当前位置:网站首页>《nlp入门+实战:第四章:使用pytorch手动实现线性回归 》
《nlp入门+实战:第四章:使用pytorch手动实现线性回归 》
2022-07-26 01:00:00 【ZNineSun】
上一篇: 《nlp入门+实战:第三章:梯度下降和反向传播 》
本章代码链接:
- https://gitee.com/ninesuntec/nlp-entry-practice/blob/master/code/4.使用pytorch完成线性回归.py
- https://gitee.com/ninesuntec/nlp-entry-practice/blob/master/code/4.线性回归的手动实现.py
1.向前计算
对于pytorch中的一个tensor,如果设置它的属性.requires_grad为True,那么它将会追踪对于该张呈的所有操作。或者可以理解为,这个tensor是一个参数,后续会被计算梯度,更新该参数。
1.1 计算过程
假设有以下条件(1/4表示求均值,xi中有4个数),使用torch完成其向前计算的过程。
o = 1 4 ∑ i z i z i = 3 ( x i + 2 ) 2 o=\frac{1}{4}\sum_{i}z_i\\ z_i=3(x_i+2)^2 o=41i∑zizi=3(xi+2)2
其中:
Z i ( x i = 1 ) = 27 Z_i(x_i=1)=27 Zi(xi=1)=27
如果x为参数,需要对其进行梯度的计算和更新
那么,在最开始随机设置x的值的过程中,需要设置他的requires_grad属性为True,其默认值为None
import torch
x = torch.ones(2, 2, requires_grad=True) # 初始化参数x,并设置requires_grad=True用于追踪其计算历史
print("x=", x)
y = x + 2
print("y=", y)
z = y * y * 3 # 平方*3
print("z=", z)
out = z.mean() # 求均值
print("out=", out)

从上述代码可以看出:
- 1.x的requires_grad属性为True
- 2.之后的每次计算都会修改其grad_fn属性,用来记录做过的操作
- 1.通过这个函数和grad_fn能够组成一个和上一章类似的计算图
1.2 requires_grade和grad_fn
a = torch.randn(2, 2)
a = ((a * 3) / (a - 1))
print(a.requires_grad)
a.requires_grad_(True) # 就地修改
print(a.requires_grad)
b = (a * a).sum()
print(b.requires_grad)
with torch.no_grad():
c = (a * a).sum()
print(c.requires_grad)
注意:
为了防止跟踪历史记录(和使用内存),可以将代码块包装在with torch.no_grad():中。在评估模型时特别有用,因为模型可能具有requires_grad = True的可训练的参数,但是我们不需要在此过程中对他们进行梯度计算。
2.梯度计算
对于1.1中的out而言,我们可以使用backward方法来进行反向传播,计算梯度out.backward(),此时便能够求出导数 d o u t d x \frac{d_{out}}{d_x} dxdout,调用x.gard能够获取导数值
out.backward() # 反向传播
print("反向传播:", x.grad) # x.grad获取梯度

因为:
d ( O ) d ( x i ) = 1 4 ∗ 6 ( x i + 2 ) = 3 2 ( x i + 2 ) \frac{d(O)}{d(x_i)}=\frac{1}{4}*6(x_i+2)=\frac{3}{2}(x_i+2) d(xi)d(O)=41∗6(xi+2)=23(xi+2)
在 x i = 1 x_i=1 xi=1时,其值为4.5
注意:在输出为一个标量的情况下,我们可以调用输出tensor的backword()方法,但是在数据是一个向量的时候,调用backward()的时候还需要传入其他参数。
很多时候我们的损失函数都是一个标量,所以这里就不再介绍损失为向量的情况。
loss.backward()就是根据损失函数,对参数(requires_grad=True)的去计算他的梯度,并且把它累加保存到x.gard ,此时还并未更新其梯度,所以每次反向传播之前需要先把梯度置为0之后在进行新的反向传播。
注意点:
- 1.tensor.data:
- 在tensor的require grad=False,tensor.data和tensor等价
- require_grad=True时,tensor.data仅仅是获取tensor中的数据
print(a)
print(a.data)

