当前位置:网站首页>NLP introduction + practice: Chapter 4: using pytorch to manually realize linear regression
NLP introduction + practice: Chapter 4: using pytorch to manually realize linear regression
2022-07-26 01:06:00 【ZNineSun】
List of articles
Last one : 《nlp introduction + actual combat : The third chapter : Gradient descent and back propagation 》
Code link of this chapter :
- https://gitee.com/ninesuntec/nlp-entry-practice/blob/master/code/4. Use pytorch Complete linear regression .py
- https://gitee.com/ninesuntec/nlp-entry-practice/blob/master/code/4. Manual implementation of linear regression .py
1. Forward calculation
about pytorch One of them tensor, If you set its properties .requires_grad by True, Then it will track all operations for this submission . Or it can be understood as , This tensor It's a parameter , The gradient will be calculated later , Update this parameter .
1.1 The calculation process
Suppose the following conditions (1/4 Mean value ,xi There is 4 Number ), Use torch The process of completing its forward calculation .
o = 1 4 ∑ i z i z i = 3 ( x i + 2 ) 2 o=\frac{1}{4}\sum_{i}z_i\\ z_i=3(x_i+2)^2 o=41i∑zizi=3(xi+2)2
among :
Z i ( x i = 1 ) = 27 Z_i(x_i=1)=27 Zi(xi=1)=27
If x Is the parameter , The gradient needs to be calculated and updated
that , Set randomly at the beginning x The value of , Need to set his requires_grad The attribute is True, The default value is None
import torch
x = torch.ones(2, 2, requires_grad=True) # Initialize parameters x, And set up requires_grad=True Used to track its calculation history
print("x=", x)
y = x + 2
print("y=", y)
z = y * y * 3 # square *3
print("z=", z)
out = z.mean() # Calculating mean
print("out=", out)

As can be seen from the above code :
- 1.x Of requires_grad The attribute is True
- 2. Each subsequent calculation will modify its grad_fn attribute , Used to record operations done
- 1. Through this function and grad_fn It can form a calculation diagram similar to that in the previous chapter
1.2 requires_grade and grad_fn
a = torch.randn(2, 2)
a = ((a * 3) / (a - 1))
print(a.requires_grad)
a.requires_grad_(True) # Modify in place
print(a.requires_grad)
b = (a * a).sum()
print(b.requires_grad)
with torch.no_grad():
c = (a * a).sum()
print(c.requires_grad)
Be careful :
To prevent tracking history ( And using memory ), You can wrap code blocks in with torch.no_grad(): in . Especially useful when evaluating models , Because the model may have requires_grad = True Trainable parameters , But we don't need to calculate the gradient of them in the process .
2. Gradient calculation
about 1.1 Medium out for , We can use backward Method for back propagation , Calculate the gradient out.backward(), Then we can find the derivative d o u t d x \frac{d_{out}}{d_x} dxdout, call x.gard Can get the derivative value
out.backward() # Back propagation
print(" Back propagation :", x.grad) # x.grad Get the gradient

because :
d ( O ) d ( x i ) = 1 4 ∗ 6 ( x i + 2 ) = 3 2 ( x i + 2 ) \frac{d(O)}{d(x_i)}=\frac{1}{4}*6(x_i+2)=\frac{3}{2}(x_i+2) d(xi)d(O)=41∗6(xi+2)=23(xi+2)
stay x i = 1 x_i=1 xi=1 when , Its value is 4.5
Be careful : When the output is a scalar , We can call the output tensor Of backword() Method , But when the data is a vector , call backward() You also need to pass in other parameters .
Many times our loss function is a scalar , So we won't introduce the case where the loss is a vector .
loss.backward() Is based on the loss function , For parameters (requires_grad=True) To calculate his gradient , And put it Cumulative save To x.gard , Its gradient has not been updated at this time , So you need to set the gradient to 0 After that, a new back propagation is carried out .
Be careful :
- 1.tensor.data:
- stay tensor Of require grad=False,tensor.data and tensor Equivalent
- require_grad=True when ,tensor.data Just to get tensor Data in
print(a)
print(a.data)

