当前位置:网站首页>Understand redis persistence mechanism in one article
Understand redis persistence mechanism in one article
2022-07-05 12:17:00 【Xujunsheng】
Article to read Redis Persistence mechanism
In our daily development , Use Redis The common scenario of is to use cache . That is to store the data of the back-end database in memory , Then read data from memory , The response speed will be very fast . And using cache will also reduce the access pressure of the database . But there is also a problem that must not be ignored : Once the server goes down , All the data in memory will be lost .
In order to ensure the persistence of data ,Redis Two persistence schemes are provided :AOF Journal and RDB snapshot . We can according to the actual situation , Flexible configuration in the project .
Let's first take a look AOF journal .
AOF journal
AOF(Append Only File), It records Redis Every order you receive , And save as text .
AOF Related configuration
Redis Not on by default AOF Persistence mode , We can modify it redis.conf File configuration is turned on :
# Turn on aof Mechanism
appendonly yes
# aof file name
appendfilename "appendonly.aof"
# Write strategy Default everysec
# appendfsync always
appendfsync everysec
# appendfsync no
# Automatically override configuration
auto-aof-rewrite-percentage 100
auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 64mb
# Save the directory
dir ./
AOF It's a post log . Follow MySQL My prewrite log (WAL) contrary . Pre writing log refers to , Before actually writing data , First record the modified data to the log file , In order to recover in case of failure . After writing, it means ,Redis Execute the order first , Write data to memory , Then log to disk .
See here , We are going to think about , Why? AOF Execute the order first , Keep a log ?
Redis in order to Avoid additional performance overhead , Again to AOF When recording the log , You won't check the syntax correctness of the command first , Instead, let the system execute the command first , Only after successful execution , This one will be recorded , otherwise , The system will report an error . therefore One of the benefits of post writing diary is , Prevent the problem of wrong commands .
Besides , Another advantage is , Because after the command is executed , To record the log , So it doesn't block the current write operation .
Of course, post writing diary will also bring some risks .
First, first : Data loss . If you finish executing a command , The system went down before I could write a log , At this point, there is a risk of data loss .
secondly ,AOF The log is executed in the main thread , If the log is written to the disk , Disk write pressure is high , It will lead to slow disk writing . We all know ,redis It's single threaded , If the main thread is blocked , As a result, subsequent operations cannot be carried out .
So how to solve these two risks ?
Smart you should find out , These two risks are related to AOF The timing of writing back to disk is related . If we can find a suitable time , Can these two risks be avoided ? Let's keep looking .
AOF Three writeback strategies
stay Redis In the configuration file , There are several configurations :
# appendfsync always
appendfsync everysec
# appendfsync no
- always: Synchronous write back , Each write command is executed , Write the log back to disk immediately and synchronously ;
- everysec: Write back every second ,redis Default writeback policy , That is, each write command is executed , Just write the log first AOF Memory buffer for files , Write the contents of the buffer to disk every second ;
- no: Write back controlled by the operating system , Each write command is executed , Just write the log first AOF Memory buffer for files , It's up to the operating system to decide when to write the contents of the buffer back to disk .
Let's come. Summarize these three strategies :
- always: This strategy is safe , It can basically do not lose data , But after each command is written, there is an operation to drop the disk , So it has the greatest impact on the system ;
- no: This strategy is the least secure , Because the time to fall is not redis In the hands of , In case of downtime, the corresponding data will be lost ;
- everysec: Avoided
always StrategyPerformance overhead , Also reduced.no StrategyRisk of loss , At most... May be lost 1s The data of , It is a compromise between the two .
How should we choose the three strategies ?
- If you want the high performance of the system, choose no Strategy ;
- If you want high reliability, choose always Strategy ;
- If the two are compatible, only everysec Strategy .
Be careful , There is no end here . Although we chose the writeback strategy according to the requirements of the system , however AOF It records the received commands in the form of files , Now As the number of write commands increases ,AOF The size of the file will become larger and larger .
