当前位置:网站首页>[RTOS training camp] problems of evening students
[RTOS training camp] problems of evening students
2022-07-26 00:59:00 【Weidong mountain】
1. ask : What if I have to change my mobile phone number when I go to work in other cities ?
answer : Mobile phone number change , Alone Headmaster Handle .
2. ask : Today is live text ?/ Is there a live video now ?
answer : Encounter difficult problems , Will use video live . There should be no live video today .
3. ask : The bare metal course of single chip microcomputer is expected to have several classes ?
answer : Bare metal courses 3、4 Second class .
4. ask : Do you need to read the fundamentals of single chip microcomputer to learn this course ?
answer : no need ,RTOS Focus on software , Single chip operation is not much ; The back can speak ARM framework .
5. ask : If you have no time for training that night , Look back at the after-school materials , There should be no difference with what you miss ?
answer : There is no interaction , There's no difference .
6. ask : Why are all procedures from 0x80000000 Start ?
answer : In this class, it's just a hypothetical address .
7. ask : stm A series of code runs on the chip flash Do you ?
answer : Let's assume that it is Flash Up operation , speak of ARM Architecture allows programs to RAM Running in .
8. ask : CPU How to access the Flash、RAM、GPIO These memory or peripherals ?
answer : CPU Uncle uses different addresses , visit RAM,GPIO,FLASH. Look at it this way ,GPIO、RAM、Flash Position the same .
a. RAM Its characteristic is : Write something in , Read out what is still .
b. Flash Its characteristic is : It is not easy to write data in , You can read .
c. GPIO Its characteristic is : Writing data has special meaning , It may be that the pin becomes high 、 Low level .
These sons , The functions are different . But in my eyes , All sons , They all have addresses , All are accessed using addresses .
9. ask : Can you write the address casually , For example, write an address 0?
answer : Only when the corresponding device exists in this address , Wanted 7 A gourd baby , You want to call number 8 individual , It doesn't exist . in other words , The access address must be within the address range specified by the chip . You write an address , When it comes to chips , There is no device in this address : Write it , It doesn't work .
10. ask :a=123 How do you think this is the address of writing memory ? The address is 123 Do you ? Where did it go ?
answer : a It's a variable. , Variable readable and writable , Only in RAM in .123 Is the value to be written , The address is assigned when linking the program , To check which address is assigned, debug and check when it can run .
11. ask : “Flash Its characteristic is : It is not easy to write data in , You can read ” I don't quite understand
answer : When we develop programs , Burn the program , It's burning and writing Flash On , After power failure ,Flash The content of will not be lost ,Flash What is stored on it is a program , It's precious , You can't simply write data in , Special steps must be taken : For example, write after erasing , For example, when writing, unlock it first . If Flash Can easily write data into , Your program is easy to break .
12. ask : Variables of the previous routine a and p stay flash The address is also in the burning file + Does the data form exist , there “ Address ” Can I customize the allocation ?
answer :a = 123; p =xxx; stay Flash This is how it is preserved in : Suppose the compiler gives a、p The assigned addresses are addr1, addr2.a = 123; Into several assembly instructions , as follows :
MOV R0, ADDR1
MOV R1, #123
STR R1, [R0]
It doesn't matter if you don't understand the compilation ,ARM The architecture will say . Translate :
a = 123; Into several assembly instructions :
- hold addr1 Put the value of CPU The internal register of R0;
- hold 123 Put the value of CPU The internal register of R1;
- hold R1 Write the value of to an address , Which address ?R0 Inside is the address value ;
Here comes the key :a = 123:
- hold 123 The number of , Write to variable a Go to , Is to write addr1 Corresponding memory ;
- In assembly code , Implicit addr, Implicit 123;
- After executing the assembly instructions , come from Flash The numerical 123, Written to memory addr1 place ;
13. ask :p = (volatile unsigned int *)(0x40010800 + 0x0c) Medium volatile unsigned in Don't write it ?
answer : Don't write , There will be a warning .
14. ask : cpu Not will flash Data read to RAM in , stay RAM Do you want to do it in the future ? You can also read directly gpio The address? ?
answer : It's not right .CPU It's a Flash The data of , Read in CPU Inside , stay CPU Internal implementation . Yes RAM Only 2 Kind of : read 、 Write .
Look at this a = a + b:
- Read from memory a, Deposit in CPU;
- Read from memory b, Deposit in CPU;
- CPU Inside :val = a + b;
- hold val Write to memory a It's about ;
- For memory RAM, Only reading 、 Write operations ; about Flash, There is only read operation here ,CPU from Flash Read to execute , stay CPU Internal execution instructions :
15. ask : Does the memory manager need to configure the address range of each peripheral ? Or is it configurable ? Do you need to configure ?
answer :
- Generally, it cannot be configured ;
- Whether it's 103, Or other chips, such as IMX6ULL, Every chip manual has a chapter :memory map, What it says is , Address range of each device on the chip ;
16. ask : Variables and data are stored separately in two areas ?
answer :
Variable a, The address is
0x20000000, It is determined when linking the program , When the program runs, it is in memory , Note that Runtime ;a=123This is an instruction , There is data in the instruction 123, It's in Flash On ;After execution
a=123after , Memory address0x20000000The value at is written as 123;123 This value , come from Flash, It's spread RAM
17. ask : Registers in the assembly , and GPIO What is the difference between these registers , Is the access method and address different ?
answer :
register , This word is very bad .CPU Internal registers ,GPIO Register on , It's not the same thing :
- CPU The registers inside , Use assembly instructions to read and write ;
