当前位置:网站首页>Implementing DDD based on ABP -- aggregation and aggregation root practice
Implementing DDD based on ABP -- aggregation and aggregation root practice
2022-07-26 17:01:00 【A Sheng 1990】
In the following example Repository、Issue、Label、User this 4 An aggregate root , Next, let's say Issue Take aggregation as an example , among Issue Aggregation is by Issue[ Aggregate root ]、Comment[ Entity ]、IssueLabel[ The value object ] Set of components .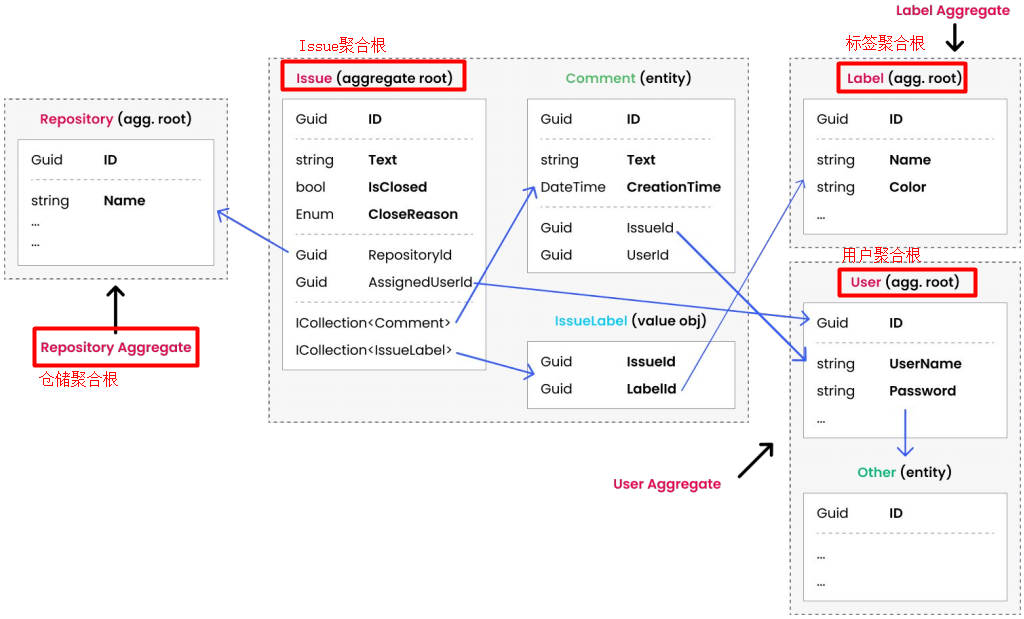
1. The single unit principle
Simple understanding , An aggregation is a collection of entities and value objects , Bind all associated objects together by aggregating roots , An aggregation is a relatively independent business unit . Aggregation and aggregation root principles include : Include business principles , The single unit principle , Transaction boundary principle , Serializability principle . Next, we will focus on the principle of single unit through examples , In essence, it is to implement business rules and maintain data consistency and integrity . such as , Want to Issue Add Comment, The operation is as follows :
- By aggregating roots Issue Load all entities Comments[ A list of comments on the issue ] And the value object IssueLabels[ The label set of the problem ] etc. .
- stay Issue There is a in the class AddComment() Method can add a new Comment.
- The database update operation will Issue polymerization , Including entities and value objects saved to the database .
add to Comment To Issue As shown below :
public class IssueAppService : ApplicationService, IIssueAppService
{
private readonly IRepository<IssueAppService, Guid> _issueRepository;
public IssueAppService(IRepository<Issue, Guid> issueRepository)
{
_issueRepository = issueRepository;
}
[Authorize]
public async Task CreateCommentAsync(CreateCommentInput input)
{
// load Issue Object and contains all subsets
var issue = await _issueRepository.GetAsync(input.IssueId);
// Which user commented on what
issue.AddComment(CurrentUser.GetId(), input.Text);
// Save changes to database , Automatically call after execution DbContext.SaveChanges()
await _issueRepository.UpdateAsync(issue);
}
}
2. Only pass ID Reference other aggregations
Repository and Issue The relationship is one to many , That is, a Repository Corresponding multiple Issue:
public class GitRepository : AggregateRoot<Guid>
{
public string name { get; set; }
public int StarCount { get; set; }
public Collection<Issue> Issues { get; set; } // Wrong practice , You cannot add navigation properties to other aggregation roots
}
public class Issue : AggregateRoot<Guid>
{
public string Text { get; set; }
public GitRepository Repository { get; set; } // Wrong practice , You cannot add navigation properties to other aggregation roots
public Guid RepositoryId { get; set; } // Correct practice
}
3. Aggregate roots should be small enough
Because an aggregate will be loaded and saved as a whole , If the aggregate root is large , When reading and writing a large object, performance problems will be affected .
using Microsoft.VisualBasic;
public class UserRole : ValueObject // The value object
{
public Guid UserId { get; set; }
public Guid RoleId { get; set; }
}
public class Role : AggregateRoot<Guid>
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public Collection<UserRole> Users { get; set; } // Wrong practice , The reason is that the users corresponding to the role are increased
}
public class User : AggregateRoot<Guid>
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public Collection<UserRole> Roles { get; set; } // Correct practice , The reason is that the corresponding roles of users are always limited
}
The official recommendation is that a subset should not contain more than 100-150 Bar record , Otherwise, it is recommended to extract the entity as a new aggregation root .
4. Aggregate root / Primary key in entity
Aggregation roots usually use Guid A primary key , Entities in the aggregation root [ It's not an aggregate root ] You can use composite primary keys .
// Aggregate root : Single primary key
public class Organization
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
// ...
}
// Entity : Composite primary key [ The value object ]
public class OrganizationUser
{
public Guid OrganizationId { get; set; } // Primary key
public Guid UserId { get; set; } // Primary key
