当前位置:网站首页>Interview questions for famous enterprises: Coins represent a given value
Interview questions for famous enterprises: Coins represent a given value
2022-07-05 22:03:00 【Advanced Xiaoxin】
subject :
Yes 1 branch ,5 branch ,10 branch ,25 There are four kinds of coins , The number of each coin is unlimited , Given n Cents , Ask how many combinations can be formed n Cents .
Input gives an integer on one line n.
The output is given on one line in several combinations .
Ideas :
It is similar to climbing stairs and robots walking in squares , First list the small-scale situations .
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6 |
1,2,3,4 There is only one way to spend money , To 5 Money sharing , You can consider whether to use 5 Coins with fractional values , Used is 1 Kind of , Don't go up for 1 Kind of .6,7,8,9 Money is like this .
To 10 Money sharing , Consider whether to use 10 Coins of face value , Use as 1 Kind of , Don't go up for 1 Kind of , The situation of not using can be divided into using 5 The situation of denomination coins and no need to use 5 Coin denomination . As shown in the figure below :
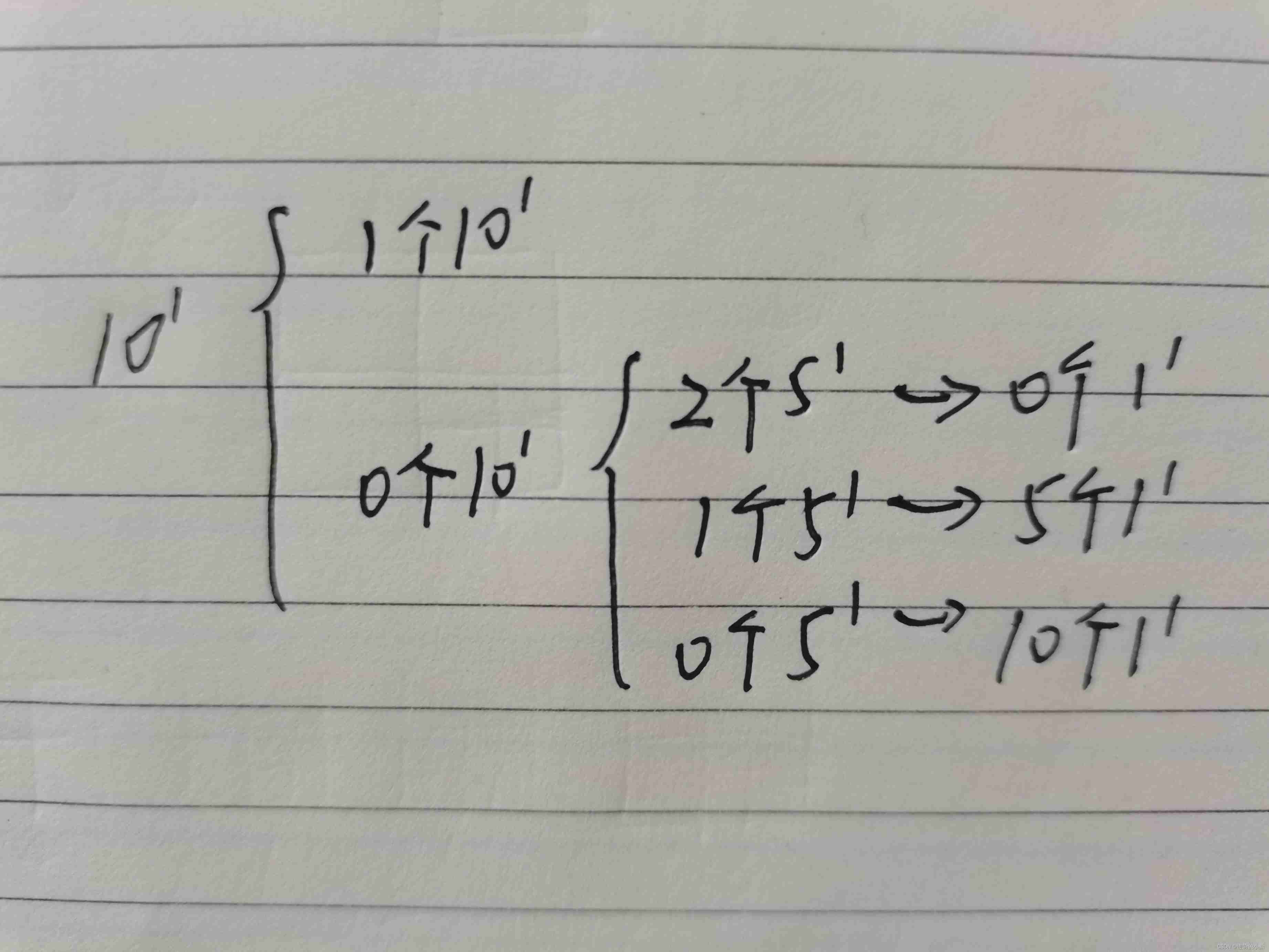
11,12,13,14 Points are also considered in this way .
To 15 time-sharing , Also consider whether to use 10 Coins with fractional values , Then consider whether to use 5 Coins with fractional values , As shown in the figure below :

