当前位置:网站首页>[datawhale202206] pytorch recommendation system: multi task learning esmm & MMOE
[datawhale202206] pytorch recommendation system: multi task learning esmm & MMOE
2022-07-01 12:11:00 【SheltonXiao】
Conclusion Express
Multi task learning is a development of sequencing model , Born in the background of multitasking . Practice shows , Multi task joint modeling can effectively improve the model effect , Because it can : Task assistance ; Achieve implicit data enhancement ; Learn common expressions , Improve the generalization ability ( Especially for some tasks with insufficient data ); Regularization ( For a task , The learning of other tasks has regularization effect on this task )
At present, there are three main forms of multi task joint modeling :hard parameter sharing;soft parameter sharing (MMOE It belongs to this category ); Task sequence dependency modeling (ESMM It belongs to this category )
This study involves two models :
- ESMM
ESMM Considering the traditional CVR problem ( Conversion rate ) The problem is : Sample selection bias and Sparse data Two questions , Import task (CTR) To enrich the main task CVR The data of , At the same time, introduce tasks (CVCTR) And CTR And the main task CVR Form Bayesian probability relation .
Thus, the problem of sparse samples is improved ( By introducing data rich CTR), It also improves the problem of sample selection deviation ( By introducing CVCTR And CTR stay loss Form Bayesian formula , Make the modeling fall into the whole exposure space ).
On the concrete implementation , Use two networks , A set of main learning tasks CVR, A set of learning CTR, Finally, Loss To deal with ,Loss by pCTR And by pCTR And pCVR Calculated pCVCTR The linear superposition of . - MMOE
MMOE Then consider hard parameter sharing Not flexible enough to deal with multitasking , Problems requiring model decoupling , First, introduce gating to pay attention to the task , At the same time, considering that multiple tasks need to be considered separately , Introduce multi gating . Make multi task flexible combination , Solve similar problems together .
On the concrete implementation , By the same several DNN As an expert , The same amount DNN As a door control , Then together as feature Extracted input .
Previous review
0 Multi task learning
0.1 Definition
Multi task learning is simple Multiple objective functions loss Learning at the same time , The comparison with single task learning can be seen in the figure below ( originate Collection | On multi task learning (Multi-task Learning))

And Multi purpose learning And The migration study The concept comparison of is shown in the following figure .
Simply speaking , Multi task learning is a kind of transfer learning , A typical kind of multi task learning is multi-objective learning , And the goal is divided into label and class In the form of .

0.2 Why do we need to use multi task learning
There are several reasons :
- From industry demand : Many recommended businesses in the industry are naturally multi-objective modeling scenarios , Multi objective optimization is required .
Such as : Wechat video Number recommendation , On the home page, in addition to the automatic video playback “ The broadcast time ”、“ Completion rate ”( The proportion of user playback time to video length ) Out of goal , There are also a lot of interactive tags , for example “ Click on your friend's Avatar ”、“ Enter home page ”、“ Focus on ”、“ Collection ”、“ Share ”、“ give the thumbs-up ”、“ Comment on ” etc. .
We should base our recommendation on “ User satisfaction ”, but “ User satisfaction ” It cannot be expressed explicitly .
The industry generally uses “DAU”、“ Average daily use time of users ”、“ Retention ” As objective and indirect “ User satisfaction ”( Or Algorithm Engineer performance ) The evaluation index . These indicators are difficult to model through a single objective , Take the usage time as an example , The playback length of long video is naturally larger than that of short video . fortunately , Although there is no explicit user satisfaction evaluation index , But now app There are rich and specific implicit feedback similar to the above video Number recommendation scenarios . But these independent implicit feedbacks also present some challenges :
- Target deviation : give the thumbs-up 、 The satisfaction of sharing expression may be higher than that of playing
- Item deviation : The playing duration of different videos shows different satisfaction , Some videos may trick users into seeing the tail ( Similar to the headlines in news recommendations )
- User bias : Some users expressed satisfaction and liked to use likes , Some users may like to use collections
Therefore, we need to use multi task learning model to predict multiple goals , And on-line fusion of multi-objective prediction results to sort . Multi task learning can not directly express user satisfaction , However, we can make full use of the available user feedback information for full representation learning , And the relationship between businesses can be modeled , So as to efficiently and collaboratively learn specific tasks .
- The project is convenient : There is no need to train different models for different tasks , It can shorten the time requirement of independent calculation of multiple models , Convenient cost control .
After the merger , It can make more efficient use of training resources and carry out iterative upgrading of models .
0.3 Why multi task learning is effective
When business independent modeling is changed into multi task joint modeling , There are four possible outcomes :
- Multiple tasks have negative migration , The result is unacceptable
- Some tasks are getting better , Some tasks get worse
- Some tasks are getting better , Some tasks have the same effect
- The effects of multiple tasks are better
But for now , Most of them can achieve multi-objective common improvement . How can this result be achieved ?
There are four reasons given in the tutorial , The writing is relatively simple , Reference resources Collection | On multi task learning (Multi-task Learning) For example, to understand :
- Task assistance : Characteristics that are difficult to learn about a task , You can learn through other tasks
For example, tasks A Due to various restrictions, I can't learn well W1, But the task B But you can easily W1 Fit to the task A Required state ,A and B collocation , Work is not tiring ~.