- 2.tensor.numpy():
- require_grad=True不能够直接转换,需要使用tensor.detach().numpy(),换句话说,tensor.detach().numpy()能够实现对tensor数据的深拷贝,转化为ndarray
3.手动完成线性回归的实现
下面,我们使用一个自定义的数据,来使用torch实现一个简单的线性回归
假设我们的基础模型就是y = wx+b
其中w和b均为参数,我们使用y = 3x+0.8来构造数据x、y,所以最后通过模型应该能够得出w和b应该分别接近3和0.8
- 1.准备数据
- 2.计算预测值
- 3.计算损失,把参数的梯度置为0,进行反向传播
- 4.更新参数
在完成本小节内容之前,我们需要安装一个图形化显示的包:matplotlib
自己可以通过pip install matplotlib 进行安装,我是直接在anaconda里进行安装的,大家按照自己的需求来,不会的可以自行百度哈
import torch
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
learning_rate = 0.01
# 1.准备数据 y=3x+0.8,准备参数
x = torch.rand([500, 1]) # 1阶,50行1列
y = 3 * x + 0.8
# 2.通过模型计算y_predict
w = torch.rand([1, 1], requires_grad=True)
b = torch.tensor(0, requires_grad=True, dtype=torch.float32)
y_predict = x * w + b
# 4.通过循环,反向传播,更新参数
for i in range(50): # 训练3000次
# 计算预测值
y_predict = x * w + b
# 3.计算loss
loss = (y_predict - y).pow(2).mean()
if w.grad is not None:
w.grad.data.zero_()
if b.grad is not None:
b.grad.data.zero_()
loss.backward() # 反向传播
w.data = w.data - learning_rate * w.grad
b.data = b.data - learning_rate * b.grad
print("w:{},b:{},loss:{}".format(w.item(), b.item(), loss.item()))
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8))
plt.scatter(x.numpy().reshape(-1), y.numpy().reshape(-1)) # 散点图
y_predict = x * w + b
# y_predict包含gard,所以我们需要深拷贝之后转numpy
plt.plot(x.numpy().reshape(-1), y_predict.detach().numpy().reshape(-1),color = "red",linewidth=2,label="predict") # 直线
plt.show()
我解释一下:numpy().reshape(-1)
z.reshape(-1)或z.reshape(1,-1)将数组横向平铺
z.reshape(-1)
array([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16])
z.reshape(-1, 1)将数组纵向平铺
z.reshape(-1,1)
array([[ 1],
[ 2],
[ 3],
[ 4],
[ 5],
[ 6],
[ 7],
[ 8],
[ 9],
[10],
[11],
[12],
[13],
[14],
[15],
[16]])
我们先把训练次数设置为50次,运行之后可以看到预测值和真实值之间的偏差: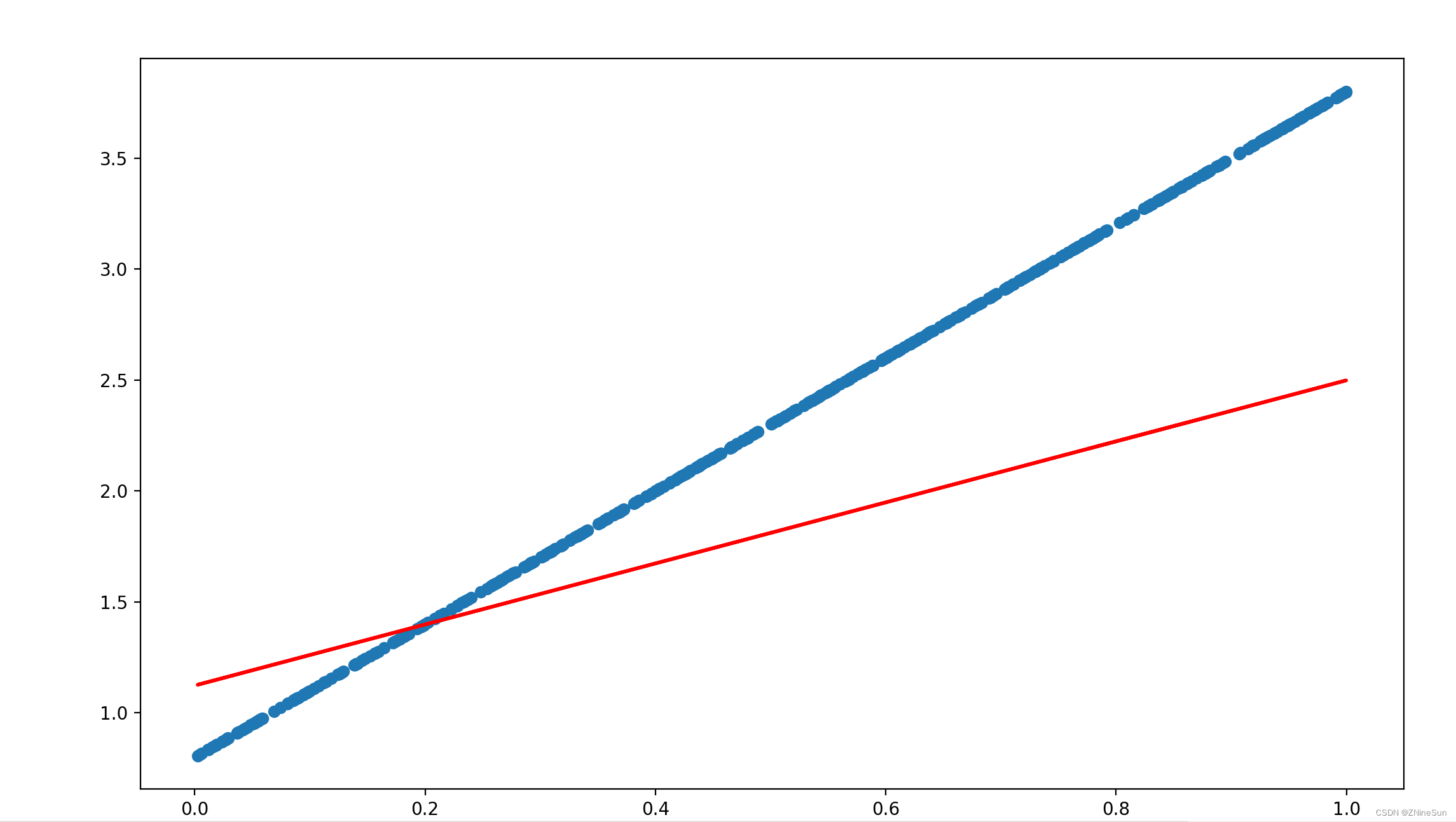
在把训练次数调整为5000次,可以看到:
可以看到预测的结果基本和真实值接近了
边栏推荐
- If the native family is general, and the school is also a college on the rotten street, how to go on the next journey
- 中心对称的二进制模式CSLBP,matlab
- Open download! Alibaba Devops Practice Manual
- Seretod2022 track1 code analysis - task-based dialogue system challenge for semi supervised and reinforcement learning
- [RTOS training camp] ring buffer, at instruction, preview arrangement and evening class questions
- Unityvr -- robot arm scene 4- gifts and Christmas tree
- [RTOS training camp] about classes and Q & A
- User defined variables and extracted public variables of JMeter
- [RTOS training camp] operation explanation, queue and ring buffer, queue - transmission data, queue - synchronization tasks and evening class questions
- RHCE之at和crontab命令详解及chrony部署
猜你喜欢
![[RTOS training camp] problems of evening students](/img/4a/9d781a28751c15e9e42cd5743e97db.jpg)
[RTOS training camp] problems of evening students