public bool IsOwner { get; set; }
// ...
}
Generally, entities in the aggregation root [ It's not an aggregate root ] It is a single primary key , Value objects are basically compound primary keys , such as IssueLabel, Associate through a composite primary key Issue and Label this 2 An aggregate root .
5. Exception handling in business logic and entities
Suppose there is 2 Business principles : The first 1 One is locked Issue Can't reopen , The first 2 You cannot lock a closed Issue:
public class Issue:AggregateRoot<Guid>
{
//...
public bool IsLocked {get;private set;}
public bool IsClosed{get;private set;}
public IssueCloseReason? CloseReason {get;private set;}
public void Close(IssueCloseReason reason)
{
IsClose = true;
CloseReason =reason;
}
public void ReOpen() // Reopen
{
if(IsLocked)
{
throw new IssueStateException(" Can't open ⼀ A locking problem ! Please unlock first !");
}
IsClosed=false;
CloseReason=null;
}
public void Lock() // lock
{
if(!IsClosed)
{
throw new IssueStateException(" Can't lock ⼀ A closing question ! Please open it first !");
}
}
public void Unlock() // Unlock
{
IsLocked = false;
}
}
At this time, you will encounter 2 A question , One is exception message localization , The other is HTTP Status code . adopt ABP Our exception handling system can solve these problems , namely IssueStateException Class inherits from BusinessException class [1]. rewrite ReOpen Method :
public void ReOpen()
{
if (IsLocked)
{
throw new IssueStateException("IssueTracking:CanNotOpenLockedIssue");
}
IsClosed = false;
CloseReason = null;
}
In order to realize localized message processing , Only add in localized resources "IssueTracking:CanNotOpenLockedIssue":" Can't open ⼀ A locking problem ! Please unlock first !" that will do .HTTP The status code is BusinessException Class has been handled , such as 403 Indicates the request to disable ,500 Indicates internal server error, etc .
6. External services are needed for business logic in entities
If the business rule is : A user cannot assign more than 3 An unsolved problem . Then you need a service , according to User Of Id Get the number of outstanding issues that have been allocated . How to implement it in entity classes ? The idea to temporarily solve the problem is to take external dependencies as the parameters of the method :
public class Issue : AggregateRoot<Guid>
{
// ...
public Guid? AssignedUserId { get; private set; } // Set the entity property accessor private , This can only be accessed through methods
// Problem allocation method
// IUserIssueService: Used to get the number of unresolved issues assigned to users
public async Task AssignToAsync(AppUser user, IUserIssueService userIssueService)
{
var openIssueCount = await userIssueService.GetOpenIssueCountAsync(user.Id);
if (openIssueCount >= 3)
{
throw new BusinessException("IssueTracking:CanNotOpenLockedIssue");
}
AssignedUserId = user.Id;
}
// Empty the allocation method
public void CleanAssignment()
{
AssignedUserId = null;
}
}
Although this implementation method meets the business implementation , But entities become complex and difficult to use , On the one hand, entity classes rely on external services , On the other hand, it calls methods AssignToAsync You need to inject dependent external services IUserIssueService As a parameter . A more elegant way to implement this business logic is to introduce domain services .
explain : Aggregation and aggregation root best practices are used for EF Core And relational databases 、 Aggregate root / Entity constructor 、 Entity attribute accessors and methods 3 I won't introduce this part , Interested reference 《 be based on ABP Framework Implement domain-driven design 》[2].
reference :
[1]ABP exception handling :https://docs.abp.io/zh-Hans/abp/latest/Exception-Handling
[2] be based on ABP Framework Implement domain-driven design :https://url39.ctfile.com/f/2501739-616007877-f3e258?p=2096 ( Access password : 2096)
边栏推荐
- 搭建typora图床
- PXE高效批量网络装机
- My SQL is OK. Why is it still so slow? MySQL locking rules
- 浅谈云原生边缘计算框架演进
- Alibaba cloud Toolkit - project one click deployment tool
- Win11 auto delete file setting method
- Digital intelligence transformation, management first | jnpf strives to build a "full life cycle management" platform
- Thinkphp历史漏洞复现
- maximum likelihood estimation
- [ctfshow web] deserialization
猜你喜欢