- Implicit data enhancement : Different tasks have different noises , Learning together can counteract part of the noise
Different tasks have different noises , Suppose that the noise of different tasks tends to different directions , Learning together will offset part of the noise to a certain extent , Make learning better , The model can also be more robust .NLP and CV Data enhancement is often used to improve the effect of a single model , Multi task learning is achieved by introducing data from different tasks , Naturally, it has a similar effect .
- Learn common expressions , Improve the generalization ability : The model learns the weights that are preferred for all tasks , Help to spread to new tasks in the future
For some tasks, the data set is sparse , For example, short video forwarding , Most people will not forward a short video , Such sparse behavior , Models are hard to learn ( Over fitting is a serious problem ), If we put it together, we can predict whether users forward this sparse thing and whether users click to watch this frequent thing , To some extent, it will alleviate the over fitting of the model , The generalization ability of the model is improved .
Look at it from another Angle , For new tasks with little data , Also solved the so-called “ Cold start problem ”.
- Regularization : For a task , The learning of other tasks has regularization effect on this task
Multitasking learning provides a priori hypothesis (inductive knowledge) To improve the effect of the model , This Apriori assumption is made by adding auxiliary tasks ( Specifically, add one loss) To provide , Compared with L1 Regularization is more convenient (L1 The canonical prior assumption is : It is better to have fewer model parameters ).
0.4 The basic framework of multi task learning
For this part, please refer to Collection | On multi task learning (Multi-task Learning).
Multi task learning methods are usually divided into :hard parameter sharing and soft parameter sharing. The difference lies in the mapping 1 On the right MTL That square .
As you can see from the diagram , There are two ways
- hard parameter sharing( The way to grow old )
No matter how many tasks there are in the end , The underlying parameters are uniformly shared , The top-level parameters are independent of each model . Because most parameters are shared , The over fitting probability of the model will be reduced , The more parameters are shared , The smaller the probability of over fitting , The fewer parameters are shared , It is closer to single task learning and learning separately .
The image is understood as : Several people eat several dishes on a table , I have my own rice in my bowl ( It doesn't matter if you eat noodles in the North First ), What we share is the table 、 Several dishes , What you don't share is what you have in your bowl , The more food on the table , The less you have in your bowl , The probability of getting bored is smaller ; One's own rice in one's own bowl , There are few dishes on the table , After a while, I'm tired of eating orz.
- soft parameter sharing( The tendency of modern research )
The bottom layer shares some parameters , There are some unique parameters that are not shared ; The top layer has its own parameters . therefore Shared at the bottom 、 How to fuse unshared parameters and send them to the top , That is the focus of researchers .
Here we can put our classic MMOE Model structure , It will be clear at a glance .
And the leftmost (a) Of hard sharing comparison ,(b) and (c) It's all right first Expert0-2( Every expert It can be understood as a hidden layer neural network ) After weighted summation, it is sent into Tower A and B( It is also a hidden neural network ), adopt Gate( Or a hidden layer ) To decide what the weighting is .
Record a small card here : Smart little buddy sees this weighted sum , Did you immediately think of Attention La ? Why don't we put this Gate Change to a Attention? For different experts Attention To determine the sum weight , Then you have to find a way to design Attention Of query La , It's an interesting point .
0.5 The improvement direction of multi task learning
Mainly focused on soft parameter sharing On , It mainly focuses on two directions :
- Model structure design : Which parameters are shared , Which parameters are not shared ?
It can be further subdivided into two directions :
- Differentiate between shared layers , Find a way to give each task a unique way of sharing layer integration .
With google Of SNR The model, for example
- For different tasks , Design with the integration of different sharing levels .
With Tencent PCG PLE Take the Internet for example
- MTL The goal of loss Design and optimization improvements
Main solution loss The values vary 、 Learning speed is fast or slow 、 The update direction is sometimes the opposite problem . The two most classic jobs are UWL(Uncertainty Weight): Through automatic learning tasks uncertainty, to uncertainty Large tasks with small weights ,uncertainty Small tasks are big and heavy ;GradNorm: Combine the two norm sum of task gradient loss Descent gradient , The loss function with weight is introduced Gradient Loss, And update the weight by gradient descent .
You can also directly integrate different tasks loss Weighted fusion . But this is not multi-objective modeling in essence !
1 ESMM
Different goals due to business logic , There are explicit dependencies , For example, exposure → Click on → conversion . The user must be in the commodity exposure interface , Click on the product first , It is possible to buy conversion . Ali proposed ESMM(Entire Space Multi-Task Model) The Internet , Explicit modeling of joint task training with dependencies . Although this model is a multi task learning model , But in essence, it is CVR Main task , introduce CTR and CTCVR As an auxiliary task , solve CVR Estimated challenges .
