当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to thread pool: ThreadPoolExecutor
Introduction to thread pool: ThreadPoolExecutor
2022-06-11 10:58:00 【iiiiiiiiiooooo】
Introduction to thread pool
Why thread pools
Multithreading technology mainly solves the problem of multi thread execution in processor unit , It can reduce the idle time of the processor unit , Increase the throughput of processor unit , Multithreading can really maximize the computing power of multi-core processors , But if you use threads at will , On the contrary, it is unfavorable to the system performance
- It takes time to create and destroy threads : Suppose that the time required for a server to complete the intended task is :T1 Indicates the thread creation time ,T2 Indicates the thread execution time ,T3 Indicates the time of destruction , If T1+T3 Far greater than T2, It's not worth the loss
- Threads also need to occupy free memory , A large number of threads will occupy precious memory resources , May lead to OOM It's abnormal
- A lot of thread recycling will also give GC There's a lot of pressure , extend GC The pause time
- A large number of threads will also preempt CPU resources ,CPU Keep switching in the context of each thread , Instead, there is no time to deal with the tasks that should be handled when the thread is running
What is a thread pool
Thread pool is to create several executable threads and put them into a pool , Get threads from the pool when needed , You don't have to create it yourself , Use completion does not need to destroy threads, but put them into the thread pool , This reduces the overhead of creating and destroying objects
Therefore, pool resources to avoid frequent creation and destruction of threads , Let the created thread be reused , There is the concept of thread pool , Some active threads are maintained in the thread pool , If necessary , Go to the thread pool to get threads to use , Return to the thread pool after use , Eliminates the overhead of creating and destroying threads , And the thread pool will also have a certain limit on the number of threads , The essence of thread pool is the reuse of thread resources
Advantages of thread pool
1. Reduce resource consumption , Reduces the cost of thread creation and destruction by reusing created threads
2. Improve response time , When the mission arrives , Tasks can be executed immediately without waiting for a thread to be created
3. Improved thread manageability , It can not only reduce the consumption of system resources , At the same time, the system stability is improved
4. Thread pool can realize unified allocation , Tune and monitor
Architecture of thread pool

Executor Interface is the most basic interface
ExecutorService Interface inherited Executor Interface , Add some extension methods to it , A true thread pool interface, so to speak
AbstractExecutorService The abstract class is implemented ExecutorService Most of the interfaces in
ThreadPoolExecutor Inherited AbstractExecutorService, Is the specific implementation of thread pool
ScheduledExecutorService Interface inherited from ExecutorService Interface , Provides " Periodically " The function of
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor Class inherits from ThreadPoolExecutor Class and implemented ScheduledExecutorService Interface , yes ” With periodic execution “ Function thread pool
Executors Is a static factory for thread pools , Provides a static method to quickly create a thread pool
Executor Interface : Submit task interface , Only one is provided Executor Method , perform Runnable Type of task
public interface Executor {
void execute(Runnable command);
}ExecutorService Interface :ExecutorService Interface is the interface of the real thread pool , stay Executor On this basis, some extensions have been made , Mainly to submit tasks , Terminate task
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
// Close thread pool
void shutdown();
// Shut down immediately
List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
// Whether to shut down
boolean isShutdown();
// Whether to terminate
boolean isTerminated();
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
// Submit tasks , There are various types of submitted tasks , It also has asynchronous function
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException;
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}ScheduledExecutorService Interface : It provides a method to perform tasks periodically
public interface ScheduledExecutorService extends ExecutorService {
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command,
long delay, TimeUnit unit);
public <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable,
long delay, TimeUnit unit);
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit);
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit);
}Executors Create common thread pools :
Executor Factory classes provide initialization interfaces , Mainly as follows
newFixedThreadPool: A fixed number of thread pools
demonstration :10 Tasks submitted to at the same time newFixedThreadPool
private static AtomicInteger num=new AtomicInteger();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// A fixed number of thread pools
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
fixedThreadPool.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Random random = new Random();
System.out.println(" The thread of :"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+": Perform tasks :"+num.getAndIncrement());
try {
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(100));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}Output results :

