当前位置:网站首页>[data structure Python description] use hash table to manually implement a dictionary class based on Python interpreter
[data structure Python description] use hash table to manually implement a dictionary class based on Python interpreter
2020-11-08 09:40:00 【I'm sorry.】
List of articles
- One 、 Hash table Introduction
- Two 、 Hash map implementation table
- 3、 ... and 、 The efficiency of hash table for mapping
- Four 、 Hash table implementation mapping test code
In the article 【 data structure Python describe 】 Manually implement a dictionary class using the list in , Yes UnsortedListMap Of 5 There are three main methods for efficiency analysis Later known , The efficiency of mapping using the data structure of list is low , In this paper, we will use hash table as a data structure to realize the mapping , The mapping implemented in this way , Its efficiency is much higher than the former .
One 、 Hash table Introduction
Save the mapping of key value pairs to the implementation through the list The reason why it's inefficient , The reason is that at worst ,__getitem__、__setitem__、__delitem__、__iter__ Methods need to traverse the entire list .
However , Because the list naturally has an index to O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) Time complexity accesses the characteristics of the elements in it , Therefore, we can consider whether the key in the key value pair can be passed through some kind of Switch relationships Converted to the index value of the list , The key value pairs are then stored in the list cell identified by the index .
actually , The special list described above is Hashtable , The transformation relationship can be regarded as hash function .
1. Introduction to hash function
therefore , hash function h h h The goal is to align the key in each key value pair k k k Convert to [ 0 , N − 1 ] [0, N-1] [0,N−1] An integer in the range h ( k ) h(k) h(k) namely Hash value , among N N N yes Hashtable A A A This special list The capacity of , And the key value is right (k, v) It's stored in A [ h ( k ) ] A[h(k)] A[h(k)] Unit .
When you want to get a key value pair , Just look at k k k Perform the same hash function Get the hash value , Then, we can get the key value pairs at the corresponding units of the hash table by hash value .
2. Introduction to hash collision
It should be noted that , For different keys , If you get the same hash value through the hash function , At this point, the so-called Hash collision , Additional processing of the hash table is required , This kind of extra processing generally reduces the efficiency of the hash table , Specific solutions include Separate link method 、 Open addressing as well as Linear search etc. , It will be introduced in detail later .
3. Hash function delves into
actually , The hash function is usually divided into two parts , namely Hash code and Compression function :
- Hash code Responsible for putting a key k k k Convert to an integer , The integer can even be negative ;
- Compression function Responsible for further conversion of the above integers to [ 0 , N − 1 ] [0, N-1] [0,N−1] An integer in the range .
The advantage of dividing hash function into hash code and compression function is that hash code calculation can be independent of the capacity of hash table ( Just like a regular list , The capacity of hash table needs to be adjusted dynamically according to the number of elements in it ).
thus , We can Any immutable object as a key First, the hash code is calculated in a unified way , Then, the compression function uses the hash code and calculates the hash value corresponding to the key according to the capacity of the hash table .
Hash code
The first part of the hash function first uses any immutable object that is the key k k k Work out an integer , This integer is called Hash code .
Python There is a built-in function specifically used to calculate hash codes hash(x), This function is applied to any object x An integer that can be used as a hash code can be returned , And as this article has always emphasized , stay Python Only immutable types in are hashable .
This limit ensures that the hash code of an object remains unchanged for its life cycle , The hash value of the object remains unchanged throughout its lifetime .
These important properties can avoid such possible anomalies : When a key value pair is inserted into the hash table , The hash value of the key corresponds to a unit in the table ; When getting a key value pair , The hash value of the key may correspond to another cell in the table .
stay Python In all built-in data types , because int、float、str、tuple、 as well as frozenset The objects of are immutable , So these types of objects are hashable ; and list The object of the , about list Instance object of x, perform hash(x) Will throw out TypeError abnormal .
Compression function
generally speaking , key k k k The hash code of the hash table cannot be used as the index reference of the hash table immediately , Because the hash code can be negative , It may even exceed the capacity of the hash table .
therefore , We need a way to map hash codes to [ 0 , N − 1 ] [0, N-1] [0,N−1] A certificate in scope , The way is Compression function . The criterion for evaluating the quality of a compression function is : For a given set of different hash codes , Compression function can minimize the possibility of hash collision .
