当前位置:网站首页>The interviewer asked: how to judge whether an element is in the visible area?
The interviewer asked: how to judge whether an element is in the visible area?
2022-07-27 14:43:00 【Xia an】
Interviewer asked : How to judge whether an element is in the visible area ?
- Interviewer asked : How to judge whether an element is in the visible area ?
Interviewer asked : How to judge whether an element is in the visible area ?
I've been interviewing for a job recently , We met two or three companies one after another . One of the interviewers asked a question : How to judge whether an element is in the visible area ? Because I don't deal with much at ordinary times , So I didn't answer for the moment , Later, I studied , So with this article .
1. Through the position information of the element and the scrolling height of the scroll bar
ad locum , Let's first introduce the location information and size of several elements :
Element.clientWidth
Element.clientWidth Attribute represents the internal height of the element , In pixel . This attribute includes the inside margin padding, But it doesn't include borders border、 Margin margin And horizontal scroll bar ( If any ). therefore clientHeight Can pass CSS height + CSS padding - Horizontal scroll bar height ( If there is ) To calculate . In the same way and Element.clientHeight attribute .
remarks : This property rounds the obtained value to an integer .
window.innerHeight
window.innerHeight Property represents the viewport of the browser window (viewport) Height ( In pixels ); If there is a horizontal scroll bar , It also includes the height of the scroll bar . In the same way and Element.clientWidth attribute .
HTMLElement.offsetTop
HTMLElement.offsetTop Returns the current element relative to its offsetParent The distance from the top inner edge of an element . that offsetParent What's the matter ?
HTMLElement.offsetParent
HTMLElement.offsetParent Returns a point to the nearest ( Refers to the most recent... At the inclusion level ) Contains the location element of the element or the nearest table,td,th,body Elements . When the element of style.display Set to "none" when ,offsetParent return null.offsetParent It is useful to , because offsetTop and offsetLeft It's all relative to the inner margin .
Okay , After understanding these attributes , Naturally, I understand the following judgment method :
function isInViewPort(element) {
// Get the height of the visual window .
const screenHeight = window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight || document.body.clientHeight;
// Get the scroll height of the scroll bar
const scrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop;
// Gets the height of the element offset . Is the offset from the visual window .
const offsetTop = element.offsetTop;
return offsetTop - scrollTop <= screenHeight;
}
Maybe readers will have questions at this time : Why use screenHeight = window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight || document.body.clientHeight Such a long code to get the height of the visual window ? Here is to be compatible with all browser writing .
2. adopt getBoundingClientRect Method to get the location information of the element
Element.getBoundingClientRect() Method returns a DOMRect object , It provides the size of the element and its position relative to the viewport . So here comes the question ,DOMRect What is the object ?DOMRect It can be understood as seeing the element as a rectangle , This object contains the position of the rectangle 、 Size information , You can get the left , On , The position of the right and bottom relative to the browser window respectively .
Element.getBoundingClientRect().topIndicates the distance between the upper edge of the element and the upper edge of the pageElement.getBoundingClientRect().rightIndicates the distance between the right side of the element and the left side of the pageElement.getBoundingClientRect().bottomIndicates the distance between the lower edge of the element and the upper edge of the pageElement.getBoundingClientRect().leftIndicates the distance from the left of the element to the left of the page