If AOF Too big , When adding commands to it , Efficiency will be reduced . And in case of downtime , use AOF The speed of recovery will also be very slow .
To avoid this problem , Let's move on AOF The rewriting mechanism of .
AOF Rewrite mechanism
Simply put, it is based on the original AOF file , Recreate a new AOF file , It's just this new AOF The file is smaller than the original .
that Redis How to make the file smaller ?
original ,Redis The rewriting mechanism of has Changeable one The function of , That is, check the key value pairs of the database , Record the final status of the key value pair , So as to achieve The effect of compressing multiple commands generated by multiple operations on a key value pair into one .
We know ,AOF The document is in the form of appending , Record the received command . When modifying a key value pair repeatedly , Multiple commands will be recorded . However, in When rewriting, it only records the current latest state , In this way, we can achieve changeability .
See this , You may have asked , since redis It's single threaded , It needs to execute the write command , At the same time, the logs should be synchronized to the disk , Here comes another rewriting mechanism , But its response speed is still very fast , What the hell is going on ?
Redis To avoid blocking the main thread , Cause database performance degradation . A child thread will be created —bgrewriteaof, The rewriting process is completed by the sub thread .
Rewrite process :
- First , The main thread fork Out
bgrewriteaofSub thread ; At the same time, it will also copy the memory of the main thread tobgrewriteaofSub thread , The copy here refers to that the child process copies the page table of the parent process , At this point, the child thread can share and access the memory data of the parent process ; - then , The sub thread can record the new content Rewrite log 了 ; Be careful , Is to rewrite the log !!!
- For new operation commands , Continue parent thread processing ,redis This operation will be recorded to the in use AOF Log buffer , In this way, you don't have to worry about downtime . Again , A copy will also be recorded in the buffer of the rewrite log ;
- When the child thread finishes rewriting , These new operations in the buffer will also be recorded AOF file . here , We can use the new AOF The document replaced the old one .
Rewrite the trigger timing :
- Manual trigger : Send manually
bgrewriteaofInstructions - Automatic triggering : Two configuration parameters are involved , Only AOF When the file size exceeds both of the following configuration items , Will trigger AOF rewrite :
auto-aof-rewrite-min-size:AOF The minimum size of the file when rewriting , The default is 64MB;auto-aof-rewrite-percentage: Rewrite percentage , At present AOF The file was rewritten last time AOF The incremental size of the file , And after the last rewrite AOF The ratio of file size .
Come here AOF The log is basically finished , Next, let's move on to another persistence method : memory dump .
RDB
RDB(Redis DataBase) memory dump , yes redis Default persistence method . The concrete is Save the memory data at a certain time to the disk in the form of a file .
Please note that , Here is Data is saved !!! It's not an operation . therefore , At the time of data recovery , We can just RDB File read into memory , Fast recovery .
RDB Related configuration
# Frequency of backup :900 Snapshot if at least one key is changed within seconds
save 900 1
save 300 10
save 60 10000
# After snapshot creation error , Whether to continue to execute the write command
stop-writes-on-bgsave-error yes
# Whether to compress the snapshot file
rdbcompression yes
# File name
dbfilename dump.rdb
# File save location
dir ./
RDB Persistence process
The first thing we need to confirm is , When we snapshot the memory data , Do is Full snapshot , Because our data is in memory , To ensure reliability , You must record all the data in memory to disk .
Redis We are provided with two commands to create snapshots : Namely save and bgsave.
- save : Execute... In the main thread , It can cause congestion ;
- bgsave:bgsave Orders will fork A subprocess , Specifically for writing RDB file , It avoids the blocking of the main thread , This is also redis RDB File generated The default configuration .
This is the time , We can go through bgsave Command to execute a full snapshot , This ensures the reliability of the data , At the same time, it also avoids the right redis Performance impact .
Next , We need to pay attention to one problem . When taking a snapshot of memory data , Can these data be modified ?