Here are some typical compression functions :
Modular operation algorithm
A simple compression function is modulus operation algorithm , Take away :
i m o d N i \ mod \ N i mod N
among i i i For Hashima , N N N Is the capacity of the hash table , And in N N N When it is a prime number, the probability of hash collision will be less .
When N N N When it's not prime , The possibility of hash collision will be greatly increased , for example : When the hash code of a set of keys is { 200 , 205 , 210 , 215 , 220 , ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ , 600 } \{200, 205, 210, 215, 220, \cdot\cdot\cdot, 600\} { 200,205,210,215,220,⋅⋅⋅,600}, And the capacity of hash table is 100 when , Then each hash code will be associated with another 3 Hash code collision .
If the compression function is chosen properly , Then the probability of collision between two different hash codes is 1 / N {\left. 1\middle/ N\right.} 1/N.
MAD Method
One disadvantage of the above algorithm is , When the hash code is p N + q pN+q pN+q In the form of , The probability of hash collision is still very high , The so-called MAD(Multiply-Add-and-Divide) The method can improve the problem very well , namely :
[ ( a i + b ) m o d p ] m o d N [(ai+b) \ mod \ p] \ mod \ N [(ai+b) mod p] mod N
among N N N It's still the capacity of the hash table , p p p It's better than N N N Larger prime numbers , and a a a and b b b All are [ 0 , p − 1 ] [0, p-1] [0,p−1] An integer in the range and a > 0 a\gt0 a>0.
4. Handling hash collisions
It can be seen from the above discussion that , The main idea of using hash table to implement mapping to save key value pairs is : Given a hash table table A A A, And a hash function h h h, Implement the key value pair (k, v) Stored in the hash table A [ h ( k ) ] A[h(k)] A[h(k)] unit .
However , The problem lies in : When it comes to two different keys k 1 k_1 k1 and k 2 k_2 k2 Yes h ( k 1 ) = h ( k 2 ) h(k_1)=h(k_2) h(k1)=h(k2), That is, a hash collision occurs , In this case, the key value cannot be simple (k, v) Insert hash table . Again , In search of 、 Delete and other operations need to consider this situation .
therefore , Next, we will introduce several schemes to deal with hash collision :
Separate link method
A simple and efficient way to deal with hash collisions is Separate link method (Separate Chaining), About to satisfy all h ( k ) = j h(k)=j h(k)=j The key/value pair (k, v) Save a secondary container ( Such as : Use the list to save the mapping object implemented by the key value pair ) in , And the unit of the hash table A [ j ] A[j] A[j] Reference the secondary container .
As shown in the figure below , One capacity is 13 The hash table of is saved 10 Key value pairs ( All key value pairs are omitted in the figure ), And the hash function is h ( k ) = k m o d 13 h(k)=k \ mod \ 13 h(k)=k mod 13:
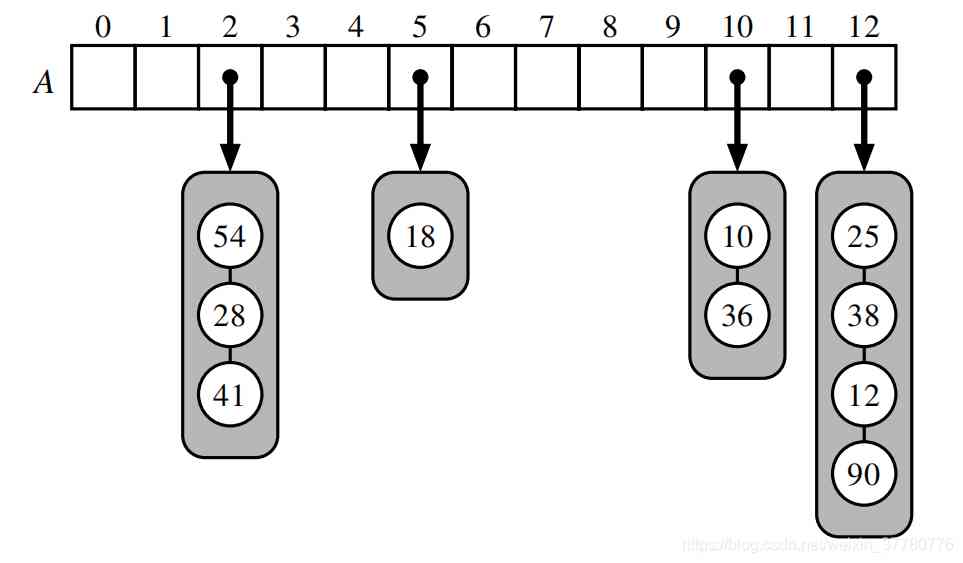
For the above scheme of handling hash collision , For a unit A [ j ] A[j] A[j] When the secondary container referenced is looking up , In the worst case , The time complexity is proportional to the size of the secondary container .
