当前位置:网站首页>[fuzzy neural network] simulation of fuzzy neural network based on MATLAB
[fuzzy neural network] simulation of fuzzy neural network based on MATLAB
2022-06-28 02:43:00 【FPGA and MATLAB】
1. Software version
matlab2013b
2. System Overview
· The first model :
 ;
;![]()
· The second model
 ;
;![]() ,U=13.012
,U=13.012
First of all : Design of membership function

Design of membership function , You can use the blur editor , It can also be designed through the above code .
second : Design of fuzzy rules
Design by inputting fuzzy rule quantification table , The resulting fuzzy rules are as follows :
1. If (e is NB) and (ec is NB) then (u is PB) (1)
2. If (e is NB) and (ec is NM) then (u is PB) (1)
3. If (e is NB) and (ec is NS) then (u is PM) (1)
4. If (e is NB) and (ec is Z) then (u is PM) (1)
5. If (e is NB) and (ec is PS) then (u is PS) (1)
6. If (e is NB) and (ec is PM) then (u is PS) (1)
7. If (e is NB) and (ec is PB) then (u is Z) (1)
8. If (e is NM) and (ec is NB) then (u is PB) (1)
9. If (e is NM) and (ec is NM) then (u is PM) (1)
10. If (e is NM) and (ec is NS) then (u is PM) (1)
11. If (e is NM) and (ec is Z) then (u is PS) (1)
12. If (e is NM) and (ec is PS) then (u is PS) (1)
13. If (e is NM) and (ec is PM) then (u is Z) (1)
14. If (e is NM) and (ec is PB) then (u is NS) (1)
15. If (e is NS) and (ec is NB) then (u is PM) (1)
16. If (e is NS) and (ec is NM) then (u is PM) (1)
17. If (e is NS) and (ec is NS) then (u is PS) (1)
18. If (e is NS) and (ec is Z) then (u is PS) (1)
19. If (e is NS) and (ec is PS) then (u is Z) (1)
20. If (e is NS) and (ec is PM) then (u is NS) (1)
21. If (e is NS) and (ec is PB) then (u is NS) (1)
22. If (e is Z) and (ec is NB) then (u is PM) (1)
23. If (e is Z) and (ec is NM) then (u is PS) (1)
24. If (e is Z) and (ec is NS) then (u is PS) (1)
25. If (e is Z) and (ec is Z) then (u is Z) (1)
26. If (e is Z) and (ec is PS) then (u is NS) (1)
27. If (e is Z) and (ec is PM) then (u is NS) (1)
28. If (e is Z) and (ec is PB) then (u is NM) (1)
29. If (e is PS) and (ec is NB) then (u is PS) (1)
30. If (e is PS) and (ec is NM) then (u is PS) (1)
31. If (e is PS) and (ec is NS) then (u is Z) (1)
32. If (e is PS) and (ec is Z) then (u is NS) (1)
33. If (e is PS) and (ec is PS) then (u is NS) (1)
34. If (e is PS) and (ec is PM) then (u is NM) (1)
35. If (e is PS) and (ec is PB) then (u is NM) (1)
36. If (e is PM) and (ec is NB) then (u is PS) (1)
37. If (e is PM) and (ec is NM) then (u is PS) (1)
38. If (e is PM) and (ec is NS) then (u is Z) (1)
39. If (e is PM) and (ec is Z) then (u is NS) (1)
40. If (e is PM) and (ec is PS) then (u is NM) (1)
41. If (e is PM) and (ec is PM) then (u is NM) (1)
42. If (e is PM) and (ec is PB) then (u is NB) (1)
43. If (e is PB) and (ec is NB) then (u is Z) (1)
44. If (e is PB) and (ec is NM) then (u is NS) (1)
45. If (e is PB) and (ec is NS) then (u is NS) (1)
46. If (e is PB) and (ec is Z) then (u is NM) (1)
47. If (e is PB) and (ec is PS) then (u is NM) (1)
48. If (e is PB) and (ec is PM) then (u is NB) (1)
49. If (e is PB) and (ec is PB) then (u is NB) (1)
Third : Design of control loop
Usually , The closed-loop structure of a traditional fuzzy controller is as follows :

The basic structure of fuzzy controller :