If it can be modified , signify Redis It can also handle write operations normally , Otherwise , You can't execute until all snapshots are written , This can greatly degrade performance .
Here we give the answer first : When taking a snapshot of memory , These data can certainly be modified .
RDB use When writing copy (COW,copy on write) Strategy . While executing the snapshot , Normal processing of write operations .
Simply speaking ,Redis Will be called on persistence glibc Function of fork, Generate a subprocess , Snapshot persistence is now left to the child process , The parent process continues to process client requests .
When the subprocess is doing persistence , The existing memory data structure will not be modified , It just does traversal reading , Then serialization is written to disk . But the parent process is different , It must continue to accept client requests , Then modify the memory data structure .
As shown in the figure below : If the main thread reads data , that , The main thread and child processes do not affect each other . If the main thread wants to modify a piece of data , Then this data will be copied , Make a copy of the data . Then the main thread modifies the copy .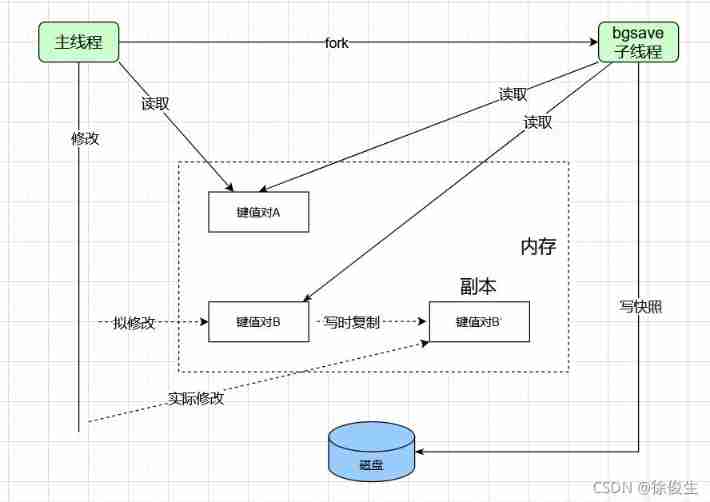
This ensures the integrity of the snapshot , It also allows the main thread to modify the data at the same time , Avoid the impact on normal business .
Frequency of snapshots
In order to improve the reliability of the system , Prevent data loss caused by downtime , We certainly hope that the shorter the snapshot time, the better . We might think , adopt bgsave Sub threads to execute snapshots , This will not block the main thread , At the same time, data loss should be minimized . But is this really perfect ?
The answer is No . although bgsave Execution does not block the main thread , But if Frequent execution of full snapshots also has two costs :
- Write full data to disk frequently , Will give disk There's a lot of pressure ;
- bgsave Child processes need to pass through fork Operations are created from the main thread , Although the child process will not block the main thread after it is created , But in fork It will block the main thread itself , If called frequently fork Create child process , The main thread will be blocked frequently .
So how do we deal with it ?
here , We can do incremental snapshots , That is to say , After taking a full snapshot , The subsequent snapshot records only the modified data , This avoids the overhead of every full snapshot .
however , The premise is , We need to remember which data has been modified . There's an extra cost of space .
Comparison of two persistence methods
AOF Operation commands are recorded every time , Generally, the amount of data that needs to be persisted is small . As long as it is not set always The way , It won't have much impact on performance . But in data recovery , You need to execute all the commands . If there are many operation logs ,redis The speed of recovery will be very slow , May affect normal use .
and RDB Snapshots make up for this , It records data every time ,redis When the fault recovers, the speed will be very fast . however ,RDB The problem is , The frequency of snapshot execution is difficult to control , If the frequency is too fast, it will affect the performance of the system , If the frequency is too slow, more data will be lost .
that , Is there any way to make use of RDB Fast recovery of , At the same time, it can reduce the loss of data with a small cost ?
Of course. , The following to continue Redis 4.0 Mix persistence .
Mix persistence
Mix persistence , Will be RDB The content of the file and the incremental AOF Log files exist together .