1.1 The background of the birth of the model
Mainly for traditional CVR problem ( Conversion rate ) The problem is : Sample selection bias and Sparse data . Specifically, you can use the following figure to illustrate :
Here's the picture ( White background is exposure data , The gray background is the click behavior data , The black background is the purchase behavior data . Tradition CVR The training samples used for estimation are only gray and black data )
This leads to two problems
- Sample selection bias (sample selection bias,SSB): As shown in the figure ,
CVR The positive and negative sample set of the model ={ Negative samples not converted after clicking + Click to convert the positive sample }, But the online prediction is once the sample is exposed , You need to predict CVR and CTR Sort by ,Sample set ={ Exposed samples }. The constructed training sample set is equivalent to that obtained by sampling from a distribution that is inconsistent with the real distribution , To some extent, this violates the assumption that training data and test data are independent and identically distributed in machine learning .- The training data is sparse (data sparsity,DS): The click sample only accounts for a small part of the whole exposure sample , The transformed samples only account for a small part of the click samples . If you only use the data after clicking to train CVR Model , The available samples will be extremely sparse .
1.2 ESMM Model
In this context , Ali proposed ESMM, Learn from the idea of multi task learning , Introduce two auxiliary tasks CTR、CTCVR( Clicked and converted ), Eliminate the above two problems at the same time .
1.2.1 Multitasking design
The three prediction tasks are as follows :
- pCTR:
p(click=1 | impression); - pCVR( If the user clicks , The probability of buying ):
p(conversion=1 | click=1,impression); - pCTCVR( When the user has clicked , The probability that the user will buy ):
p(conversion=1, click=1 | impression) = p(click=1 | impression) * p(conversion=1 | click=1, impression);
Described in the form of probability .
The relationship between the three tasks is :
among x It means exposure ,y It means to click ,z It means transformation .
1.2.2 Model design
For these three tasks , The model structure shown in the figure is designed :
It can be seen that the characteristic is :
- It is divided into main task and auxiliary task , The primary and secondary tasks share features , Different task output layers use different networks
( Obviously, it does not directly belong to 0.5 Mentioned direction )
Specific for ( Here is an introduction not mentioned before CTR Why : Is the main task CVR The data is too sparse , Introduce a task with richer data to provide some basic knowledge )
Provide Transfer learning of feature expression (embedding Layer sharing ).
CVR and CTR The two subnetworks of the task share embedding layer , Online embedding Layer maps large-scale sparse input data to low dimensional representation vectors , The parameters of this layer account for most of the network parameters , It requires a large number of training samples to fully learn . because CTR The training sample size of the task is much larger than CVR The training sample size of the task ,ESMM The sharing mechanism of feature representation in the model can make CVR Subtasks can also learn from samples that show no clicks , Thus, it can greatly help to alleviate the sparsity of training data .
- The loss function has a special design : take cvr The predicted value of *ctr The predicted value of as ctcvr The predicted value of the task , utilize ctcvr and ctr Of label Constructing loss function
That is to say cvr Not explicitly ( As a single item ) Appears in the loss function
Doing so can help CVR The model is modeled in the complete sample space , Introduce Bayesian formula ( Conditional probability ) To illustrate this :
pCVR Can be pCTR and pCTCVR Deduce . In principle , It is equivalent to training two models separately to fit pCTR and pCTCVR, Re pass pCTCVR Divide pCTR Get the final fitting target pCVR . In the process of training , The model only needs to predict pCTCVR and pCTR, Using two additive combinations loss Update parameters .pCVR It's just an intermediate variable . and pCTCVR and pCTR The data of is extracted in the complete sample space , Thus, it is equivalent to pCVR It is also modeled in the whole exposure sample space .
Make a simple summary in your own words :
Import task (CTR) To enrich the main task CVR The data of , Also consider the task (CVCTR) And CTR And the main task CVR Bayesian probability relation , Also introduce .
This not only improves the problem of sparse samples ( By introducing data rich CTR), It also improves the problem of sample selection deviation ( By introducing CVCTR And CTR stay loss Form Bayesian formula , Make the modeling fall into the whole exposure space ).
This multi task learning model integrates hard parameter sharing The bottom of the sharing and soft parameter sharing about loss The reconstruction of , But it's not exactly the same , It can be separately called task sequence dependency modeling , It is applicable to scenarios with certain dependencies between different tasks .
1.2.3 Model thinking
- Can you change multiplication into division ?
In fact, considering the introduction of CTR And CVCTR The logic of , The composition of the model is obviously more than ESMM A kind of , Division is also feasible ( It means to train alone CTR,CVCTR Target model , And then divide them ). The reason for not doing this here is pCTR Usually small , Values tend to be unstable .
The results of ablation experiments are presented , In the table DIVISION Model , Compared with BASE Model direct modeling CTCVRR and CVR, Significantly improve , But lower than ESMM. as a result of pCTR Usually very small. , Dividing by a small floating-point number can cause numerical instability .
- Network structure optimization ,Tower Model replacement ? The two towers do not coincide ?
The base model here adopts pure MLP Model , In fact, the industry generally adopts more advanced models in the process of use ( for example DeepFM、DIN etc. ), The two towers can also set different models according to their own characteristics . This is also ESMM Advantages of frameworks , Subnetworks can be replaced arbitrarily , Very easy to integrate with other learning models .
ESMM It's a framework ! - Than loss A better way to add directly ?
loss Direct addition is not a strict multi-objective problem , The effect of true multi-target may be better , So we can consider introducing dynamic weighted learning mechanism . - Longer sequence dependent modeling ?
Some business dependencies go beyond exposure - Click on - Three layers of transformation , The subsequent improved model proposes a deeper task dependency modeling .