- GPIO Register on , Like memory ,CPU Send address signal 、 Data signals , To read and write it ;
18. ask : Is this messenger programmed by us ? For example, send it an address , Then send a chip selection signal ?
answer : Chip design , The hardware is designed , The software cannot be changed .
19. ask : Why is the address length 4?
answer : ① First , There is a premise here : Is in 32 Under the machine .② this 32 Bits limit the length of the memory address to 32 Bit is 4 Bytes , So we use sizeof When getting the length of a pointer variable , You can only get one result , That's it 4 Byte length .③ about 32 position CPU,CPU Uncle can send 32 Address lines , So the value of the address , Just use 32bit To express .④ Various variables have different sizes , But its address , To be exact, the first address , All are 32 Bit .⑤ Pointer to the variable , Used to save the address , So any pointer variable ,sizeof(XXX *) All are 4 byte , That is to say 32 position .
20. ask : char buf[1000] , Not initialized ,sizeof(buf) It's also 4 Well ?
** answer :** yes 1000. No initialization means that the value inside is not set , But the occupied space CPU Keep it for you .
21. ask :
ldr r0, =0x20000000
ldr r1, =123
str r1, [r0]
How to judge whether it is data or address ?
answer : It is impossible to judge whether it is data or address , Only when it is used can we know whether it is data or address . In the 3 Orders :STR R1, [R0] This is a write memory instruction ,R1 Is the data ,R0 It's the address . If you write it this way :STR R0, [R1], that R0 Is the data ,R1 It's the address .STR yes store It means .
22. ask : Can you understand the process of program operation in this way :
Programs are stored in Flash in ( To be processed ) CPU Execute one sentence of code at a time ( Deal with a sentence of code ), Store the results of each execution in RAM in ( Whether heap or stack ), If necessary, just RAM Extract data from ( such as GPIOS-ODR register ).
answer : The results may not be saved to RAM, such as :*p = 1;p Point to GPIO register , Then this instruction is To write GPIO register , The result is written GPIO Went to the . Of course ,p The value of is from RAM.“ The results of each execution are stored in RAM in ”: Wrong **“ Every time ”**
23. ask : arm Instruction sets and thumb Instruction sets are 32 For addressing ?
answer : Yes .Flash Upper each thumb When the command 16 Bit , however CPU To read Flash、 Reading and writing RAM、 Reading and writing GPIO when , The address line sent is 32 Bit .CPU Got it 16 Bit instruction , according to 16 Bit instruction : such as STR R0, [R1], It is a handle. R1 Of 32 The digit value is sent to the address line . therefore thumb still arm Instructions , It does not affect the address line length of addressing .
24. ask : stay Linux Run your own program in , You can delete your own executable , Why is the program in the single chip microcomputer Flash?
answer : Linux Is to read the program into RAM, And then run ; SCM can also put Flash The program on reads RAM function , And then erase Flash, It's just a single chip computer RAM Not that big. , We can not put Flash Copy the code on to RAM.
25. ask : Mentioned the first address , The teacher has time to talk about pack Instructions ? When do I need to use alignment , How to use :
struct {
char c;
int a;
};
answer : First , How big is this structure ? Logically speaking ,char yes 1 byte ,int yes 4 byte , So this structure is 5 byte . however , If you allocate space like this ,int a The address of is odd , Inefficient access . therefore , This structure is for char c, Still allocate 4 byte , Even if only 1 byte . Can we force it to allocate 5 byte ? Sure , use pack Instructions , Specific usage can be Baidu search .
26. ask : cortex-m Series I can understand as code located in Flash On , The variable is located in RAM On? ? So from Flash Will the instruction fetch speed be limited ? This is a cortex-m Features of the series ?
answer : There is no problem with this understanding . In fact, you can M series Flash Put the code on it RAM Run in , If RAM If there's enough space . stay Flash The speed will be a little slower , Considering the cost, we can tolerate .
27. ask : FreeRTOS Is the task stack of generally dynamically allocated ? Dynamic allocation generally does not overflow ?
answer : Dynamic allocation is more convenient , But some systems that pursue extreme stability do not allow dynamic allocation .
28. ask : stay 32 Bits will be among them , Why is it more efficient to allocate four byte aligned access to the structure ?
answer : First look at this picture :
CPU The access bit width is 32 Of RAM when , The last time the hardware read and write was 32 Bit as a unit of , such as : Even read one char c, Memory controller also goes RAM I read that 32 Bit data is 4 Bytes of data , Return one of the stanzas to CPU.① For the variables in the above figure a, It can be read at one time 、 finish writing sth. ;② For the variables in the above figure b, Read 2 Time : The first 1 Read the following ellipse for the second time 4 byte :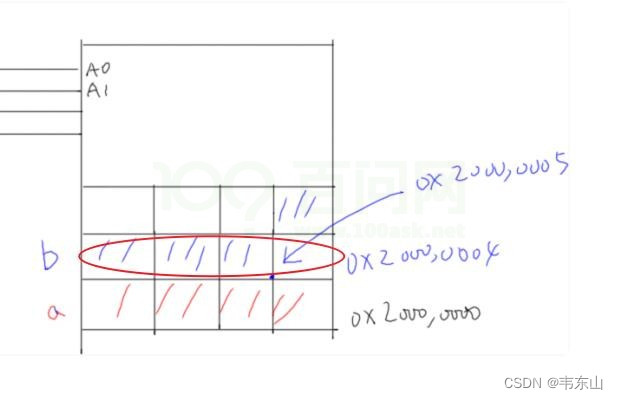
The first 2 Secondary reading , Get 4 byte :
Then combine the contents of the ellipse in the figure below :
What's the problem with such an operation ? Especially inefficient , The speed is particularly slow ! And the hardware does not necessarily support such addressing and reading .
29. ask : A memory controller uses chip selection to address the corresponding devices , Since each device has its own fixed memory address , Why do you need to select a device for film selection
answer : Because everyone shares the address line 、 cable , Address purely through the address line CPU It's impossible to tell which family is found .
边栏推荐
- AI knows everything: build and deploy sign language recognition system from 0
- Download exclusively | Alibaba cloud maxcompute questions and answers to unlock SaaS mode cloud data warehouse in this electronic manual!
- Getting started with D3D calculation shaders
- 进程与线程
- [oops framework] interface management
- What is the difference between request forwarding and request redirection?
- openvino安装踩坑笔记
- Data is written into excel and filled with color
- 阿明的告白
- How can I become an irreplaceable programmer?
猜你喜欢

