当前位置:网站首页>Microservice architecture | how to solve the problem of fragment uploading of large attachments?
Microservice architecture | how to solve the problem of fragment uploading of large attachments?
2022-06-23 21:11:00 【Code farming architecture】
Reading guide : Patch uploading 、 Breakpoint continuation , These two nouns should not be unfamiliar to friends who have done or are familiar with file uploading , Summarize this article, hoping to be helpful or enlightening to students engaged in related work .
When our files are very large , Does it take a long time to upload , Such a long connection , What if the network fluctuates ? The intermediate network is disconnected ? In such a long process, if there is instability , All the content uploaded this time has failed , Upload again .
Patch uploading , Is to upload the file , According to a certain size , Separate the entire file into blocks ( We call it Part) To upload separately , After uploading, the server will summarize all the uploaded files and integrate them into the original files . Piecemeal upload can not only avoid the problem of always having to upload from the starting position of the file due to the poor network environment , Multithreading can also be used to send different block data concurrently , Improve transmission efficiency , Reduce sending time .
One 、 background
After the sudden increase in the number of system users , In order to better adapt to the customized needs of various groups . Business support is slowly realized C End user defined layout and configuration , Causes configuration data to be read IO a surge .
To better optimize such scenarios , Manage user-defined configuration statically ! The configuration file that will be generated is the static configuration file , There are thorny problems in the process of generating static files , The configuration file is too large, resulting in long waiting time in the file upload server , As a result, the overall performance of the whole business scenario declines .
Two 、 Generate configuration files
Three elements of generating files
- file name
- The contents of the document
- File store Format
The contents of the document 、 File storage formats are easy to understand and handle , Of course, I've sorted out the encryption methods commonly used in microservices
- Microservice architecture | What are the common encryption methods for microservices ( One )
- Microservice architecture | What are the common encryption methods for data encryption ( Two )
Here is a supplementary explanation , If you want to encrypt the file content, you can consider . However, the case scenario in this paper has a low degree of confidentiality for the configuration information , There's no expansion here .
The naming criteria for file names are determined in combination with business scenarios , It's usually based on a profile + Timestamp format is the main format . However, such naming conventions can easily lead to file name conflicts , Cause unnecessary follow-up trouble .
So I made a special treatment for the naming of file names here , I have handled the front end Route Routing experience should be associated with , The filename can be accessed through Content based generation Hash value Instead of .
stay Spring 3.0 Then the method of calculating the summary is provided .
DigestUtils#md
Returns the of the given byte MD5 Hexadecimal string representation of the abstract .
md5DigestAsHex Source code
/**
* Calculate the bytes of the summary
* @param A hexadecimal summary character
* @return String returns the of a given byte MD5 Hexadecimal string representation of the abstract .
*/
public static String md5DigestAsHex(byte[] bytes) {
return digestAsHexString(MD5_ALGORITHM_NAME, bytes);
}file name 、 Content 、 suffix ( Storage format ) Generate the file directly after confirmation
/**
* Generate... Directly from content file
*/
public static void generateFile(String destDirPath, String fileName, String content) throws FileZipException {
File targetFile = new File(destDirPath + File.separator + fileName);
// Ensure that the parent directory exists
if (!targetFile.getParentFile().exists()) {
if (!targetFile.getParentFile().mkdirs()) {
throw new FileZipException(" path is not found ");
}
}
// Set file encoding format
try (PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(targetFile), ENCODING)))
) {
writer.write(content);
return;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new FileZipException("create file error",e);
}
}The advantages of generating files through content are self-evident , It can greatly reduce our initiative to generate new files based on content comparison 、 If the file content is large and the corresponding file name is the same, it means that the content has not been adjusted , At this time, we don't need to do subsequent file update operations .
3、 ... and 、 Upload attachments in pieces
The so-called fragment upload , Is to upload the file , According to a certain size , Separate the entire file into blocks ( We call it Part) To upload separately , After uploading, the server will summarize all the uploaded files and integrate them into the original files . Piecemeal upload can not only avoid the problem of always having to upload from the starting position of the file due to the poor network environment , Multithreading can also be used to send different block data concurrently , Improve transmission efficiency , Reduce sending time .