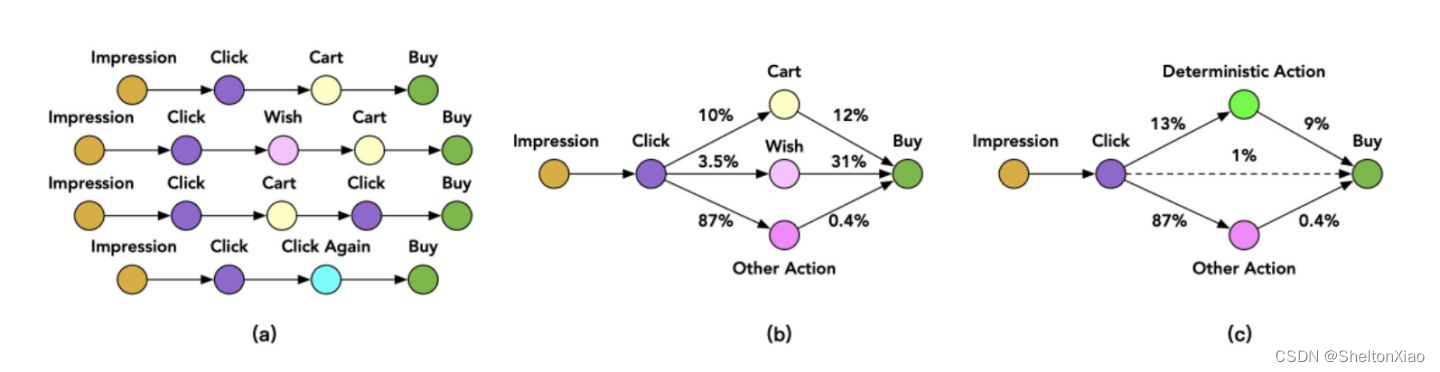
Ali's ESMM2: Before clicking to buy , Users may also add to the shopping cart (Cart)、 Join the wish list (Wish) Such behavior .
Compared with direct learning click->buy ( The sparsity is about 2.6%), Can pass Action The path decomposes the target , With Cart For example :click->cart ( sparse Degree is 10%),cart->buy( The sparsity is 12%), By decomposing the path , Build a multi task learning model to solve the problem step by step CVR Model , Alleviate sparse problem , The model also introduces feature sharing mechanism .
1.3 Code practice
1.3.1 be based on tf.keras Realization
ESMM There are four main points to pay attention to in the implementation of :
- Model structure : Share the underlying mechanism , Then two independent Tower The Internet , Output, respectively, CVR and CTR;
- loss Calculation : Calculation loss Only use CTR And CTCVR Of loss;
- net update :CVR Tower Complete your own network update ,CTR Tower At the same time, it completes its own network and Embedding Parameters are updated ;
- Model to evaluate : When evaluating model performance , The focus is on evaluating the main task CVR Of auc.
The following code uses tf.keras Realization ESMM
def ESSM(dnn_feature_columns, task_type='binary', task_names=['ctr', 'ctcvr'],
tower_dnn_units_lists=[[128, 128],[128, 128]], l2_reg_embedding=0.00001, l2_reg_dnn=0,
seed=1024, dnn_dropout=0,dnn_activation='relu', dnn_use_bn=False):
features = build_input_features(dnn_feature_columns)
inputs_list = list(features.values())
# Splicing sparse and dense Input characteristics
sparse_embedding_list, dense_value_list = input_from_feature_columns(features, dnn_feature_columns, l2_reg_embedding,seed)
# Model input layer ( It's also DNN Input layer )
dnn_input = combined_dnn_input(sparse_embedding_list, dense_value_list)
# DNN Output layer
ctr_output = DNN(tower_dnn_units_lists[0], dnn_activation, l2_reg_dnn, dnn_dropout, dnn_use_bn, seed=seed)(dnn_input)
cvr_output = DNN(tower_dnn_units_lists[1], dnn_activation, l2_reg_dnn, dnn_dropout, dnn_use_bn, seed=seed)(dnn_input)
# Dense layer
ctr_logit = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, use_bias=False, activation=None)(ctr_output)
cvr_logit = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, use_bias=False, activation=None)(cvr_output)
ctr_pred = PredictionLayer(task_type, name=task_names[0])(ctr_logit)
cvr_pred = PredictionLayer(task_type)(cvr_logit)
# Calculation ctcvr
ctcvr_pred = tf.keras.layers.Multiply(name=task_names[1])([ctr_pred, cvr_pred])#CTCVR = CTR * CVR
model = tf.keras.models.Model(inputs=inputs_list, outputs=[ctr_pred, cvr_pred, ctcvr_pred])
return model
Note the above code , Does not implement the field element-wise + modular . The implementation of this module is relatively simple , That is to say, the users 、 Of the relevant characteristics of a commodity embedding Sum and splice , Then input Tower The Internet . The data we use does not have this attribute , No distinction has been made yet .
1.3.2 be based on rechub The implementation of the
See github.