- 2.tensor.numpy():
- require_grad=True Cannot convert directly , Need to use tensor.detach().numpy(), let me put it another way ,tensor.detach().numpy() Be able to achieve the right tensor Deep copy of data , Turn into ndarray
3. Manually complete the implementation of linear regression
below , We use a custom data , To use torch Implement a simple linear regression
Suppose our basic model is y = wx+b
among w and b All parameters , We use y = 3x+0.8 To construct data x、y, So finally, through the model, we should be able to get w and b Should be close to 3 and 0.8
- 1. Prepare the data
- 2. Calculate the predicted value
- 3. Calculate the loss , Set the gradient of the parameter to 0, Back propagation
- 4. Update parameters
Before completing this section , We need to install a graphical display package :matplotlib
I can go through pip install matplotlib Installation , I was directly in anaconda Installed in , Everyone according to their own needs , No, you can baidu by yourself
import torch
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
learning_rate = 0.01
# 1. Prepare the data y=3x+0.8, Prepare parameters
x = torch.rand([500, 1]) # 1 rank ,50 That's ok 1 Column
y = 3 * x + 0.8
# 2. By model calculation y_predict
w = torch.rand([1, 1], requires_grad=True)
b = torch.tensor(0, requires_grad=True, dtype=torch.float32)
y_predict = x * w + b
# 4. Through the loop , Back propagation , Update parameters
for i in range(50): # Training 3000 Time
# Calculate the predicted value
y_predict = x * w + b
# 3. Calculation loss
loss = (y_predict - y).pow(2).mean()
if w.grad is not None:
w.grad.data.zero_()
if b.grad is not None:
b.grad.data.zero_()
loss.backward() # Back propagation
w.data = w.data - learning_rate * w.grad
b.data = b.data - learning_rate * b.grad
print("w:{},b:{},loss:{}".format(w.item(), b.item(), loss.item()))
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8))
plt.scatter(x.numpy().reshape(-1), y.numpy().reshape(-1)) # Scatter plot
y_predict = x * w + b
# y_predict contain gard, So we need to make a deep copy and then transfer numpy
plt.plot(x.numpy().reshape(-1), y_predict.detach().numpy().reshape(-1),color = "red",linewidth=2,label="predict") # A straight line
plt.show()
Let me explain :numpy().reshape(-1)
z.reshape(-1) or z.reshape(1,-1) Tile the array horizontally
z.reshape(-1)
array([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16])
z.reshape(-1, 1) Tile the array vertically
z.reshape(-1,1)
array([[ 1],
[ 2],
[ 3],
[ 4],
[ 5],
[ 6],
[ 7],
[ 8],
[ 9],
[10],
[11],
[12],
[13],
[14],
[15],
[16]])
Let's set the training times to 50 Time , After running, you can see the deviation between the predicted value and the real value :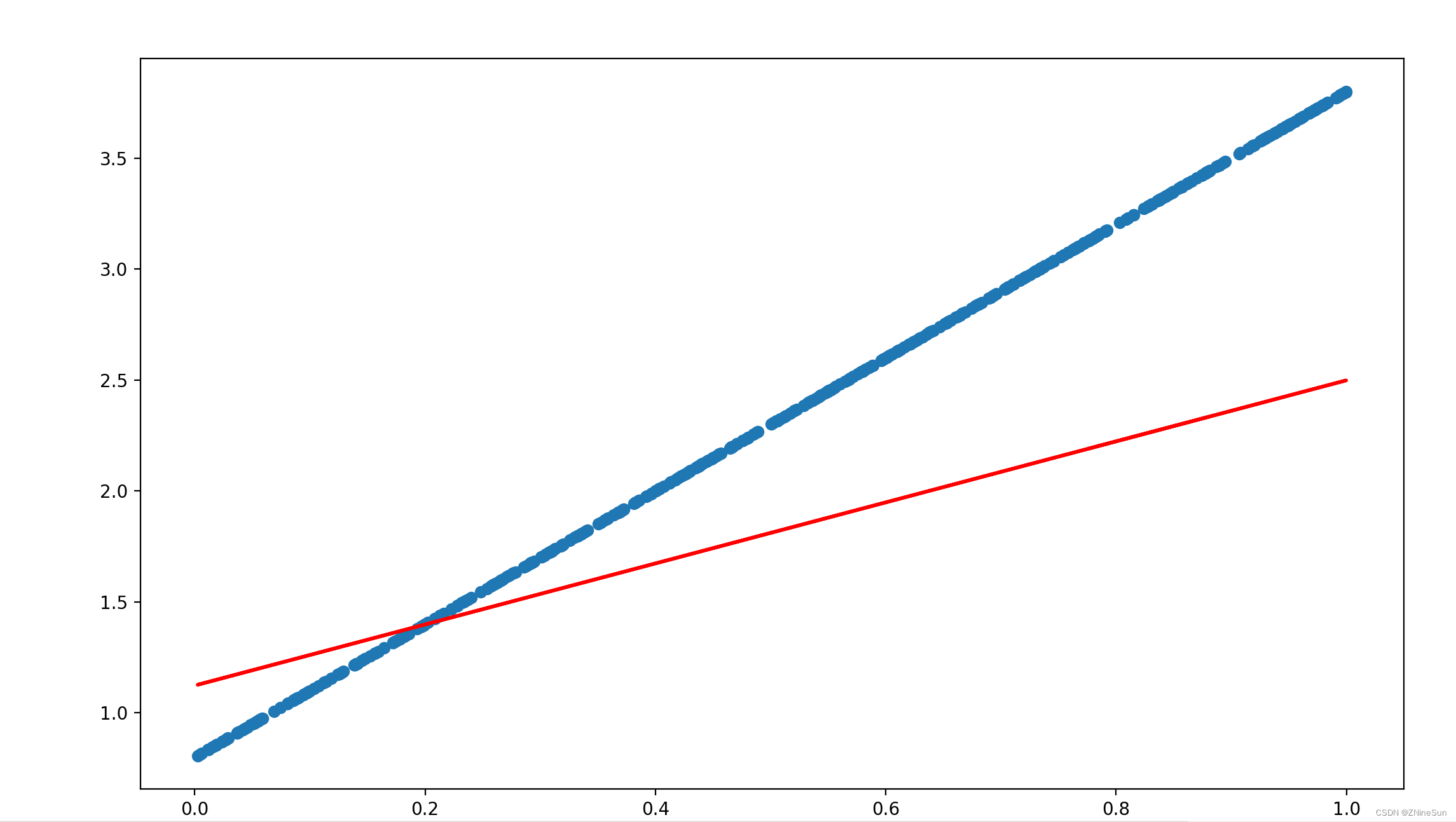
Adjust the training times to 5000 Time , You can see :
It can be seen that the predicted result is basically close to the real value
边栏推荐
- The Chinese input (Pinyin input method) component created by lvgl official +100ask enables lvgl to support Chinese input!
- How to choose social e-commerce model in the early stage? Taishan crowdfunding
- matlab 移位操作基础
- Fundamentals of MATLAB shift operation
- “元气可乐”不是终点,“中国可乐”才是
- 1.30 升级bin文件添加后缀及文件长度
- Detailed explanation of at and crontab commands of RHCE and deployment of Chrony
- Some abnormal error reports and precautions of flowable (1)
- How to switch IP and move bricks with mobile game simulator
- Lock upgrade: no lock, bias lock, lightweight lock, heavyweight lock
猜你喜欢