Fragment upload is mainly applicable to the following scenarios :
- The network environment is not good : When the upload fails , You can deal with failed Part Make an independent retry , There is no need to upload other Part.
- Breakpoint continuation : After a pause , It can be uploaded from the last time Part Continue to upload .
- Speed up upload : To upload to OSS When your local file is large , You can upload multiple files in parallel Part To speed up upload .
- Stream upload : You can start uploading when the size of the file you want to upload is uncertain . This kind of scene is quite common in video surveillance and other industry applications .
- Larger files : Generally, when the file is relatively large , By default, fragment upload is generally adopted .
The whole process of fragment upload is roughly as follows :
- Will need to upload the file according to certain segmentation rules , Split into blocks of the same size ;
- Initialize a fragment upload task , Return to the unique identification of this fragment upload ;
- Follow a certain strategy ( Serial or parallel ) Send each piece of data block ;
- After sending , The server judges whether the data upload is complete according to the data , If it's complete , Then the data block is synthesized to get the original file
▐ Define the fragment rule size
By default, files are used to achieve 20MB Perform forced segmentation
/** * Force fragment file size (20MB) */ long FORCE_SLICE_FILE_SIZE = 20L* 1024 * 1024;
For the convenience of debugging , Force the threshold of fragmented files to be adjusted to 1KB
▐ Define fragment upload objects
As shown in the figure above, the file fragment with red serial number , Define the basic attributes of the fragment upload object, including the attachment file name 、 Original file size 、 The original document MD5 value 、 Total number of segments 、 Each slice size 、 Current slice size 、 Current slice serial number, etc
The basis of definition is to facilitate the reasonable division of documents in the future 、 Business expansion such as slice merger , Of course, you can define expansion attributes according to business scenarios .
- Total number of segments
long totalSlices = fileSize % forceSliceSize == 0 ?
fileSize / forceSliceSize : fileSize / forceSliceSize + 1;- Each slice size
long eachSize = fileSize % totalSlices == 0 ?
fileSize / totalSlices : fileSize / totalSlices + 1;- Of the original document MD5 value
MD5Util.hex(file)
Such as :
The current attachment size is :3382KB, The forced partition size is limited to 1024KB
By the above calculation : The number of slices is 4 individual , The size of each slice is 846KB
▐ Read the data bytes of each partition
Mark the current byte subscript , Cyclic reading 4 Fragmented data bytes
try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(uploadVO.getFile())) {
for (int i = 0; i < sliceBytesVO.getFdTotalSlices(); i++) {
// Read the data bytes of each partition
this.readSliceBytes(i, inputStream, sliceBytesVO);
// Call fragment upload API Function of
String result = sliceApiCallFunction.apply(sliceBytesVO);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(result)) {
continue;
}
return result;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw e;
}3、 ... and 、 summary
The so-called fragment upload , Is to upload the file , According to a certain size , Separate the entire file into blocks ( We call it Part) To upload separately .
Dealing with large files and slicing, the main core is to determine three points
- File fragmentation granularity
- How to read slices
- How to store slices
This article mainly analyzes and deals with how to compare the contents of large files in the process of uploading large files 、 Shard processing . Reasonably set the segmentation threshold and how to read and mark the segmentation . I hope it can help or inspire students engaged in related work . Later, we will discuss how to store the fragments 、 Mark 、 Combine documents for detailed interpretation .
边栏推荐
- Where should DNS start? I -- from the failure of Facebook
- [Debian] Debian usage notes
- What cloud disk types does Tencent cloud provide? What are the characteristics of cloud disk service?