When the page scrolls , They will change with it . If an element is in the window , Then it must meet the following four conditions :
topGreater than or equal to 0leftGreater than or equal to 0bottomLess than or equal to the window heightrightLess than or equal to the window width
function isContain(dom) {
const viewHeigh = window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight;
const viewWidth = window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth;
// When the scroll bar scrolls ,top, left, bottom, right The moment will change .
const {
top,
right,
bottom,
left
} = dom.getBoundingClientRect();
return (top >= 0 && left >= 0 && right <= viewWidth && bottom <= viewHeight);
}
3. adopt Intersection Observer To monitor
Intersection Observer Interface ( be subordinate to Intersection Observer API) Provides an asynchronous view of the target element and its ancestor elements or top-level document window (viewport) The method of cross state . Ancestral elements and windows (viewport) It's called root (root).
When one Intersection Observer When the object is created , It is configured to listen for a given proportion of the visible area in the root . once Intersection Observer Be created , Can't change its configuration , So a given observer object can only be used to monitor the specific change value of the visible area ; However , You can configure listening to multiple target elements in the same observer object .
Next, let's take a look at its usage :
3.1 API
var io = new IntersectionObserver(callback, option);
In the above code ,IntersectionObserver It's the browser's native constructor , Take two parameters :
callbackIs a callback function when visibility changesoptionIt's the configuration object ( This parameter is optional )
The return value of the constructor is an observer instance . Example of observe Methods can specify which to observe DOM node .
// Start to observe
io.observe(document.getElementById('example'));
// Stop observing
io.unobserve(element);
// Turn off the viewer
io.disconnect();
In the above code ,observe The parameter of is a DOM Node object . If you're looking at multiple nodes , You have to call this method many times .
io.observe(elementA);
io.observe(elementB);
3.2 callback Parameters
When the visibility of the target element changes , The viewer's callback function is called callback.callback It usually triggers twice . Once the target element has just entered the viewport ( Start to see ), The other is to leave the view completely ( It's not visible at first ).
var io = new IntersectionObserver(
entries => {
console.log(entries);
}
);
In the above code , The callback function adopts the writing method of arrow function .callback The parameters of the function (entries) Is an array , Each member is a IntersectionObserverEntry object . for instance , If the visibility of two observed objects changes at the same time ,entries The array will have two members
3.3 IntersectionObserverEntry object
IntersectionObserverEntry Object provides information about the target element , There are six attributes .
{
time: 3893.92,
rootBounds: ClientRect {
bottom: 920,
height: 1024,
left: 0,
right: 1024,
top: 0,
width: 920
},
boundingClientRect: ClientRect {
// ...
},
intersectionRect: ClientRect {
// ...
},
intersectionRatio: 0.54,
target: element
}
The meaning of each attribute is as follows .
time: When visibility changes , It's a high-precision timestamp , The unit is millisecondtarget: Observed target elements , It's a DOM Node objectrootBounds: Information about the rectangular area of the root element ,getBoundingClientRect()Return value of method , If there is no root element ( That is, scrolling directly relative to the viewport ), Then return tonullboundingClientRect: Information about the rectangular area of the target elementintersectionRect: Target element and viewport ( Or root element ) The information of the intersection areaintersectionRatio: The visible proportion of the target element , namelyintersectionRectOccupyboundingClientRectThe proportion of , When fully visible 1, Less than or equal to when completely invisible 0
3.4 Option object
IntersectionObserver The second argument to the constructor is a configuration object . It can set the following properties .
thresholdattribute
threshold Property determines when the callback function is triggered . It's an array , Each member is a threshold , The default is [0], That is, the cross ratio (intersectionRatio) achieve 0 Trigger callback function .
new IntersectionObserver(
entries => {
/* ... */},
{
threshold: [0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1]
}
);
You can customize this array . such as ,[0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1] It means when the target element 0%、25%、50%、75%、100% When visible , Will trigger the callback function .
rootattribute ,rootMarginattribute
A lot of times , The target element will not only scroll with the window , And roll in the container ( For example iframe Scroll through the window ). Scrolling within the container also affects the visibility of the target element .
IntersectionObserver API Supports scrolling in containers .root Property specifies the container node where the target element is located ( The root element ). Be careful , The container element must be the ancestor node of the target element .
var opts = {
root: document.querySelector('.container'),
rootMargin: "500px 0px"
};
var observer = new IntersectionObserver(
callback,
opts
);
In the above code , except root attribute , also rootMargin attribute . The latter defines the root element margin, Used to expand or shrink rootBounds The size of this rectangle , Thereby affecting intersectionRect The size of the crossing area . It USES CSS How to define , such as 10px 20px 30px 40px, Express top、right、bottom and left Values in four directions . After this setting , Whether it's window scrolling or container scrolling , As long as the visibility of the target element changes , Will trigger the observer .
4. Application scenarios
- Lazy loading of pictures
Sometimes , We want some static resources ( Such as the picture ), Only the user scrolls down , They don't load until they're in the viewport , This saves bandwidth , Improve web performance .
- Infinite scrolling list
When rolling infinitely , It's best to have a tail bar at the bottom of the page . Once the tail of the page is visible , It means that the user has reached the bottom of the page , To load a new entry and put it in front of the tail bar .
边栏推荐
- 融合迁移学习与文本增强的中文成语隐喻知识识别与关联研究
- JS epidemic at home, learning can't stop, 7000 word long text to help you thoroughly understand the prototype and prototype chain
- Docker practical experience: deploy mysql8 master-slave replication on docker
- 汉字风格迁移篇---对抗性区分域适应(L1)Adversarial Discriminative Domain Adaptation
- STM32——电容触摸按键实验
- Construction of knowledge map of financial securities and discovery of related stocks from the perspective of knowledge relevance
- 面试官问:如何判断一个元素是否在可视区域?
- 获取Unity打开摄像头第一帧有画面的数据
- Recursive method to realize the greatest common divisor
- User question understanding and answer content organization for epidemic disease Science Popularization
猜你喜欢