【RTOS训练营】环形缓冲区、AT指令、预习安排和晚课提问

Half of the people in the country run in Changsha. Where do half of the people in Changsha run?
【Code】剑指offer 03数组中重复的数字

Upload local file trial version using SAP ui5 fileuploader control

C language_ The use and implementation of string comparison function StrCmp

Spine_ Adnexal skin

【RTOS训练营】任务调度(续)、任务礼让、调度总结、队列和晚课提问

【RTOS训练营】程序框架、预习、课后作业和晚课提问
![[Jizhong] July 16, 2022 1432. Oil pipeline](/img/60/55a7e35cd067948598332d08eccfb1.jpg)
[Jizhong] July 16, 2022 1432. Oil pipeline
![[RTOS training camp] task scheduling (Continued), task comity, scheduling summary, queue and evening class questions](/img/0f/ca576a2f90aba4ddbb1f8b3e8a8ced.jpg)
[RTOS training camp] task scheduling (Continued), task comity, scheduling summary, queue and evening class questions
随机推荐
[translation paper] analysis of land cover classification using multi wavelength lidar system (2017)
《nlp入门+实战:第三章:梯度下降和反向传播 》
The Chinese input (Pinyin input method) component created by lvgl official +100ask enables lvgl to support Chinese input!
matlab 移位操作基础
[RTOS training camp] course learning methods and structural knowledge review + linked list knowledge
用 QuestPDF操作生成PDF更快更高效!
代理IP服务器如何保证自身在网络中的信息安全呢
pip install --upgrade can‘t find Rust compiler
Some abnormal error reports and precautions of flowable (1)
【RTOS训练营】作业讲解、队列和环形缓冲区、队列——传输数据、队列——同步任务和晚课提问
Four common simple and effective methods for changing IP addresses
Jupyter changes the main interface and imports the dataset
Sqli-labs Less7
Detailed explanation of at and crontab commands of RHCE and deployment of Chrony
《nlp入门+实战:第四章:使用pytorch手动实现线性回归 》
加载dll失败
[CTF] crypto preliminary basic outline
Fundamentals of MATLAB shift operation
Subarray with 19 and K
[install software after computer reset] software that can search all files of the computer, the best screenshot software in the world, free music player, JDK installation, MySQL installation, installa