Suppose there is now a hash function that can minimize the probability of hash collisions , The number of key value pairs to be stored is n n n, Hash table capacity is N N N, The capacity of the secondary container referenced at each hash table cell is expected to be n / N {\left. n\middle/ N\right.} n/N.
Based on the above settings , Then mapping __getitem__、__setitem__ as well as __delitem__ The worst-case time complexity of these three core methods is O ( ⌈ n / N ⌉ ) O(\lceil {\left. n\middle/ N\right.} \rceil) O(⌈n/N⌉). Generally will λ = n / N \lambda={\left. n\middle/ N\right.} λ=n/N Recorded as a hash table Load factor . obviously λ \lambda λ It is better to be less than 1, Otherwise, there will be hash collisions , At this time, the expected time complexity of mapping several core methods is O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1).
Linear search
The above-mentioned hash collision resolution of the separation link method is more convenient to implement , But it also has a flaw : A secondary container is required to hold the key value pairs that have hash collisions . This is not good for memory sensitive wearable devices . Here's what we're going to talk about Linear search This ensures that no additional secondary containers are used to avoid hash conflicts :
In the use of Linear search when , When trying to set the key value to (k, v) To hash table A [ j ] A[j] A[j]( among j = h ( k ) j=h(k) j=h(k)) The latter was found to be occupied by the unit insertion , Then try A [ ( j + 1 ) m o d N ] A[(j+1) \ mod \ N] A[(j+1) mod N] unit . If A [ ( j + 1 ) m o d N ] A[(j+1) \ mod \ N] A[(j+1) mod N] If it's still occupied, try A [ ( j + 2 ) m o d N ] A[(j+2) \ mod \ N] A[(j+2) mod N], And so on , Until an empty cell is found in the hash table .
To explain the above process , Suppose the hash table capacity is 11, Keys are integers , The hash function is h ( k ) = k m o d 11 h(k) = k \ mod \ 11 h(k)=k mod 11, So the picture below ( Omit the value in the key value pair ) It indicates that the key inserted in the figure state is 15 The key value for the operation to be tried :
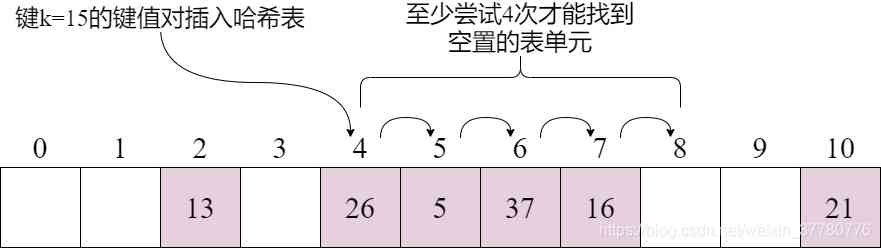
The above strategy makes the three core methods of mapping __getitem__、__setitem__ as well as __delitem__ Special consideration is needed in the first step of implementation .