Simply speaking , Memory snapshots are performed at a certain frequency , Then between two snapshots , Use AOF Log incremental operations that occur . As shown in the figure below :
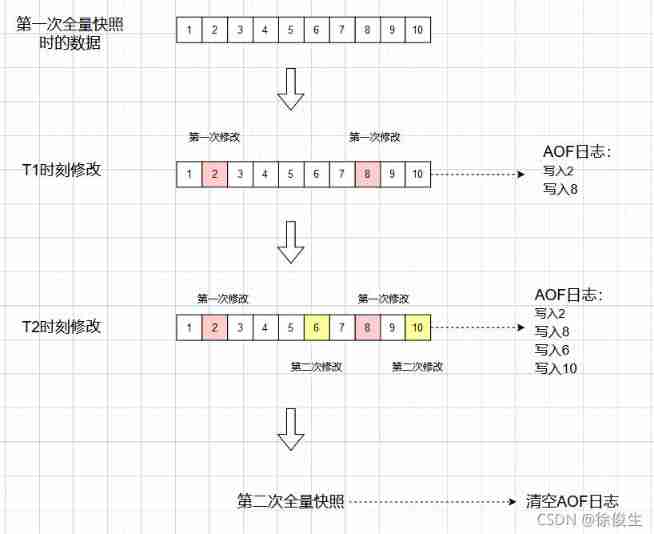
T1 and T2 The change of time , use AOF logging , Wait until the second full snapshot , You can empty AOF journal , Because the changes have been recorded in the snapshot , Log is no longer used when recovering .
This method can enjoy RDB The benefits of fast file recovery , And enjoy it again AOF The simple advantage of recording only operation commands , Improve the efficiency of data recovery , And the reliability of the data .
If you want to see more quality original articles , Welcome to my official account. 「ShawnBlog」.
边栏推荐
- 【ijkplayer】when i compile file “compile-ffmpeg.sh“ ,it show error “No such file or directory“.
- 只是巧合?苹果 iOS16 的神秘技术竟然与中国企业 5 年前产品一致!
- 投资理财适合女生吗?女生可以买哪些理财产品?
- Wireless WiFi learning 8-channel transmitting remote control module
- GPS數據格式轉換[通俗易懂]
- [HDU 2096] 小明A+B
- 手机 CPU 架构类型了解
- Check the debug port information in rancher and do idea remote JVM debug
- Hash tag usage in redis cluster
- 【ijkplayer】when i compile file “compile-ffmpeg.sh“ ,it show error “No such file or directory“.
猜你喜欢
Embedded software architecture design - message interaction
调查显示传统数据安全工具在60%情况下无法抵御勒索软件攻击
Pytorch MLP
1 plug-in to handle advertisements in web pages
![[loss functions of L1, L2 and smooth L1]](/img/c6/27eab1175766b77d4f030b691670c0.png)
[loss functions of L1, L2 and smooth L1]

Matlab struct function (structure array)
abap查表程序

Pytorch weight decay and dropout

July Huaqing learning-1
Wireless WiFi learning 8-channel transmitting remote control module
随机推荐
Recyclerview paging slide
A new WiFi option for smart home -- the application of simplewifi in wireless smart home
HiEngine:可媲美本地的云原生内存数据库引擎
自动化测试生命周期
【ijkplayer】when i compile file “compile-ffmpeg.sh“ ,it show error “No such file or directory“.
嵌入式软件架构设计-消息交互
互联网公司实习岗位选择与简易版职业发展规划
Learn memory management of JVM 01 - first memory
SENT协议译码的深入探讨
Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2)
7月华清学习-1
II. Data type
MySQL index - extended data
MySQL basic operation -dql
Is investment and finance suitable for girls? What financial products can girls buy?
PXE startup configuration and principle
Application of a class of identities (vandermond convolution and hypergeometric functions)
Hiengine: comparable to the local cloud native memory database engine
What is the difference between canvas and SVG?
1 plug-in to handle advertisements in web pages