First deal with input features
from torch_rechub.models.multi_task import ESMM
from torch_rechub.basic.features import DenseFeature, SparseFeature
col_names = data.columns.values.tolist()
dense_cols = ['D109_14', 'D110_14', 'D127_14', 'D150_14', 'D508', 'D509', 'D702', 'D853']
sparse_cols = [col for col in col_names if col not in dense_cols and col not in ['cvr_label', 'ctr_label']]
print("sparse cols:%d dense cols:%d" % (len(sparse_cols), len(dense_cols)))
Rename the feature
label_cols = ['cvr_label', 'ctr_label', "ctcvr_label"] #the order of 3 labels must fixed as this
used_cols = sparse_cols #ESMM only for sparse features in origin paper
item_cols = ['129', '205', '206', '207', '210', '216'] #assumption features split for user and item
user_cols = [col for col in used_cols if col not in item_cols]
user_features = [SparseFeature(col, data[col].max() + 1, embed_dim=16) for col in user_cols]
item_features = [SparseFeature(col, data[col].max() + 1, embed_dim=16) for col in item_cols]
Then call the model definition . The corresponding parameter is :
user_featuresIt refers to the characteristics of the user side , You can only import sparse type ( In this paper, we need to do some research on user and item Side features sum_pooling operation )item_featuresReferring to item Side features , You can only import sparse typecvr_paramsAppoint CVR Tower in MLP Parameters of the layerctr_paramsAppoint CTR Tower in MLP Parameters of the layer
model = ESMM(user_features, item_features, cvr_params={
"dims": [16, 8]}, ctr_params={
"dims": [16, 8]})
In order to complete the training , Need to build dataloader
structure dataloader Usually by
- Build input dictionary ( The key of the dictionary is the feature name used to define the model , The value is the data of the corresponding feature )
- Build the corresponding dataset and dataloader
With the help of rechub Built-in class DataGenerator Realization :
from torch_rechub.utils.data import DataGenerator
x_train, y_train = {
name: data[name].values[:train_idx] for name in used_cols}, data[label_cols].values[:train_idx]
x_val, y_val = {
name: data[name].values[train_idx:val_idx] for name in used_cols}, data[label_cols].values[train_idx:val_idx]
x_test, y_test = {
name: data[name].values[val_idx:] for name in used_cols}, data[label_cols].values[val_idx:]
dg = DataGenerator(x_train, y_train)
train_dataloader, val_dataloader, test_dataloader = dg.generate_dataloader(x_val=x_val, y_val=y_val,
x_test=x_test, y_test=y_test, batch_size=1024)
For multitasking training , You need to set the task type , Optimizer hyperparameters and optimization strategies . With the help of MLTrainer Realization .
from torch_rechub.trainers import MTLTrainer
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
learning_rate = 1e-3
epoch = 1 #10
weight_decay = 1e-5
save_dir = '../examples/ranking/data/ali-ccp/saved'
if not os.path.exists(save_dir):
os.makedirs(save_dir)
# Task type definition
task_types = ["classification", "classification"] #CTR And CVR All tasks are classified into two categories
mtl_trainer = MTLTrainer(model, task_types=task_types,
optimizer_params={
"lr": learning_rate, "weight_decay": weight_decay},
n_epoch=epoch, earlystop_patience=1, device=device, model_path=save_dir)
mtl_trainer.fit(train_dataloader, val_dataloader)
auc = mtl_trainer.evaluate(mtl_trainer.model, test_dataloader)
2 MMOE
MMOE yes 2018 Google put forward , The full name is Multi-gate Mixture-of-Experts, For multiple optimization tasks , Several experts are introduced to make different decisions and combinations , Finally complete the multi-objective prediction . The solution is hard sharing. If the similarity of multiple tasks is not very strong , At the bottom embedding Instead, learning affects each other , Finally, the pain points of learning well .
2.1 The background of the birth of the model
Synthesize the previous 0.4 and 1.2.2, Three paradigms of multitasking model can be summarized :
- hard parameter sharing
The biggest advantage of this method is Task The more , Single task is more impossible to over fit , That is, it can reduce the risk of over fitting between tasks . But the disadvantages are also very obvious , It's mandatory at the bottom shared layers It is difficult to learn effective expressions for all tasks . Especially when there is conflict between tasks . - soft parameter sharing
In multi task learning , To different tower Assign different weights , So for different tasks , It can allow the use of different combinations of experts at the bottom to make predictions , Compared with the above, all tasks share the bottom , This method is more flexible - Task sequence dependency modeling
MMOE One of the motives for proposing , It's about dealing with hard parameter sharing A question of : Can't weigh the conflict relationship between the goal of a specific task and the task well .
2.2 MMOE Theory and details of the model
The model structure is as follows :
2.2.1 Hybrid expert model MOE
First of all, let's talk about MOE, The one in the middle of the corresponding structure diagram .
The conventional hard parameter sharing It can be regarded as a shared expert , Tasks may not converge well , You can't train a good expert . that , How about multiple experts ?
Put aside the task relationship , We found that an expert's expressive ability in multitasking learning is very limited , So , Try to bring in multiple experts , This slowly evolved into a hybrid expert model .