Briefly summarize the ideas :( Summary is to start thinking in a large-scale to small-scale way )
Consider whether to use the current face value each time , In fact, from the maximum face value 25 Start thinking about , It's just that the above situation doesn't work at all 25 The face value of cents , So I didn't think about it . This is a way of thinking from a large scale ( recursive ). It can be understood as a kind of boss thinking , The boss only considers how many coins are needed for the current denomination , The rest is given to the next small boss , This layer by layer distribution . Finally, each boss summarizes the number of methods in his hand , The final result .
Here's the thing to watch out for , When the boss is considering how many coins of current denomination are needed , There will be many situations , This requires a for Loop to control ( difficulty ).
I know the train of thought , So how to design recursion . obviously , The recursively repeated part is the allocation of the boss, that is, recycling . Part of the change is how much money remains to be allocated , And the face value in charge of the current boss . The recursive cut-off condition is to allocate to the lowest boss .
Code up :
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int coins[] = {1,5,10,25};
int countWays(int n,int cur);
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
cout << countWays(n,3);// Start with the maximum face value
return 0;
}
int countWays(int n,int cur) {
if(cur==0) return 1;
int res = 0;// The current boss is only responsible for the number of methods recovered after his own allocation , So to initialize .
for(int i=0;i*coins[cur]<=n;i++) {// With circular control, each boss has several ways
int remain = n-i*coins[cur];
res += countWays(remain,cur-1);// The distribution and withdrawal of the boss
}
return res;
}Next, we still consider whether we can use iterative form , First, analyze those variables , What determining relationships exist . for instance , The robot in the previous question walks in a square , Row and column coordinates are variables , Determine the number of methods in the next step . In this question , In fact, the previous analysis shows , The remaining amount to be allocated before and after the boss is responsible for the face value of the coin is the variable , How many ways to decide the next boss . So you can Total amount in lines , List values Create the following table .
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 9 |
| 25 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 9 |
As needed 20 Example of money , Consider whether to use 10 Penny , use 2 The remaining amount is 0, Use 1 Points and 5 The par value needs to be rounded up 0 Cents , The number of methods is 1( This is why 0 The reason why the column is the starting column ).
use 1 The remaining amount is 10, Use 1 Points and 5 The par value needs to be rounded up 10 Cents , The data in the table itself is recorded from the smallest boss , Accumulate to the next level of the current boss , So you can directly put the upper layer 10 Use the method number corresponding to the money , The number of methods is 3.
Empathy , use 0 individual 10 branch , The remaining 20 branch , Check the last line 20 The corresponding number of methods is 5, Sum to 9.
It's used here 3 The data calculated by the previous little boss , The actual total is different , The number of data needed is different ,( The number of data = Current total current / Face value ), So you still need to use for Cycle control ( difficulty ). The code is as follows :
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int coins[] = {1,5,10,25};
void countWays2(int n);
int dp[4][10005];// The line represents the denomination , The list shows the amount of money that needs to be scraped up
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
countWays2(n);
cout << dp[3][n] << endl;
return 0;
}
void countWays2(int n) {
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
dp[i][0] = 1;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
dp[0][i] = 1;
for(int i=1;i<4;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
for(int k=0;k<=j/coins[i];k++)// The amount to be expressed by adding several numbers forward is coins How many times the face value
dp[i][j] += dp[i-1][j-k*coins[i]];
}Note that this is a small-scale to large-scale way of thinking , After controlling the boundary , Just calculate the number of methods that the current boss can give steadily . The difficulty lies in what variables are used to construct this array and the use of loops .
above ~
边栏推荐
- Huawei game multimedia service calls the method of shielding the voice of the specified player, and the error code 3010 is returned
- datagrid直接编辑保存“设计缺陷”
- Microservice link risk analysis
- Two stage locking protocol for concurrency control
- [Yugong series] go teaching course 003-ide installation and basic use in July 2022
- MMAP learning
- crm创建基于fetch自己的自定义报告
- Database tuning solution
- 科技云报道荣膺全球云计算大会“云鼎奖”2013-2022十周年特别贡献奖
- Official clarification statement of Jihu company
猜你喜欢

Defect detection - Halcon surface scratch detection

数博会精彩回顾 | 彰显科研实力,中创算力荣获数字化影响力企业奖
matlab绘制hsv色轮图

Stored procedures and stored functions
MMAP学习

Database tuning solution

元宇宙中的三大“派系”
Dbeaver executes multiple insert into error processing at the same time
Leetcode simple question: check whether each row and column contain all integers

科技云报道:算力网络,还需跨越几道坎?
随机推荐
CA certificate trampled pit
[Yugong series] go teaching course 003-ide installation and basic use in July 2022
笔记本电脑蓝牙怎么用来连接耳机
Oracle hint understanding
Database tuning solution
How to organize an actual attack and defense drill
MMAP学习
How to develop and introduce applet plug-ins
极狐公司官方澄清声明
微服务链路风险分析
database mirroring
Summary of concurrency control
MMAP
regular expression
Implementing Lmax disruptor queue from scratch (IV) principle analysis of multithreaded producer multiproducersequencer
Tips for using SecureCRT
AD637 usage notes
Scenario interview: ten questions and ten answers about distributed locks
Pl/sql basic syntax
如何向mongoDB中添加新的字段附代码(全)