Fixed number of threads thread pool bottom implementation :
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}Create a thread pool with a specified number of worker threads , among corepoolsize and maximumPoolSize equal , Blocking queues are based on LinkedBlockingQueue Realized
FixedThreadPool: The number of incoming core threads is fixed , So it becomes a bounded process pool , The maximum number of threads is equal to the number of core threads . Suppose the number of core threads is 3, One time submission 10 A mission , Start three threads to execute three tasks , The remaining seven tasks enter the blocking queue , Because the number of core threads is equal to the maximum number of threads , therefore keepAlivetime Parameters have no meaning , Waiting for any thread to finish execution will continue to get a task from the blocking queue for execution
A thread pool with a fixed number of threads can improve program efficiency , At the same time, it can save the time of creating threads
newCachedThreadPool: Cacheable worker thread pool
demonstration :10 Tasks submitted to at the same time newCachedThreadPool
private static AtomicInteger num=new AtomicInteger();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Thread pool that caches worker threads
ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
cachedThreadPool.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Random random = new Random();
System.out.println(" The thread of :"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+": Perform tasks :"+num.getAndIncrement());
try {
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(100));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}Execution results :

The demonstration shows that , Multiple threads are created to execute the task body
Cacheable worker pool underlying implementation :
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}Create a cacheable worker thread pool , The core thread is 0, The number of threads in the thread pool can reach Integer.MAX_VALUE, namely 2^32, Default thread lifetime 60 second , Internally used queues SynchronousQueue Synchronous blocking queue , When there is no task to perform , When the thread is idle for more than 60 second , The worker thread will terminate , When a new task is submitted , If there are no idle threads , Then create a new thread to execute the task
Cacheable thread pool , If there are new tasks and no idle threads available , New thread , If the thread is idle for a long time ( exceed 60s) The thread is recycled
There is no limit to the size of the thread pool , The size of the thread pool depends entirely on the maximum thread size that the operating system can create ,
Cacheable thread pools are suitable for applications that require less time , There is no need to consider the occasion of synchronization
newSingleThreadExecutor: The thread pool of a single thread
demonstration :10 Tasks submitted to at the same time newSingleThreadExecutor
private static AtomicInteger num=new AtomicInteger();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// The thread pool of a single thread
ExecutorService singleThreadExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
singleThreadExecutor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Random random = new Random();
System.out.println(" The thread of :"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+": Perform tasks :"+num.getAndIncrement());
try {
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(100));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}Execution results :

There can only be one thread in the thread pool to execute tasks
The underlying implementation of single thread pool :
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}There is only one thread in the single thread pool , If the thread ends abnormally , A new thread is recreated to continue the task , The only thread can ensure the sequential execution of submitted tasks , For internal use LinkedBlockingQueue As a blocking queue
newFixedThreadPool(1): The thread pool of a fixed number of threads in the given parameter is 1 It can be regarded as newSingleThreadExecutor
newScheduledThreadPool: Periodic execution task thread pool
public class DIYRunable implements Runnable {
private Integer num;
public DIYRunable(Integer num) {
this.num = num;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(" The thread of :"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+": Execution task No :"+num+": current time :"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
public class TestExecutors {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// A pool of threads that periodically execute tasks
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(
new DIYRunable(i),2,2,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
}
Execution results :