MMOE The first feature of the model is : Hybrid expert model
The formula is as follows
y = ∑ i = 1 n g ( x ) i f i ( x ) y= \sum_{i=1}^{n}{g(x)_i f_i(x)} y=i=1∑ng(x)ifi(x)
among
f i ( x ) f_i(x) fi(x)
It is the output of every expert
On this basis, a gating network mechanism is added , Attention network , To learn the weight of each expert ∑ i = 1 n g ( x ) i \sum_{i=1}^{n}g(x)_i i=1∑ng(x)i
Although I feel this thing , It is nothing more than the introduction of several fully connected networks on the basis of a single expert , Then weight these fully connected networks , But it contains several powerful ideas .
- Model integration idea : This thing is very similar bagging The idea of , That is, train multiple models to make decisions , The effectiveness of this decision is obviously a little more reliable than a single model , Whether from generalization ability , Presentation skills , Learning ability , Should be stronger than a model
- Attention, thought : To increase flexibility , Importance weights are also learned for different models , This may take into account the common pattern of learning tasks , Different models have different learning modes , So when you aggregate , Obviously, it cannot be aggregated according to the same importance , So learn the weight for each expert , By default, different experts have different decision-making positions . At present, this idea is also very common .
- multi-head Mechanism : Look at it from another Angle , Many experts actually represent many different head, And different head Represent different nonlinear spaces , The reason to say that the expression ability has been enhanced , Because the input features are mapped into different spaces to learn the common patterns between tasks . It can be understood as capturing the common feature patterns between tasks from multiple angles .
reflection : The understanding of the tutorial is actually quite interesting , But it's the same as what I saw before Collection | On multi task learning (Multi-task Learning) The understanding of the , In fact, this may be the embodiment of attention thought , But it can't be called attention mechanism , Attention mechanism pays more attention to an implementation process (query The design of the )?
Only this and nothing more , Namely MOE, Hybrid expert model , however MOE Contains only one gating , A gating is not very flexible .
Because all these tasks , Finally, only one group of experts can be selected , That is, this expert group is the result of comprehensive measurement on multiple tasks , There is no pertinence . If these tasks are similar , That's equivalent to using this group of experts to deal with these multiple tasks , Learn the commonness of multiple similar tasks . But if there is a big difference between tasks , This single door control method is not good , Because at this time, the feature patterns learned by multiple experts at the bottom may differ greatly , After all, the task is different , When choosing expert combination for single gating mechanism , It must be the choice of experts who are conducive to most tasks , For some special tasks , May study in a mess .
The feeling here can still be understood as the difference between true multi-target and pseudo multi-target .
2.2.2 MMOE structure
Multi-gate Mixture-of-Experts(MMOE) stay MOE On the basis of , For each task, a gating network is involved , Corresponding to the one on the right of the structure diagram .
such , For each specific task , Can have a corresponding group of experts to predict . More to the point , The parameter quantity will not increase too much . The formula is as follows :
y k = h k ( f k ( x ) ) y_k = h^k (f ^k(x)) yk=hk(fk(x))
among
f k ( x ) = ∑ i = 1 n g k ( x ) i f i ( x ) f ^k(x)= \sum_{i=1}^{n}{g^k(x)_i f_i(x)} fk(x)=i=1∑ngk(x)ifi(x)
k k k Indicates the number of tasks .
Every gated network is an attention network :
g k ( x ) = s o f t m a x ( W g k x ) g^k(x) = softmax(W_{gk}x) gk(x)=softmax(Wgkx)
W g k W_{gk} Wgk Represent the weight matrix , n n n It's the number of experts , d d d It's the dimension of the feature .
The tutorial shares some understanding
- MMOE There is a separate gating selection expert group for each task , So even if the task conflicts , It can also be adjusted according to different door controls , Select a group of experts that are helpful for the current task . therefore , I think the single door control has achieved Decoupling of expert selection for all tasks , And multi gating has done Decoupling of expert portfolio selection for each task .
- Multi gated mechanism can model the relationship between tasks . If all tasks conflict , At this time, how much gating can help , At this time, let each task have an expert , If tasks can be grouped into several similar classes , Then there should be different expert groups corresponding to these categories , Then the gating mechanism can also be selected . If all tasks are similar , The weights learned by these gating networks will also be similar , So this mechanism makes the task irrelevant , Partial correlation and full correlation are unified .
- Flexible parameter sharing , This we can do with hard Patterns or model comparisons that are modeled separately for each task , about hard Pattern , All tasks share the underlying parameters , Each task is modeled separately , All tasks have a separate set of parameters , It's the two extremes of sharing and not sharing , For the extreme of sharing , Fear of task conflict , And for the extreme of not sharing at all , Unable to take advantage of transfer learning , There is no way to share information between models , Complement each other , Easy to suffer from the dilemma of fitting , In addition, the amount of calculation and parameters will be increased . and MMOE In the middle of the two , Both take into account if there are similar tasks , Then parameter sharing , Mode sharing , Complement each other , If there is no similar task , Then study independently , They don't influence each other . These two extremes are unified .
- It can converge quickly during training , This is because similar tasks contribute to specific expert group training , Go through a round like this epoch, It is equivalent to multiple rounds of single task training epoch.
Understanding seems a little detour , In fact, it may indeed be a simple idea , Multi task requires model decoupling , Introduce single door control experts , Multitasking requires expert decoupling , Just more gating experts . This makes multitasking flexible , Solve similar problems together . Experts are responsible for problem commonality learning , Gate control determines whether it is common ?
