In this paper, we will introduce the theoretical basis of how to find similar images, and use a system for finding trademarks as an example to introduce the related technical implementation , This article provides background information about the recommended methods used in image retrieval tasks . After reading this article, you will have the ability to create a similar image search engine from scratch .
image retrieval ( Also known as content-based image retrieval Content-Based Image Retrieval or CBIR) Is the basis of any search involving images .

The above picture is from the article Recent Advance in Content-based Image Retrieval: A Literature Survey (2017) arxiv:1706.06064
“ Search by photo ” Methods have appeared in various fields , Especially in e-commerce websites ( For example, Taobao. ), also “ Search for pictures by keywords ”( Understanding of the picture content ) Has long been Google 、 Baidu ,bing Wait for search engines to use ( Image search ). I think since the computer vision world made a sensation CLIP: Connecting Text and Images When it appears , The globalization of this approach will accelerate .
In this paper , This paper will only discuss the image search method of neural network in computer vision .
Basic service components

step 1. Training models . This model can be used in classical CV Or based on neural network . Model input —— Images , Output ——D Feature embedding of dimension . In the traditional situation , It can be SIFT-descriptor + Bag of Visual Words The combination of . In the case of neural networks , It can be like ResNet、EfficientNet And so on + Complex pooling layer . If there's enough data , Neural networks almost always perform well , So we will focus on them .
step 2. Index image . Indexing is running a trained model on all images , And write the obtained embedding into a special index for fast search .
step 3. Search for . Use the image uploaded by the user , Get embedded through the model , And embed it into the database ( Indexes ) Compare the embedding of other images in , And search results can be sorted by relevance .
Neural networks and metric learning

In the task of finding similarity , The function of neural network is feature extractor ( Backbone network ). The choice of backbone depends on the amount and complexity of data —— It can be considered from ResNet18 To Visual Transformer All models of .
The first feature of the model in image retrieval is the design of neural network head . stay Image Retrieval Ranking List (https://kobiso.github.io/Comp...) On , They use parallel pools 、Batch Drop Block Technology , The best image feature description that makes the activation distribution of the output feature map more uniform can be obtained .
The second main feature is the choice of loss function . Only in Deep Image Retrieval: A Survey (arxiv 2101.11282) in , There are a dozen recommended loss functions that can be used for pairing training . The main purpose of all these losses is to train the neural network to transform the image into a vector in a linearly separable space , To further compare these vectors by cosine or Euclidean distance : Similar images will have tight embeddedness , Dissimilar images will be far away . Let's look at some of the main loss functions .

Loss function
1、Contrastive Loss

This is a double loss , That is, objects are compared by their distance from each other .

If these images are actually similar , Then the neural network will be affected by the image p and q The embeddedness of is too far away from each other and is punished . If the images are actually different from each other , However, if the embedding distance is close, it will also be punished , But in this case, the boundary is set m( for example ,0.5), This setting considers that the neural network has already dealt with “ Separate ” Different image tasks , There is no need for too much punishment .
2、Triplet Loss

The goal of this loss is to minimize anchor To positive Distance of , Maximize anchor To negative Distance of . Triplet Loss The first is in the Google Of FaceNet Introduced in the paper on face recognition , It has long been the most advanced solution .

3、N-tupled Loss

N-tupled Loss yes Triplet Loss A development of , It also uses anchor and positive, But use multiple negative A sample, not a negative sample .

3、Angular Additive Margin (ArcFace)
The problem of double loss is the choice anchor、positive and negative The combination of —— If they are just evenly and randomly extracted from the data set , Then there will be “light pairs” The problem of , The loss of some image pairs will be 0 In this way, the network will converge to a state very quickly , Because most of the samples in our input are very “ Easy to ”, When the loss is 0 When the network stops learning . To avoid this problem ,ArcFace Propose complex mining techniques for sample pairing —— hard negative and hard positive mining . Those who are interested in this aspect can take a look at one called PML library , It implements many mining methods , The library contains a lot about PyTorch Upper Metric Learning Useful information about the task , Those who are interested can pay more attention to .
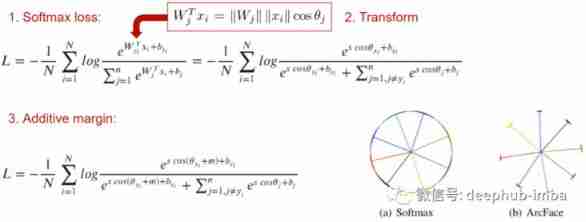
light pairs Another solution to the problem is classification loss . ArcFace The main idea is to add an indentation to the usual cross entropy m, It can make the embedding of similar images distributed around the center of the centroid region of the class , So that they are separated from the embedded clusters of other classes by the smallest angle m.
This is a perfect loss function , Especially in use MegaFace When benchmarking . however ArcFace It only works when there is a classification mark . After all, it is impossible to calculate cross entropy without classified markers , Right .

The above figure shows the recommendation for selecting loss functions with single class and multi class tags ( If there is no tag, the matching tag can be generated from the latter by calculating the intersection percentage between the multi tag vectors of the sample ).
Pooling
Pooling is also often used in neural network architectures , The following describes several pooling layers used in image retrieval tasks .
1、R-MAC
Regional Maximum Activation of Convolutions (R-MAC) It can be regarded as a pool layer , It receives the output characteristic graph of the neural network ( Before global pooling or classification layer ) And return the vector description for calculating the output activation sum according to different windows , The activation of each window is that each channel independently takes the maximum value of this window .