The thread pool can periodically execute the submitted tasks within the execution interval , In the actual business scenario, the thread pool can be used to synchronize data regularly
The low-level implementation of the thread pool for periodic execution tasks :
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}advice :
Executors Careful use of
《 Alibaba Java Development Manual 》 There is a rule
【 mandatory 】 Thread pools are not allowed Executors To create , But through ThreadPoolExecutor The way , This way of processing makes the students who write more clear about the running rules of the thread pool , Avoid the risk of resource depletion .
Executors The disadvantages of the returned thread pool object are as follows :
FixedThreadPool and SingleThreadPool : The allowed request queue length is Integer.MAX_VALUE, A large number of requests may pile up , Which leads to OOM.
CachedThreadPool and ScheduledThreadPool : The number of threads allowed to be created is Integer.MAX_VALUE, A large number of threads may be created , Which leads to OOM.
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor: Periodic thread pool
Two main methods are provided :
/**
* Create and perform a periodic operation that is enabled for the first time after a given initial delay , Subsequent operations have a given period
* That is to say, it will be in initialDelay After execution , And then in initialDelay+period After execution , And then initialDelay + 2 * period After execution , And so on
* If an exception occurs in the task execution , Subsequent tasks will be banned , Otherwise, the task will only be cancelled or Executor To stop after being terminated
* If any task performed exceeds the cycle , Subsequent execution will be delayed , No concurrent execution
*/
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(
Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit);
/**
* Create and perform a periodic operation that is enabled for the first time after a given initial delay , And then , There is a given delay between the termination of each execution and the start of the next
* If an exception occurs in the task execution , Subsequent tasks will be banned , Otherwise, the task will only be cancelled or Executor To stop after being terminated
*/
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(
Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit);among schedule Method is used to schedule the execution of a single task . Here we mainly understand the latter two methods :
- scheduleAtFixedRate: The method in initialDelay Execute the task for the first time , After every period Duration , Execute the task again . Be careful ,period It starts with the task . After the mission , Timer intervals period The duration checks whether the task is completed , If complete, start a new task , Otherwise, start a new task after the task is completed , See the legend below
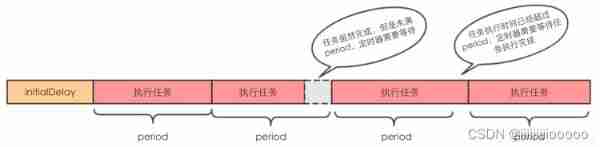
- scheduleWithFixDelay: The method in initialDelay Execute the task for the first time , After each task is completed , wait for delay Duration , Execute the task again , See the legend below :

ThreadPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExecutor Constructors
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
corePoolSize: Number of core threads
The number of core threads in the thread pool , When a task is submitted , Thread pool creates a new thread to execute tasks , Until the current number of threads is equal to corePoolSize, If the current number of threads is corePoolSize, Tasks that continue to be submitted will be stored in the blocking queue , Waiting to be executed
maximumPoolSize: Maximum number of threads
The maximum number of threads allowed in the thread pool , If the current blocking queue is full , And continue to submit tasks , Create a new thread to execute the task , If the current number of threads is less than maximumPoolSize
keepAliveTime: Idle thread lifetime
Thread lifetime when idle , That is, when the current thread has no task execution , The thread will continue to live keepAliveTime, combination TimeUnit Given time unit , By default , Only the number of threads is greater than corePoolSize I'll use it when I'm sick
workQueue: Blocking queues
workQueue Must be BlockingQueue Blocking queue , When the number of threads in the thread pool exceeds corePoolSize when , The thread will enter the blocking queue and wait , adopt workQueue The thread pool implements blocking
Several blocking queues :
Synchronous blocking queue :SyschronousQueue: The submitted task is submitted directly to the thread without saving it
Infinite blocking queue :LinkedBlockingQueue: Unbounded queue based on linked list , You can store an unlimited number of submitted tasks
Bounded blocking queue :ArrayBlockingQueue: Bounded queue based on array implementation , Specifies the maximum length of the queue , Prevent resource depletion
threadFactory: Thread factory
A factory for creating threads , Through the custom thread factory, you can set a thread name with recognition degree for each new thread , Default thread name :pool-X-Thread-XX
Realization ThreadFactory Interface , The interface declaration is as follows :
public interface ThreadFactory {
Thread newThread(Runnable r);
}RejectedExecutorsHandler: Saturated strategy
Thread pool saturation strategy , When the blocking queue is full , There are no idle worker threads , If you continue to submit the task , A strategy must be adopted to deal with the task , Thread pools are provided 4 Strategies
AbortPolicy: Throw an exception directly , The default policy
CallerRunsPolicy: Use the thread of the caller to execute the task
DiscardOldestPolicy: Discard the top task in the blocking queue , And add the current task to the queue
DiscardPolicy: Discard tasks directly
You can also customize the saturation strategy according to the application scenario :RejectedExecutorsHandler
ThreadPoolExecutors Thread pool execution task flow