In particular , When implementing __delitem__ when , We can't simply delete the key value pairs found , for example : If the insert key is 15 After the key value of , If you delete the key, it will be 37 The key/value pair , Then the following key is 15 The search for key value pairs will fail , Because the linear search strategy will start from the index to 4 Start at the unit of , And then to the index 5 It's about , And then it turns out that the index is 6 Unit of is empty . therefore :
- about
__delitem__: After deleting a key value pair at a cell , Reference it to an object used for marking ( It's usuallyobjectExample ); - about
__getitem__: When looking for key value pairs , When you meetobjectThe instance of , Until you find the desired key value pair or empty unit , Or go back to the unit where you started ; - about
__setitem__:
5. Load factor and rehash
Load factor
Load factor λ = n / N \lambda={\left. n\middle/ N\right.} λ=n/N It will greatly affect the efficiency of hash table operation , because :
For the use of Separate link method Hash table dealing with hash collisions , When λ \lambda λ Very close to 1 when , The probability of hash collision will be greatly increased , This will reduce the efficiency of subsequent operations , Therefore, the experiment shows that the load factor of this hash table should satisfy λ < 0.9 \lambda\lt0.9 λ<0.9.
For the use of Linear search Hash table dealing with hash collisions , Experiments show that when λ \lambda λ from 0.5 Getting close to 1 when , Key value pairs will occur at a series of consecutive units in the hash table aggregation , This will also reduce the efficiency of subsequent operations , Therefore, the experiment shows that the load factor of this hash table should satisfy λ < 0.5 \lambda\lt0.5 λ<0.5.
Hash again
In order to keep the load factor of the hash table in a reasonable range , When the key value pair is inserted, the load factor exceeds a certain range , The usual way is to expand the capacity of hash tables to reduce the load factor , Then insert all key value pairs into the expanded hash table again , This process is called Hash again .
actually , Because the hash function is divided into two parts , The first part of the hash table has nothing to do with the capacity of the hash table , So when hashing again, only the final hash value of the computing place is needed through the compression function ( Represents the index of the hash table unit that the key value pair should hold ) that will do .
Two 、 Hash map implementation table
According to the hash function used, we use separate link method or linear search method to deal with hash collision , Here are two mapping classes based on hash table .
1. Based on hash table to implement the mapping base class HashMapBase
Although the two strategies for handling hash collisions are different , But there are still a lot in common between the two , For this reason, we will first Mapping base class MapBase Expand to get HashMapBase, In particular :
- The hash table of key value pairs in the map is represented by a list , In other words, there is
self._tableInstance attributes , And all units are initialized toNone; - The number of key value pairs in the map uses instance properties
self._nTo express ; - If the load factor of the hash table exceeds 0.5, Then multiply the hash table capacity and re hash all key value pairs to the new hash table ;
- A new practical method is defined
_hash_function(), This method is based on Python Built in functionshash()First calculate a hash code , And then use the MAD Method as a compression function .
Extended base class HashMapBase What the subclass implementation is left in is how to represent each unit of the hash table . For the split link method , A unit is a secondary container ( Such as : list 、 Chain list, etc ); For linear search , The meaning of a cell is not necessarily the position represented by an index in the hash table , It is possible that several indexes represent the location .
therefore , there HashMapBase Class assumes that the following methods are Abstract method , It's left to the concrete subclass implementation :
_bucket_getitem(j, k): According to the key k k k Hash value of j j j Search page j j j The key at each unit is k k k The key/value pair , Return the key value pairs found , Otherwise throwKeyErrorabnormal ;_bucket_setitem(j, k, v): According to the key k k k Hash value of j j j Amendment No j j j The key at each unit is k k k The key/value pair , If key k k k If it already exists, modify the existing value , Otherwise, insert a new key value pair and thenself._nAdd one ;_bucket_delitem(j, k): According to the key k k k Hash value of j j j Delete the first j j j The key at each unit is k k k The key value of and will beself._nMinus one , If the key value pair does not existKeyErrorabnormal .