3. Part of the source code
addpath 'func\'
title_function
% initialization
fnn_parameter;
% The object of the charge
a1 = 1.2;
b1 = 1;
b2 = 0.8;
b3 = 0;
ta = 40;
sys = tf(a1,[b1,b2,b3]);
dsys = c2d(sys,0.1,'z');
[num,den] = tfdata(dsys,'v');
ts = 0.1;% Sampling time T=0.1
% Closed loop controller
for k=1:SIM_times
k
time(k) = k*ts;
% Define the input signal
yd(k) = 2;
% Define output signal
if k < ta
yn = 0;
else
yn = -den(2)*y1 - den(3)*y2 + num(2)*u1 + num(3)*u2;
end
y2 = y1;
y1 = yn;
y(k) = yn;
u2 = u1;
e2 = e1;
e1 = yd(k)-yn;
e(k) = e1;
ec =(e1-e2);
x1 =(1-exp(-10*e1))/(1+exp(-10*e1));
x2 =(1-exp(-ec))/(1+exp(-ec));
% The first 1 Layer output
for i=1:7
o11(i) = x1;
o12(i) = x2;
end
o1=[o11;o12];
% The first 2 Layer output
for i=1:2
for j=1:7
z1(i,j) =-((o1(i,j)-a(i,j))^2)/(b(i,j));
o2(i,j) = exp(z1(i,j));
end
end
% The first 3 Layer output
for j=1:7
for l=1:7
o3((j-1)*7+l)=o2(1,j)*o2(2,l);
end
end
% The first 4 Layer output
I=0;
for i=1:49
I = I + o3(i)*Weight(i)/4;
end
o4 = I/(sum(o3));
u(k) = o4;
u1 = o4;
% Gradient descent method to adjust the weight
for i=1:49
dwp = e1*du*o3(i)/(sum(o3));
% iteration
Weight(i) = Weight(i) + eta*dwp;
end
% Center value update
da11=zeros(1,7);
for j=1:7
for l=1:7
da11(j) = da11(j)+(o2(2,l)*((Weight((j-1)*7+l)*sum(o3))-I));
end
da12(1,j) = -e1*du*(2*(o1(1,j)-a(1,j))*(o2(1,j)))/((b(1,j)^2)*(sum(o3))^2);
da1(j) = (da12(1,j))*(da11(j));
end
da21 = zeros(1,7);
for j=1:7
for l=1:7
da21(j) = da21(j)+(o2(1,l)*((Weight((l-1)*7+j)*sum(o3))-I));
end
da22(2,j) = -e1*du*(2*(o1(2,j)-a(2,j))*(o2(2,j))/((b(2,j)^2)*(sum(o3))^2));
da2(j) = (da22(2,j))*(da21(j));
end
da=[da1;da2];
for i=1:2
for j=1:7
a(i,j)=a(i,j)-eta*da(i,j);
end
end
a_s(:,:,k) = a;
if k == 1
a_(:,:,k) = a_s(:,:,1);
else
for i = 1:2
for j = 1:7
dist_tmp(i,j) = (a_s(i,j,k) - a_(i,j))^2;
end
end
dist = sqrt(sum(sum(dist_tmp)));
if dist < 0.1
tmps(:,:,1) = a_(:,:,k-1);
tmps(:,:,2) = a_s(:,:,k);
a_(:,:,k) = mean(tmps(:,:,1:2),3);
else
a_(:,:,k) = a_(:,:,k-1);
end
end
a = a_(:,:,k);
% Width update
db11=zeros(1,7);
for j=1:7
for l=1:7
db11(j)=db11(j)+(o2(2,l)*((Weight((j-1)*7+l)*sum(o3))-I));
end
db12(1,j)=-e1*du*(2*(o1(1,j)-a(1,j))^2)*(o2(1,j))/((b(1,j)^3)*(sum(o3))^2);
db1(j)=(db12(1,j))*(db11(j));
end
db21=zeros(1,7);
for j=1:7
for l=1:7
db21(j)=db21(j)+(o2(1,l)*((Weight((l-1)*7+j)*sum(o3))-I));
end
db22(2,j)=-e1*du*(2*(o1(2,j)-a(2,j))^2)*(o2(2,j))/((b(2,j)^3)*(sum(o3))^2);
db2(j)=(db22(2,j))*(db21(j));
end
db=[db1;db2];
for i=1:2
for j=1:7
b(i,j)=b(i,j)-eta*db(i,j);
end
end
b_s(:,:,k) = b;
if k == 1
b_(:,:,k) = b_s(:,:,1);
else
for i = 1:2
for j = 1:7
dist_tmp(i,j) = (b_s(i,j,k) - b_(i,j))^2;
end
end
dist = sqrt(sum(sum(dist_tmp)));
if dist < 0.1
tmps(:,:,1) = b_(:,:,k-1);
tmps(:,:,2) = b_s(:,:,k);
b_(:,:,k) = mean(tmps(:,:,1:2),3);
else
b_(:,:,k) = b_(:,:,k-1);
end
end
b = b_(:,:,k);
% Algorithm
s11 = y1;
s12 = y2;
s13 = u1;
s14 = u2;
s1 =[s11;s12;s13;s14];
for i=1:5
net2(i) = w2(i,:)*s1 + theta2(i);
s2(i) = (1-exp(-net2(i)))/(1+exp(-net2(i)));
end
net3 = w3*s2+theta3;
yg = am*(1-exp(-net3))/(1+exp(-net3));
for i=1:5
delta2(i)=0.5*(1-s2(i))*(1+s2(i));
end
delta3=0.5*am*(1-yg/am)*(1+yg/am);
for i=1:5
theta22(i) = theta2(i)-theta21(i);
theta21(i) = theta2(i);
theta2(i) = theta2(i)+eta1*(yn-yg)*delta3*w3(i)*delta2(i)+beta1*theta22(i);
end
theta32 = theta3-theta31;
theta31 = theta3;
theta3 = theta3+eta1*(yn-yg)*delta3+beta1*theta32;
for i=1:5
for j=1:4
w22(i,j) = w2(i,j)-w21(i,j);
w21(i,j) = w2(i,j);
w2(i,j) = w2(i,j)-eta1*(yn-yg)*delta3*w3(i)*delta2(i)*s1(j)+beta1*w22(i,j);
end
w32(i) = w3(i)-w31(i);
w31(i) = w3(i);
w3(i) = w3(i)-eta1*(yn-yg)*delta3*s2(i)+beta1*w32(i);
end
a2 = am-a1;
a1 = am;
am = am+eta1*(yn-yg)*yg/am+beta1*a2;
sum1 = 0;
for i=1:5
sum1 = sum1 + w3(i)*delta2(i)*w2(i,3);
end
du = delta3*sum1;
end
figure;
plot(time,y,'r', time,yd,'b');
grid on
figure;
subplot(121);
plot(a_s(1,:,SIM_times),a_s(2,:,SIM_times),'o');
grid on
axis square
subplot(122);
plot(b_s(1,:,SIM_times),b_s(2,:,SIM_times),'o');
grid on
axis square
save Simu_Results\fnn_result.mat time y
save Simu_Results\nfis.mat a b
This paper mainly introduces the design of fuzzy neural network controller ,
First of all : The structure design of four layered neural network layer :
The first 1 layer :