(1) If the number of threads in the thread pool is less than corePoolSize, Create a new thread to perform the newly added task ;
(2) If the number of threads in the thread pool is greater than or equal to corePoolSize, But the queue workQueue under , Put the newly added task in workQueue in , according to FIFO The principle of waiting for implementation in turn ( When a thread in the thread pool is idle, it will deliver the tasks in the queue to the idle thread for execution )
(3) If the number of threads in the thread pool is greater than or equal to corePoolSize, And the queue workQueue Is full , But the number of threads in the thread pool is less than maximumPoolSize, A new thread will be created to handle the added task ;
(4) If the number of threads in the thread pool equals maximumPoolSize, Just use RejectedExecutionHandler To handle rejection
summary , When there are new tasks to deal with , Let's see if the number of threads in the thread pool is greater than corePoolSize, Look at the buffer queue workQueue Full or not , Finally, see if the number of threads in the thread pool is greater than maximumPoolSize
in addition , When the number of threads in the thread pool is greater than corePoolSize when , If the idle time of a thread exceeds keepAliveTime, Remove it from the thread pool
边栏推荐
- 杰理之BLEPR0 和 PR1 当普通 IO 口使用【篇】
- Half of the property rights of the house are registered in the woman's name when they are in love, and they want to return after they break up
- 为什么说Web3会是「创作者经济」的游戏规则改变者
- White screen time, first screen time
- Bad navigation category bar code version
- Arbitrum infrastructure: a quick start
- (key points of software engineering review) Chapter IV overall design exercises
- 地铁路线图云开发小程序源码和配置教程
- 1712. 将数组分成三个子数组的方案数 ●●
- Beginning an excellent emlog theme
猜你喜欢

使用国产MCU(国民技术 N32G031F8S7) 实现 PWM+DMA 控制 WS2812

PHP仿网易云原创音乐分享平台网站源码

把程序写进微控制器里可以更方便快捷的控制电机正反转

Leetcode 1995. 统计特殊四元组(暴力枚举)
![Jerry's acquisition of ble OTA dual backup upgrade (can only be used for chips above 4mbits) [article]](/img/25/e90d23f5c3d2aa6790538b289137bf.png)
Jerry's acquisition of ble OTA dual backup upgrade (can only be used for chips above 4mbits) [article]

Mn Monet pagoda host system v1.5 release

施一公:我直到博士毕业,对研究也没兴趣!对未来很迷茫,也不知道将来要干什么......

杰理之获取 BLE 查看代码异常复位等异常情况原因【篇】

云画质助手iApp源码

杰理之BLE 芯片供电范围及防烧芯片措施【篇】
随机推荐
Window管理深入了解WindowManagerService
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=${bound}
Update failed to update bytea type PostgreSQL
5.读取指定路径名-dirname
NFT will change data ownership in the metauniverse
Remote monitoring project offline log specification
MySQL下载安装使用-完整详细步骤
使用 Ribbon 实现客户端负载均衡
Taking the cooperation between different banks as an example, the construction of small program ecology
Summary of common constraints in MySQL foundation part I
Arbitrum infrastructure: a quick start
国际多语言出海商城返佣产品自动匹配订单源码
Leetcode (Sword finger offer) - 10- ii Frog jumping on steps
基于C语言实现比赛评分系统
1712. number of schemes for dividing the array into three sub arrays ●●
杰理之BLE SPP 开启 pin_code 功能【篇】
NewOJ Week 2---BCD
Install MySQL version 5.7 or above on windows (install in compressed package)
PHP仿网易云原创音乐分享平台网站源码
云画质助手iApp源码