__init__
def __init__(self, cap=11, p=109345121):
""" Create an empty map """
self._table = cap * [None]
self._n = 0
self._prime = p # MAD A large prime number in a compression function that is larger than the capacity of the hash table
self._scale = 1 + randrange(p-1) # MAD The scaling factor in the contraction function a
self._shift = randrange(p) # MAD The load factor in the compression function b
_hash_function
Calculate the hash value according to the following formula :
[ ( a i + b ) m o d p ] m o d N [(ai+b) \ mod \ p] \ mod \ N [(ai+b) mod p] mod N
def _hash_function(self, k):
""" hash function """
return (self._scale * hash(k) + self._shift) % self._prime % len(self._table)
__len__
def __len__(self):
return self._n
__getitem__
def __getitem__(self, k):
j = self._hash_function(k)
return self._bucket_getitem(j, k) # May throw out KeyError abnormal
__setitem__
def __setitem__(self, k, v):
j = self._hash_function(k)
self._bucket_setitem(j, k, v)
if self._n > len(self._table) // 2: # Make sure the load factor is less than 0.5
self._resize(2 * len(self._table) - 1) # Usually 2 * n - 1 Prime number
def _resize(self, cap):
""" Adjust the hash table size to cap"""
old = list(self.items()) # All the key value pairs that exist are obtained by iteration
self._table = cap * [None]
self._n = 0
for k, v in old:
self[k] = v # Re insert the key value pair into the new hash table
It should be noted that ,items() Methods are derived from... In the inheritance chain Mapping class , stay Mapping The return value of this method in the class is ItemsView(self)(self It's a mapping object ).
and ItemsView The initialization method of is directly inherited from MappingView, So the mapping object is used to initialize ItemsView Example , Because its initialization method is :
def __init__(self, mapping):
self._mapping = mapping
therefore ,ItemsView There is an instance property _mapping For mapping instance objects , and ItemsView An instance of is an iterator object , Because of __iter__ Methods use yield (key, self._mapping[key]).
__delitem__
def __delitem__(self, k):
j = self._hash_function(k)
self._bucket_delitem(j, k) # May throw out KeyError abnormal
self._n -= 1
2. Mapping based on split link method ChainHashMap
Let's start with Hash collision is processed based on the split link method Implementation of the mapping class ChainHashMap, The first three methods implemented below use indexes j To access a unit of the hash table , And check whether the unit is empty ( That is to quote None), Only when calling _bucket_setitem And when the cell is empty, it is necessary to make it refer to a secondary container ( Here we use a mapping based on a normal list UnsortedListMap Examples ).
_bucket_getitem(j, k)
def _bucket_getitem(self, j, k):
bucket = self._table[j]
if bucket is None:
raise KeyError('Key Error: ' + repr(k))
return bucket[k]
_bucket_setitem(j, k, v)
It should be noted that , When key k When the corresponding key value pair is first inserted into the map , You need to add one to the number of key value pairs in the map .
def _bucket_setitem(self, j, k, v):
if self._table[j] is None:
self._table[j] = UnsortedListMap() # Make the hash table refer to a secondary container at this unit
oldsize = len(self._table[j])
self._table[j][k] = v
if len(self._table[j]) > oldsize: # k For the new key
self._n += 1
_bucket_delitem(j, k)
def _bucket_delitem(self, j, k):
bucket = self._table[j]
if bucket is None:
raise KeyError('Key Error: ' + repr(k))
del bucket[k]
__iter__()
It should be noted that , A secondary container is referenced at each non empty cell of the mapping object , The secondary container used here is UnsortedListMap, It's an iterator .
def __iter__(self):
for bucket in self._table:
if bucket is not None:
for key in bucket:
yield key
3. Mapping based on the linear search method ProbeHashMap
_is_available(j)
def _is_available(self, j):
""" When the hash table index is j The cell of is empty or the key value pair is deleted , Then return to True"""
return self._table[j] is None or self._table[j] is ProbeHashMap._AVAIL
_find_slot(j, k)
def _find_slot(self, j, k):
""" Search index is j Is there a key at the cell of the hash table for k
The return value of this method is a tuple , And the return situation is as follows :
- When the index is j The key is found at the hash table unit of k, Then return to (True, fisrt_avail);
- When the key is not found in any cell of the hash table k, Then return to (False, j).