Vscode batch delete
The difference and efficiency comparison of three methods of C # conversion integer

【飞控开发基础教程1】疯壳·开源编队无人机-GPIO(LED 航情灯、信号灯控制)

How to implement Devops with automation tools | including low code and Devops application practice

Thinkphp历史漏洞复现
It turns out that cappuccino information security association does this. Let's have a look.

限流对比:Sentinel vs Hystrix 到底怎么选?

Operating system migration practice: deploying MySQL database on openeuler

What is a distributed timed task framework?
Win11怎么重新安装系统?
随机推荐
【飞控开发基础教程1】疯壳·开源编队无人机-GPIO(LED 航情灯、信号灯控制)
快速学会配置yum的本地源和网络源,并学会yum的使用
Docker install redis? How to configure persistence policy?
C#读取本地文件夹中所有文件文本内容的方法
C#事件和委托的区别
匿名方法和lambda表达式使用的区别
40个高质量信息管理专业毕设项目分享【源码+论文】(六)
kubernetes之探针
Vlang's way of beating drums
Win11 auto delete file setting method
结构体和类使用的区别
Probe of kubernetes
[fluent -- advanced] packaging
How to implement Devops with automation tools | including low code and Devops application practice
How to ensure cache and database consistency
movable-view 组件(可上下左右拖动 )
How to write unit tests
【开发教程8】疯壳·开源蓝牙心率防水运动手环-三轴计步伐
Use verdaccio to build your own NPM private library
Nacos win10 安装配置教程