- JS advanced programming version 4: generator learning
- Cobalt Strike Spawn & Tunnel
- Bi-sql index
- [typescript] some summaries in actual combat
- [JS reverse hundred examples] anti climbing training platform for netizens question 6: JS encryption, environment simulation detection
- Advantages of token mechanism over cookie mechanism
- Sharelist supports simultaneous mounting of Google drive/onedrive multiple network disks
猜你喜欢

Steps for formulating the project PMO strategic plan

How PMO uses two dimensions for performance appraisal

I am 30 years old, no longer young, and have nothing
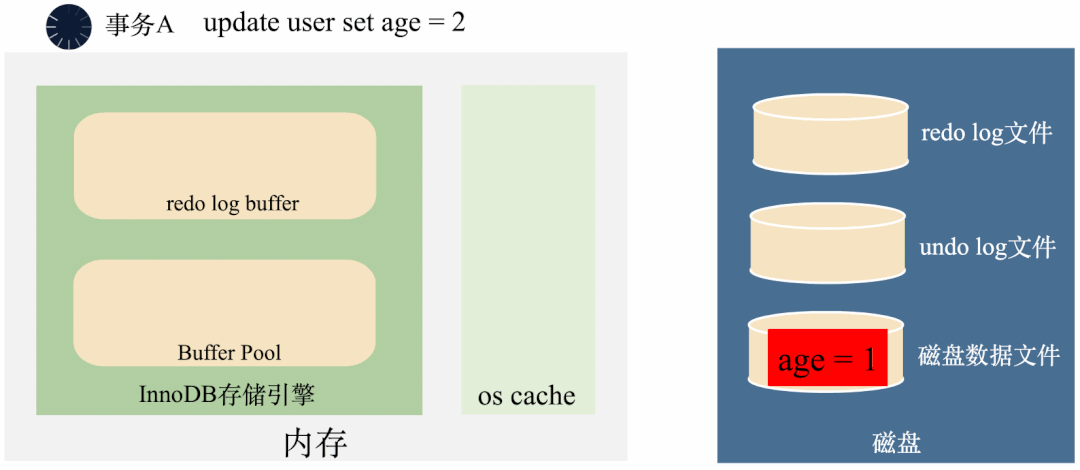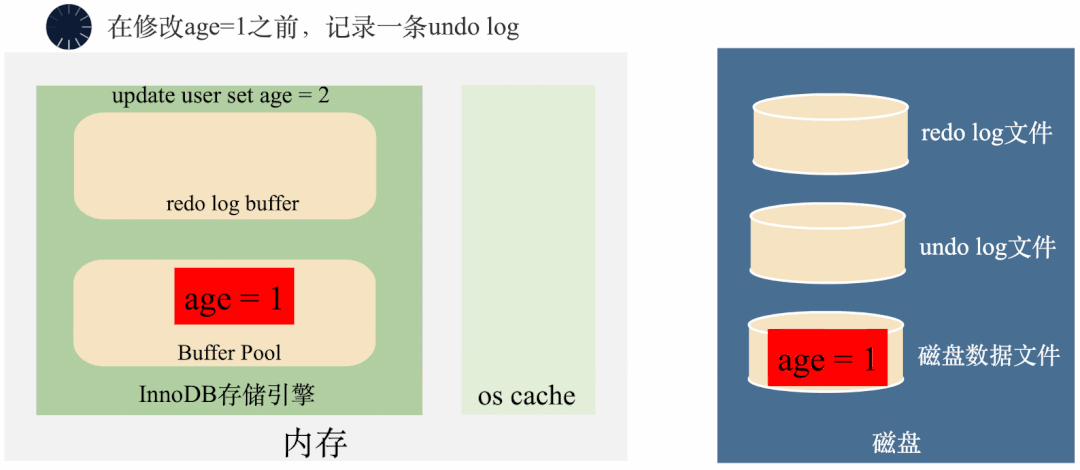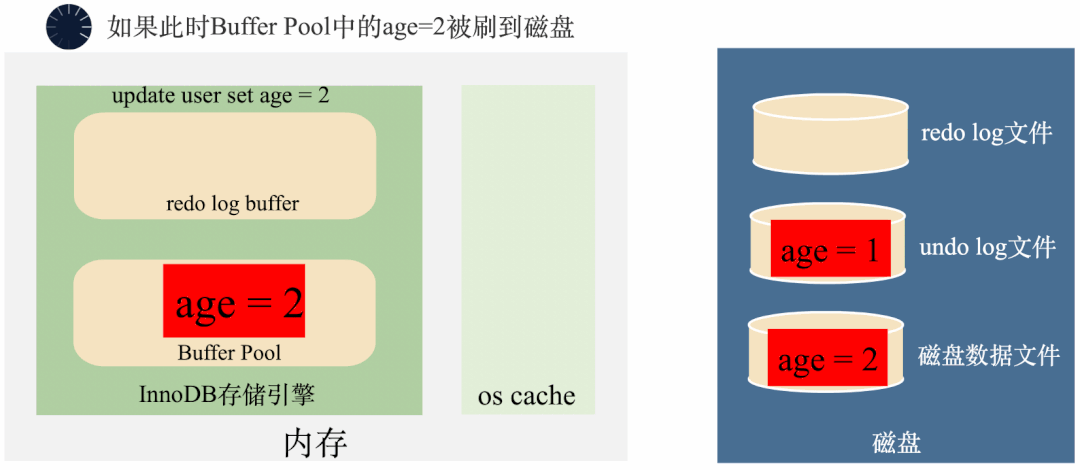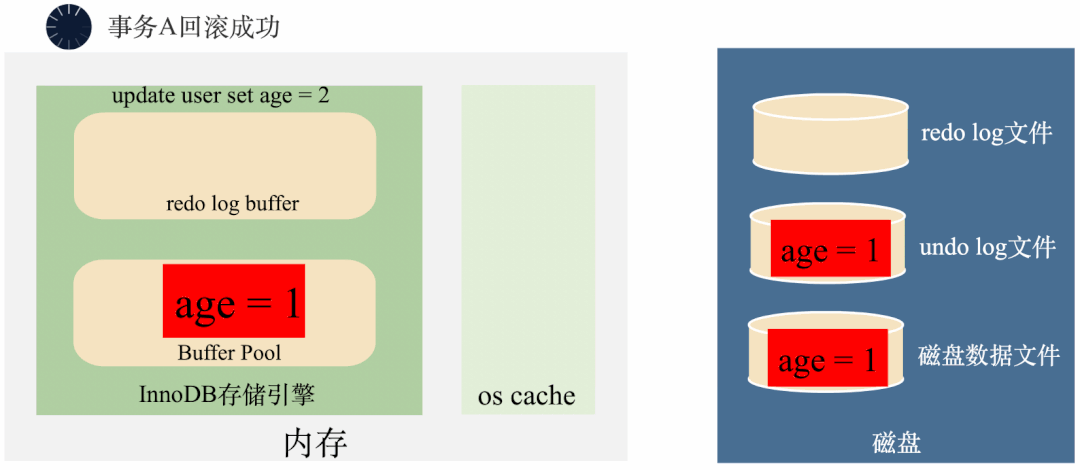
3000 frame animation illustrating why MySQL needs binlog, redo log and undo log

Four aspects of PMO Department value assessment

JS advanced programming version 4: generator learning

Applet development framework recommendation
Application of JDBC in performance test
随机推荐
Is it possible to transfer files on the fortress server? How to operate?
How PostgreSQL quickly locate blocking SQL
Global and Chinese market of gas fire pit 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
How do I close and restore ports 135, 139 and 445?
How to convert []byte to io. in go Reader?
Global and Chinese market of American football catch gloves 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
How to solve the problem that the ID is not displayed when easycvr edits the national standard channel?
What is the role of short video AI intelligent audit? Why do I need intelligent auditing?
Implementation of flashback query for PostgreSQL database compatible with Oracle Database
December 29, 2021: the elimination rules of a subsequence are as follows: 1. In a subsequence
Row height, (top line, middle line, baseline, bottom line), vertical align
[Debian] Debian usage notes
Strokeit- the joy of one handed fishing you can't imagine
SAP FICO as03 display fixed assets master data
[golang] quick review guide quickreview (I) -- string
Overview of digital circuits
Is it safe for flush to open an account online? Is the Commission high
From AIPL to grow, talking about the marketing analysis model of Internet manufacturers
Configure two databases in master-slave database mode (master and slave)
[open source] goravel (golang Web Framework) - new cache module