"""
first_avail = None
while True:
if self._is_available(j):
if first_avail is None:
first_avail = j
if self._table[j] is None:
return False, first_avail
elif k == self._table[j].key:
return True, j
j = (j + 1) % len(self._table)
_bucket_getitem(j, k)
def _bucket_getitem(self, j, k):
found, s = self._find_slot(j, k)
if not found:
raise KeyError('Key Error: ' + repr(k))
return self._table[s].value
_bucket_setitem(j, k, v)
def _bucket_setitem(self, j, k, v):
found, s = self._find_slot(j, k)
if not found:
self._table[s] = self._Item(k, v)
self._n += 1
else:
self._table[s].value = v
_bucket_delitem(j, k)
def _bucket_delitem(self, j, k):
found, s = self._find_slot(j, k)
if not found:
raise KeyError('Key Error: ' + repr(k))
self._table[s] = ProbeHashMap._AVAIL
__iter__()
def __iter__(self):
for j in range(len(self._table)):
if not self._is_available(j):
yield self._table[j].key
3、 ... and 、 The efficiency of hash table for mapping
| operation | Efficiency based on normal lists | Expected efficiency based on hash table | Worst case efficiency based on hash table |
|---|---|---|---|
__getitem__ |
O ( n ) O(n) O(n) | O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) | O ( n ) O(n) O(n) |
__setitem__ |
O ( n ) O(n) O(n) | O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) | O ( n ) O(n) O(n) |
__delitem__ |
O ( n ) O(n) O(n) | O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) | O ( n ) O(n) O(n) |
__len__ |
O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) | O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) | O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) |
__iter__ |
O ( n ) O(n) O(n) | O ( n ) O(n) O(n) | O ( n ) O(n) O(n) |
Four 、 Hash table implementation mapping test code
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from collections.abc import MutableMapping
from random import randrange
class MapBase(MutableMapping, ABC):
""" Provides a custom mapping base class for storing key value pair record classes """
class _Item:
__slots__ = 'key', 'value'
def __init__(self, key, value):
self.key = key
self.value = value
def __eq__(self, other):
return self.key == other.key # Use '==' Syntax compares two key value pairs for equality based on a key
def __ne__(self, other):
return not (self == other) # Use '!=' Syntax compares whether two key value pairs are unequal based on the key
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.key < other.key # Use '<' Syntax compares two key value pairs based on a key
class UnsortedListMap(MapBase):
def __init__(self):
""" Create an empty mapping object """
self._table = [] # The key value pairs in the map are stored in the list
def __getitem__(self, key):
""" Return and key key The value of the Association value, When key key If it doesn't exist, throw KeyError abnormal """
for item in self._table:
if key == item.key:
return item.value
raise KeyError('key error: ', repr(key))
def __setitem__(self, key, value):
""" take key-value Add to the mapping object , When there is a key value key Replace the value with value"""
for item in self._table: # Traverse whether there is a key in the query map key
if key == item.key:
item.value = value
return
self._table.append(self._Item(key, value)) # There is no key in the map key
def __delitem__(self, key):
""" Delete key key Represents the key value pair , When key key If it doesn't exist, throw KeyError abnormal """
for j in range(len(self._table)): # Traverse whether there is a key in the query map key
if key == self._table[j].key:
self._table.pop(j)
return
raise KeyError('key error: ', repr(key)) # There is no key in the map key
def __len__(self):
""" Returns the number of key value pairs in the map """
return len(self._table)
def __iter__(self):
""" Generate an iteration of all keys in a map """
for item in self._table:
yield item.key
def __str__(self):
""" Returns the string representation of the mapped object """
return str(dict(self.items()))
class HashMapBase(MapBase):
""" Use hash table to implement the base class of mapping """
def __init__(self, cap=11, p=109345121):
""" Create an empty map """
self._table = cap * [None]
self._n = 0