Windows10 installing SQL Server 2019

Recursive method to realize the greatest common divisor
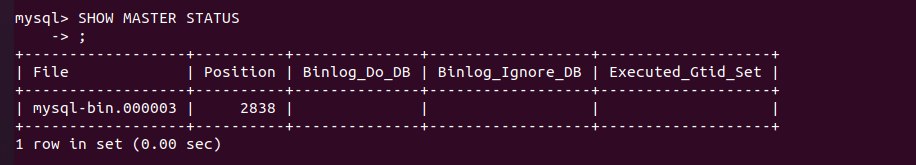
Docker实践经验:Docker 上部署 mysql8 主从复制

Slam overview Reading Note 6: slam research based on image semantics: application-oriented solutions for autonomous navigation of mobile robots 2020

Unity3D学习笔记10——纹理数组

PROFINET simulator tutorial
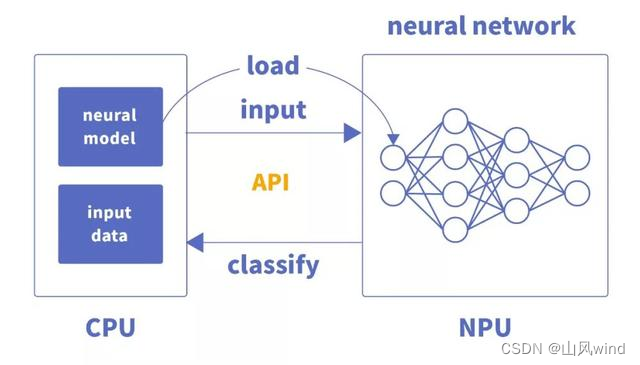
CPU、GPU、NPU的区别

面试官问:如何判断一个元素是否在可视区域?

Construction of knowledge map of financial securities and discovery of related stocks from the perspective of knowledge relevance

codeforces 1708E - DFS Trees
随机推荐
codeforces 1708E - DFS Trees
Advanced MySQL III. storage engine
Hard deduction SQL statement exercises, wrong question records
log4j2 jdbc appender
va_ List usage summary
Photo album based on gec6818 development board
telnet远程登录aaa模式详解【华为eNSP】
Rtl8762dk environment construction (I)
Getting started for beginners: build your own blog with WordPress
How to solve cache avalanche, breakdown and penetration problems
【论文精读】Grounded Language-Image Pre-training(GLIP)
获取Unity打开摄像头第一帧有画面的数据
Research on multi label patent classification based on pre training model
SLAM综述阅读笔记四:A Survey on Deep Learning for Localization and Mapping: Towards the Age of Spatial 2020
This points to problems, closures, and recursion
CPU、GPU、NPU的区别
Schematic diagram of C measuring tool
Redis
HDU1422 重温世界杯【DP】
np. Usage and difference of range() and range()