless coding does not change the entropy of the source .
Classification of codes
Source coding can be regarded as source symbol set ( news ) A mapping to a set of code symbols , A codeword is a combination of code symbols ; Only uniquely decodable is discussed in the course ( Uniquely decodable and error free coding ).
Binary code : The code symbol set is 0,1;
Equal length code / Variable length code : Are uniquely decodable ;
Strange code / Nonsingular code : Different messages of nonsingular codes correspond to different codewords ;
Original code N Secondary expansion code : Put the source N A new source symbol sequence is obtained by second extension, and a new code is obtained by concatenation of the original code ;
The only decoding : arbitrarily N The sub extended codes are all nonsingular codes ;
The shortest average code length among all the decoded codes is called the best code , Source coding is to find the best code .
Kraft inequality :
Instant code : Any code word is not the code of the prefix of other code words ( Also known as no prefix code );
The real-time code must be the only one that can be decoded ; Real time codes can be constructed by tree graph method
Information transmission rate
- Average code length :

- Information transmission rate :

- Coding efficiency :

Equal length coding theorem and variable length coding theorem
- Equal length coding theorem

- Variable length coding theorem ( Shannon's first theorem )

Three common variable length coding methods
- Shannon coding , FeNO coding , Huffman coding ( The coding efficiency is the highest )
5. Fundamentals of channel coding
Channel coding is the processing and transformation to resist channel interference and improve reliability , Such as error control code , The simplest is " Repeat encoding , Multiple choice decoding ".
Channel capacity 
I(X;Y) Is the average amount of information per symbol , For undisturbed channels, there are I(X;Y)=H(X); Channel capacity C It is to ensure the maximum information transmission capacity that the channel can accommodate under reliable communication , For fixed channels , Channel capacity is a fixed value ; To achieve channel capacity , Source distribution ( Channel input probability ) Certain conditions must be met .
- One dimensional channel and N Dimensional channel relations :

When both the source and the channel are discrete without memory , The equal sign is established , namely N The problem of dimensional sequence transmission can be reduced to the problem of single symbol transmission . - The channel capacity of several special channels and the necessary and sufficient conditions for reaching the channel capacity :

Symmetric channels / Quasi symmetric channel / Strongly symmetric channel : A little .
Channel coding theorem ( Shannon's second theorem )
- Maximum a posteriori decoding criterion : The minimum error probability is equal to the maximum a posteriori probability .
I will receive yi After all x Choose to make a posteriori probability q(x|y)( Also known as channel ambiguity ) maximal xi As decoding . - Maximum likelihood decoding criterion : received yi After all x Choose to make the transition probability q(y|x) maximal xi As decoding .
- Channel coding theorem : For any discrete memoryless channel DMC, When the information transmission rate of the channel R<C, Code length N Long enough , The decoding rule can always be found to make the minimum average error decoding probability at the channel output Pmin Reach any small ( Channel capacity C Is the information transmission rate in error free transmission R The limit value of ).
- Inverse theorem of channel coding : When R>C There is no way to make the error rate arbitrarily small ( Or go to zero ).
Rate distortion coding theorem ( Shannon's third Theorem )
- Distortion measure d(x,y): Quantization distortion .
- Average distortion : Distorted mathematical expectations .
- Distortion function :

- Properties of rate distortion function
range :
Domain of definition :
R(D) It's continuous , monotonous , Decreasing function . - Rate distortion coding theorem : Given allowable distortion D, When the information transmission rate R>R(D) when , As long as the source sequence is long enough , A coding method can always be found to make the average distortion approach D.
边栏推荐
- Pychart installation instructions
- Summary of the first week of winter vacation
- Garbled code of SecureCRT, double lines, double characters, unable to input (personal detection)
- Install MySQL (5.7+8.0) through docker and configure master-slave replication (gtid+ enhanced semi synchronization)
- Operator part
- Exercise analysis summary
- Use of higher order functions
- Epoll introduction and principle explanation
- Dynamic address book in C language (add, delete, modify, check (duplicate), delete, sort and export)
- Vs Code inadvertently disable error waveform curve
猜你喜欢
CSDN browser assistant for online translation, calculation, learning and removal of all advertisements

Using WordPress to create a MySQL based education website (learning notes 2) (technical notes 1) xampp error1045 solution

Detailed explanation of clip attribute parameters

1. Mx6u startup mode and equipment

Cmake configuration error, error configuration process, Preject files may be invalid

Data analysis method - user group analysis

Module 8 job

Do you know the memory components of MySQL InnoDB?

JS prototype and prototype chain Paramecium can understand

JS - single sign on
随机推荐
Constexpr keyword
Triangle judgment (right angle, equilateral, general)
//1.11 basic operators
Download and compile ROS source code
Anaconda creates a new environment encounter pit
Hello
Use of higher order functions
Philosopher's walk gym divide and conquer + fractal
Byte order: big endian vs little endian
Pywebio to quickly build web applications
Interviewer: why does TCP shake hands three times and break up four times? Most people can't answer!
CSDN browser assistant for online translation, calculation, learning and removal of all advertisements
Cmake simple usage
[hdu] P6964 I love counting
Three methods for solving Fibonacci sequence feibonacci (seeking rabbit) - program design
Arm assembly syntax
Uniapp View Horizontal Center
Application and challenge of ten billion level map data in Kwai security intelligence
1. Mx6u startup mode and equipment
await is only valid in async function