This operation creates a richer feature description through the local features of the image at different scales . The descriptor itself is an embedded vector , So it can be delivered directly to loss function .
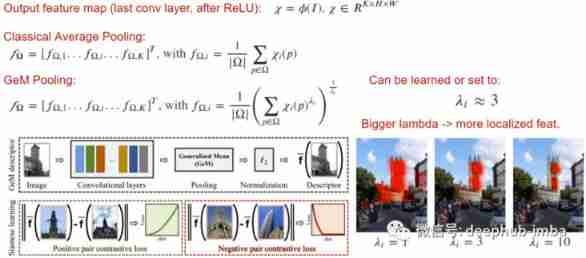
2、Generalized Mean
Generalized Mean(GeM) Is a simple pooling operation that can improve the quality of the output descriptor , It will lambda The normal form is applied to the average pooling operation . By increasing the lambda, Make the network focus on important parts of the image , This is very effective in some tasks .
Distance measurement
1、 Indexes
Another key to high-quality search for similar images is ranking , The most relevant results of a given query are displayed . Its main measure is the speed of indexing 、 Search speed and memory consumption .
The simplest method is to use the embedded vector directly to search for violence , For example, use cosine distance . But when there is a large amount of data, there will be problems —— Millions of 、 Tens of millions or more . The search speed is significantly reduced .

These problems can be solved at the expense of quality —— By compressing ( quantitative ) Instead of storing the embedded in its original form . It also changes the search strategy —— Not using violent search , Instead, try to find the embedding vector closest to a given query with the minimum number of comparisons . There are a large number of efficient frameworks to approximate search for the closest objects . for example NMSLIB, Spotify Annoy, Facebook Faiss, Google Scann. In addition to the library of machine learning , Tradition Elasticsearch stay 7.3 Support vector queries in the future .
2、 rearrangement
Researchers in the field of information retrieval have discovered : After receiving the original search results , The quality of search results can be improved by reordering collections in some way .

Use the closest search input top-k The afterlife becomes a new embedded , In the simplest case, we can take the average vector . As shown in the figure above , You can also weight the embedding , For example, weighted sorting by the distance in the question or the cosine distance from the request .
3、k-reciprocal

k-reciprocal It's a group from top-k The elements of the include those closest to the request itself k Elements , Based on this set, the process of reordering the results is constructed , One of them is in Re-ranking Person Re-identification with k-reciprocal Encoding The description in the article . k-reciprocal Than k The nearest neighbor is closer to the query . Therefore, we can roughly describe k-reciprocal The elements in the set are considered as known positive samples , And change the weighting rules . The original paper contains a lot of calculations , This is beyond the scope of this article , It is recommended that interested readers read .
Verification index
The last part is to check the search quality . Beginners may not notice many of the subtleties of this task when they first start an image retrieval project .
Let's take a look at these popular metrics in image retrieval tasks :[email protected]、[email protected]、R-precision、mAP and nDCG.

advantage : Show related top-k Percent of .
shortcoming :
- Very sensitive to the number of relevant samples for a given query , There may be a non objective assessment of the quality of the search , Because different queries have different numbers of related results
- Only if the correlation number of all queries >= k when , It's possible to achieve 1
2、R-precision

And [email protected] identical , among k Set to equal the number of related queries .
advantage : Yes [email protected] Middle number k The sensitivity of , Metrics become stable
shortcoming : You must know the total number of samples associated with the query request ( If not all relevant are marked , Can cause problems )
stay top-k Proportion of relevant items found in

advantage
- This indicator answers the question in top-k Whether relevant results are found in
- Able to process requests stably and evenly
4、mAP(mean Average Precision)
Fill the top of the search results with relevant results . It can be regarded as the number of pages that search engine users need to read when they receive the same amount of information ( The less, the better. ).
advantage : Objective and stable evaluation of retrieval quality
shortcoming : You must know the total number of samples associated with the request
5、nDCG (Normalized Discounted Gain)

This metric shows top-k Whether the elements in are sorted correctly among them . The advantages and disadvantages of this indicator will not be introduced here , Because this is the only indicator in the metric list that considers the element order . And some studies have shown that when the order needs to be considered , This indicator is fairly stable and applies to most situations .
6、 Validation protocol recommendations
6a、 Validate a set of queries and selected related queries

Input : Request images and images associated with them . You need a tag in the form of a list related to this query .
To calculate metrics : Calculate the correlation matrix for each , And according to the relevant element correlation information , Calculate the index .
6b、 Full library verification

Input : Requested image , And the images associated with them . Ideally, there should be a database of validation images , All related queries are marked in it . It should be noted that the query image should not be included in the relevant image so that it will be ranked in top-1, Our task is to find the relevant image, not himself .
To calculate metrics : Traverse all requests , Calculate to all elements ( Including related elements ) Distance of , And send them to the index calculation function .
Complete sample introduction
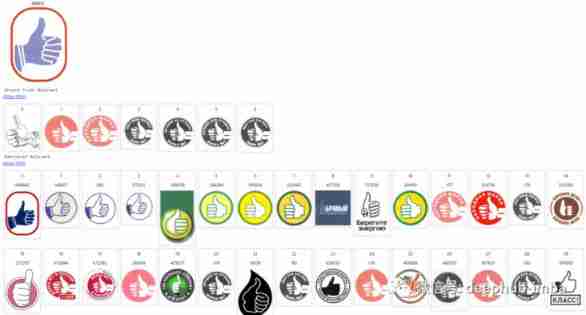
Here to search for similar trademarks logo As an example to introduce how image search engine works .
Size of image index database : Millions of trademarks . The first picture here is a query , The next line is the related list returned , The rest of the lines are given by the search engine in descending order of relevance .




summary
this is it , I hope this article can provide a complete idea for those who are building or about to build a similar image search engine , If you have any good suggestions, please leave a message .
https://www.overfit.cn/post/18b0ea4b8df04f2c82e8cf633e13660a
author :Vlad Vinogradov