Spine_附件皮肤
【RTOS训练营】站在更高的角度学习C语言

Small sample learning - getting started

Test the concept of left shift and right shift

Distributed transaction and at mode principle of Seata

超全的开源Winform UI库,满足你的一切桌面开发需求!

SQL statement exercise

The task will be launched before the joint commissioning of development

【ctf】Crypto初步基础概要
随机推荐
jupyter更改主界面并且导入数据集
[array related methods in numpy]
Distributed transaction and at mode principle of Seata
RHCE之at和crontab命令详解及chrony部署
What is the difference between request forwarding and request redirection?
Azure synapse analytics Performance Optimization Guide (1) -- optimize performance using ordered aggregate column storage indexes
【RTOS训练营】课程学习方法和结构体知识复习 + 链表知识
换ip软件的用途很广及原理 动态IP更换的四种方法来保护网络隐私
How to choose social e-commerce model in the early stage? Taishan crowdfunding
[RTOS training camp] continue the program framework, tick interrupt supplement, preview, after-school homework and evening class questions
《暗黑破坏神:不朽》手游如何多开搬砖及新手入门搬砖攻略
[RTOS training camp] learn C language from a higher perspective
ASP. Net core configuration
[plaything determination scratch children programming] ride a small motorcycle (dynamic background + camera control operation)
中心对称的二进制模式CSLBP,matlab
How to use if in sql service
旅行+战略加速落地 捷途新产品矩阵曝光
Redis Command Reference Manual - key
SQL statement exercise
Leetcode notes 20. valid parentheses