Why is multitasking effective ? Here is a good answer :
The reason why multi task learning is effective is the introduction of inductive bias , Two effects :
- Promote each other : The relationship between multi task models can be regarded as mutual prior knowledge , Also known as inductive transfer , With a priori assumption of the model , It can better improve the effect of the model . Solving data sparsity is also a feature of transfer learning , Multi task learning will also reflect
- Generalization : Different models learn different representations , Probably A What the model learned is B What the model didn't learn well ,B The model also has its own characteristics , And this is likely A Learning is not good , In this way, the model is more robust
This little card reviews the previous 0.3 What's in it, huh .
2.3 Code implementation
2.3.1 be based on torch.nn Of MMOE Reappear
Implementation involves several key points :
- Model input :sparse feature and dense feature Data encapsulation is processed together
- Multi expert : All are DNN
- Multi gated network : The number of gating networks is the same as the number of tasks , Gating network is also DNN, Receives input , Get experts' outputs as the weight of each expert , The output of each expert is weighted and combined to obtain the final output of the gated network , Put it in the list as input for the next step
- feature Study ( After all, it is a sort model ): Create for each task tower, Learn specific feature Information . also DNN; Finally get the final output .
The specific code is as follows :
def MMOE(dnn_feature_columns, num_experts=3, expert_dnn_hidden_units=(256, 128), tower_dnn_hidden_units=(64,),
gate_dnn_hidden_units=(), l2_reg_embedding=0.00001, l2_reg_dnn=0, dnn_dropout=0, dnn_activation='relu',
dnn_use_bn=False, task_types=('binary', 'binary'), task_names=('ctr', 'ctcvr')):
num_tasks = len(task_names)
# structure Input Layer and place Input The layer is converted into a list as input to the model
input_layer_dict = build_input_layers(dnn_feature_columns)
input_layers = list(input_layer_dict.values())
# Filter out... In the feature sparse and Dense features , It will be handled separately later
sparse_feature_columns = list(filter(lambda x: isinstance(x, SparseFeat), dnn_feature_columns))
dense_feature_columns = list(filter(lambda x: isinstance(x, DenseFeat), dnn_feature_columns))
# obtain Dense Input
dnn_dense_input = []
for fc in dense_feature_columns:
dnn_dense_input.append(input_layer_dict[fc.name])
# structure embedding Dictionaries
embedding_layer_dict = build_embedding_layers(dnn_feature_columns)
# These discrete features embedding after , Then joining together , Then directly as the full connection layer Dense The input of , So we need to do Flatten
dnn_sparse_embed_input = concat_embedding_list(sparse_feature_columns, input_layer_dict, embedding_layer_dict, flatten=False)
# Combine continuous features and discrete features
dnn_input = combined_dnn_input(dnn_sparse_embed_input, dnn_dense_input)
# Establish expert level
expert_outputs = []
for i in range(num_experts):
expert_network = DNN(expert_dnn_hidden_units, dnn_activation, l2_reg_dnn, dnn_dropout, dnn_use_bn, seed=2022, name='expert_'+str(i))(dnn_input)
expert_outputs.append(expert_network)
expert_concat = Lambda(lambda x: tf.stack(x, axis=1))(expert_outputs)
# Establish a multi gated mechanism layer
mmoe_outputs = []
for i in range(num_tasks): # num_tasks=num_gates
# Establish gating layer
gate_input = DNN(gate_dnn_hidden_units, dnn_activation, l2_reg_dnn, dnn_dropout, dnn_use_bn, seed=2022, name='gate_'+task_names[i])(dnn_input)
gate_out = Dense(num_experts, use_bias=False, activation='softmax', name='gate_softmax_'+task_names[i])(gate_input)
gate_out = Lambda(lambda x: tf.expand_dims(x, axis=-1))(gate_out)
# gate multiply the expert
gate_mul_expert = Lambda(lambda x: reduce_sum(x[0] * x[1], axis=1, keep_dims=False), name='gate_mul_expert_'+task_names[i])([expert_concat, gate_out])
mmoe_outputs.append(gate_mul_expert)
# Each task is independent tower
task_outputs = []
for task_type, task_name, mmoe_out in zip(task_types, task_names, mmoe_outputs):
# establish tower
tower_output = DNN(tower_dnn_hidden_units, dnn_activation, l2_reg_dnn, dnn_dropout, dnn_use_bn, seed=2022, name='tower_'+task_name)(mmoe_out)
logit = Dense(1, use_bias=False, activation=None)(tower_output)
output = PredictionLayer(task_type, name=task_name)(logit)
task_outputs.append(output)
model = Model(inputs=input_layers, outputs=task_outputs)
return model
2.3.2 be based on rechub The implementation of the
See github.