![]()
The first 2 layer :

![]()
The first 3 layer :

![]()
The first 4 layer :


second : Using the gradient descent method to update the weight


4. Simulation results
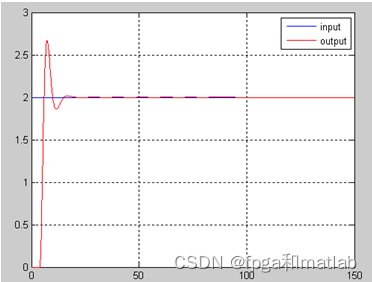
Fuzzy control effect diagram ( Model one ):
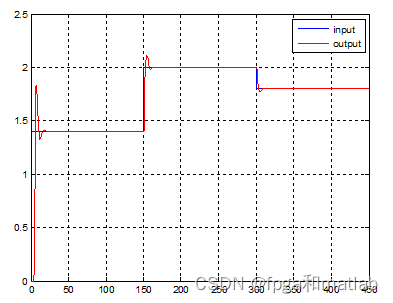
Fuzzy control effect diagram ( Model two ):
The membership function is as follows :







A05-06
边栏推荐
- 数据治理与数据标准
- Win11 ne peut pas faire glisser l'image sur le logiciel de la barre des tâches
- MySQL优化小技巧
- How to systematically learn LabVIEW?
- 4G-learn from great partners
- A set of sai2 brushes is finally finished! Share with everyone!
- Skills in schematic merging
- From how to use to how to implement a promise
- 文件傳輸協議--FTP
- 【历史上的今天】6 月 23 日:图灵诞生日;互联网奠基人出生;Reddit 上线
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
SQL reported an unusual error, which confused the new interns
关于st-link usb communication error的解决方法
【历史上的今天】6 月 19 日:iPhone 3GS 上市;帕斯卡诞生;《反恐精英》开始测试
Cvpr22 collected papers | hierarchical residual multi granularity classification network based on label relation tree
Flutter 使用 CustomPaint 绘制基本图形
NER中BiLSTM-CRF解读Forward_algorithm
原理图合并中的技巧
把腾讯搬上云:云服务器 CVM 的半部进化史
General timer and interrupt of stm32
STM32F1与STM32CubeIDE编程实例-金属触摸传感器驱动
11 timers for STM32F103
Skills in schematic merging
Leetcode topic [array] -228- summary interval
毕业总结
Solutions to st link USB communication error
Flashtext, a data cleaning tool, has directly increased the efficiency by dozens of times
图灵机启动顺序
数仓的字符截取三胞胎:substrb、substr、substring
Interpretation of the source code of scheduledthreadpoolexecutor (II)
[2D code image correction and enhancement] simulation of 2D code image correction and enhancement processing based on MATLAB