【MATLAB appdesigner】27_ How to debug and view variables in appdesigner? (examples + skills)
![[RTOS training camp] GPIO knowledge and preview arrangement + evening class questions](/img/44/f3323a16e505a7fe923b25630f62f7.jpg)
[RTOS training camp] GPIO knowledge and preview arrangement + evening class questions

Database tools duel: heidisql and Navicat

How can a team making facial mask achieve a revenue of more than 1 million a day?

Download exclusively | Alibaba cloud maxcompute questions and answers to unlock SaaS mode cloud data warehouse in this electronic manual!
Processes and threads

Unityvr robot Scene 3 gripper

The ultra comprehensive open source WinForm UI library meets all your desktop development needs!

How can I become an irreplaceable programmer?

Attack and defense world web question -favorite_ number
随机推荐
Force deduction record: Sword finger offer (2) -- jz13-22
用 QuestPDF操作生成PDF更快更高效!
使用 SAP UI5 FileUploader 控件上传本地文件试读版
Some abnormal error reports and precautions of flowable (1)
Data is written into excel and filled with color
With data-driven management transformation, the first year of science and technology was at the right time
场景之分页查询设计
Regular expression
【RTOS训练营】上节回顾、空闲任务、定时器任务、执行顺序、调度策略和晚课提问
Day06 MySql知识点总结
Embedded development: tips and tricks -- seven tips for designing powerful boot loader
pip install --upgrade can‘t find Rust compiler
Attack and defense world web question -favorite_ number
Analysis and practice of parameter parser handlermethodargumentresolver
Prefix XOR sum, XOR difference array
如何才能修炼成一名不可替代的程序员?
Rotate the minimum number of the array
以数据驱动管理转型,元年科技正当时
MMOCR使用指南
typing‘ has no attribute ‘_ SpecialForm‘