Training MMOE Model process and ESMM The model is very similar
It should be noted that MMOE The model also supports dense and sparse Features as input , And support the mixing of classification and regression tasks .
from torch_rechub.models.multi_task import MMOE
# Defining models
used_cols = sparse_cols + dense_cols
features = [SparseFeature(col, data[col].max()+1, embed_dim=4)for col in sparse_cols] \
+ [DenseFeature(col) for col in dense_cols]
model = MMOE(features, task_types, 8, expert_params={
"dims": [16]}, tower_params_list=[{
"dims": [8]}, {
"dims": [8]}])
# structure dataloader
label_cols = ['cvr_label', 'ctr_label']
x_train, y_train = {
name: data[name].values[:train_idx] for name in used_cols}, data[label_cols].values[:train_idx]
x_val, y_val = {
name: data[name].values[train_idx:val_idx] for name in used_cols}, data[label_cols].values[train_idx:val_idx]
x_test, y_test = {
name: data[name].values[val_idx:] for name in used_cols}, data[label_cols].values[val_idx:]
dg = DataGenerator(x_train, y_train)
train_dataloader, val_dataloader, test_dataloader = dg.generate_dataloader(x_val=x_val, y_val=y_val,
x_test=x_test, y_test=y_test, batch_size=1024)
# Training model and evaluation
mtl_trainer = MTLTrainer(model, task_types=task_types, optimizer_params={
"lr": learning_rate, "weight_decay": weight_decay}, n_epoch=epoch, earlystop_patience=30, device=device, model_path=save_dir)
mtl_trainer.fit(train_dataloader, val_dataloader)
auc = mtl_trainer.evaluate(mtl_trainer.model, test_dataloader)
3 summary
Multi task learning is a development of sequencing model , Born in the background of multitasking .
Practice shows , Multi task joint modeling can effectively improve the model effect , Because it can :
- Task assistance
- Achieve implicit data enhancement
- Learn common expressions , Improve the generalization ability ( Especially for some tasks with insufficient data )
- Regularization ( For a task , The learning of other tasks has regularization effect on this task )
At present, there are three main forms of multi task joint modeling :
- hard parameter sharing
- soft parameter sharing :MMOE It belongs to this category
- Task sequence dependency modeling :ESMM It belongs to this category
This study involves two models :
- ESMM
ESMM Considering the traditional CVR problem ( Conversion rate ) The problem is : Sample selection bias and Sparse data Two questions , Import task (CTR) To enrich the main task CVR The data of , At the same time, introduce tasks (CVCTR) And CTR And the main task CVR Form Bayesian probability relation .
Thus, the problem of sparse samples is improved ( By introducing data rich CTR), It also improves the problem of sample selection deviation ( By introducing CVCTR And CTR stay loss Form Bayesian formula , Make the modeling fall into the whole exposure space ).
On the concrete implementation , Use two networks , A set of main learning tasks CVR, A set of learning CTR, Finally, Loss To deal with ,Loss by pCTR And by pCTR And pCVR Calculated pCVCTR The linear superposition of . - MMOE
MMOE Then consider hard parameter sharing Not flexible enough to deal with multitasking , Problems requiring model decoupling , First, introduce gating to pay attention to the task , At the same time, considering that multiple tasks need to be considered separately , Introduce multi gating . Make multi task flexible combination , Solve similar problems together .
On the concrete implementation , By the same several DNN As an expert , The same amount DNN As a door control , Then together as feature Extracted input .
Reference reading
边栏推荐
- Impressive bug summary (continuously updated)
- 比特熊直播间一周年,英雄集结令!邀你来合影!
- JS reverse | m3u8 data decryption of a spring and autumn network
- NOV Schedule for . Net to display and organize appointments and recurring events
- Golang des-cbc
- 自定义 grpc 插件
- 二叉树的链式存储
- 使用set_handler过滤掉特定的SystemC Wraning &Error Message
- 91.(cesium篇)cesium火箭发射模拟
- Machine learning - Data Science Library Day 3 - Notes
猜你喜欢

消息队列之监控退款任务批处理过程

Redis' attack tactics

GID:旷视提出全方位的检测模型知识蒸馏 | CVPR 2021

NOV Schedule for . Net to display and organize appointments and recurring events

被锡膏坑了一把

华为HMS Core携手超图为三维GIS注入新动能

Machine learning - Data Science Library - day two

【datawhale202206】pyTorch推荐系统:多任务学习 ESMM&MMOE

easyexcel的使用

比特熊直播间一周年,英雄集结令!邀你来合影!
随机推荐
C # dependency injection (straight to the point) will be explained as soon as you see the series
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter 7 Entrepreneurial Resource test 3
Extended tree (I) - concept and C implementation
The Missing Semester
自定义 grpc 插件
Computer graduation project asp Net hotel room management system VS development SQLSERVER database web structure c programming computer web page source code project
Mechanism and type of CPU context switch
Explore the contour detection function findcontours() of OpenCV in detail with practical examples, and thoroughly understand the real role and meaning of each parameter and mode
Golang introduces the implementation method of the corresponding configuration file according to the parameters
二叉树的链式存储
easyexcel的使用
Summary of JFrame knowledge points 2
S7-1500plc simulation
Emotion analysis based on IMDB comment data set
【datawhale202206】pyTorch推荐系统:多任务学习 ESMM&MMOE
GID: open vision proposes a comprehensive detection model knowledge distillation | CVPR 2021
Onenet Internet of things platform - mqtt product devices send messages to message queues MQ
Want to ask, is there a discount for opening a securities account? Is it safe to open a mobile account?
Comment Nike a - t - il dominé la première place toute l'année? Voici les derniers résultats financiers.
用实际例子详细探究OpenCV的轮廓检测函数findContours(),彻底搞清每个参数、每种模式的真正作用与含义