self._prime = p # MAD A large prime number in a compression function that is larger than the capacity of the hash table
self._scale = 1 + randrange(p-1) # MAD The scaling factor in the contraction function a
self._shift = randrange(p) # MAD The cheap coefficient in the contraction function b
def _hash_function(self, k):
""" hash function """
return (self._scale * hash(k) + self._shift) % self._prime % len(self._table)
@abstractmethod
def _bucket_getitem(self, j, k):
pass
@abstractmethod
def _bucket_setitem(self, j, k, v):
pass
@abstractmethod
def _bucket_delitem(self, j, k):
pass
def __len__(self):
return self._n
def __getitem__(self, k):
j = self._hash_function(k)
return self._bucket_getitem(j, k) # May throw out KeyError abnormal
def __setitem__(self, k, v):
j = self._hash_function(k)
self._bucket_setitem(j, k, v)
if self._n > len(self._table) // 2: # Make sure the load factor is less than 0.5
self._resize(2 * len(self._table) - 1) # Usually 2 * n - 1 Prime number
def __delitem__(self, k):
j = self._hash_function(k)
self._bucket_delitem(j, k) # May throw out KeyError abnormal
self._n -= 1
def _resize(self, cap):
""" Adjust the hash table size to cap"""
old = list(self.items()) # All the key value pairs that exist are obtained by iteration
self._table = cap * [None]
self._n = 0
for k, v in old:
self[k] = v # Re insert the key value pair into the new hash table
class ChainHashMap(HashMapBase):
""" Using split link method to deal with hash collision implementation of hash mapping """
def _bucket_getitem(self, j, k):
bucket = self._table[j]
if bucket is None:
raise KeyError('Key Error: ' + repr(k))
return bucket[k]
def _bucket_setitem(self, j, k, v):
if self._table[j] is None:
self._table[j] = UnsortedListMap() # Make the hash table refer to a secondary container at this unit
oldsize = len(self._table[j])
self._table[j][k] = v
if len(self._table[j]) > oldsize: # k For the new key
self._n += 1
def _bucket_delitem(self, j, k):
bucket = self._table[j]
if bucket is None:
raise KeyError('Key Error: ' + repr(k))
del bucket[k]
def __iter__(self):
for bucket in self._table:
if bucket is not None:
for key in bucket:
yield key
class ProbeHashMap(HashMapBase):
""" Using linear search method to deal with hash collision implementation of hash mapping """
_AVAIL = object() # Sentinel sign , Used to identify the hash table unit to be deleted by the key value pair
def _is_available(self, j):
""" When the hash table index is j The cell of is empty or the key value pair is deleted , Then return to True"""
return self._table[j] is None or self._table[j] is ProbeHashMap._AVAIL
def _find_slot(self, j, k):
""" Search index is j Is there a key at the cell of the hash table for k
The return value of this method is a tuple , And the return situation is as follows :
- When the index is j The key is found at the hash table unit of k, Then return to (True, fisrt_avail);
- When the key is not found in any cell of the hash table k, Then return to (False, j).
"""
first_avail = None
while True:
if self._is_available(j):
if first_avail is None:
first_avail = j
if self._table[j] is None:
return False, first_avail
elif k == self._table[j].key:
return True, j
j = (j + 1) % len(self._table)
def _bucket_getitem(self, j, k):
found, s = self._find_slot(j, k)
if not found:
raise KeyError('Key Error: ' + repr(k))
return self._table[s].value
def _bucket_setitem(self, j, k, v):
found, s = self._find_slot(j, k)
if not found:
self._table[s] = self._Item(k, v)
self._n += 1
else:
self._table[s].value = v
def _bucket_delitem(self, j, k):
found, s = self._find_slot(j, k)
if not found:
raise KeyError('Key Error: ' + repr(k))
self._table[s] = ProbeHashMap._AVAIL
def __iter__(self):
for j in range(len(self._table)):
if not self._is_available(j):
yield self._table[j].key
版权声明
本文为[I'm sorry.]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- Julia 是如何风靡起来的?
- What details does C + + improve on the basis of C
- SQL Server 2008R2 18456错误解决方案
- Introduction to ucgui
- Swiper window width changes, page width height changes lead to automatic sliding solution
- Blazor 准备好为企业服务了吗?
- swiper 窗口宽度变化,页面宽度高度变化 导致自动滑动 解决方案
- 来自不同行业领域的50多个对象检测数据集
- Recommend an economic science video, very valuable!
- 比Python快20%,就问你兴不兴奋?
猜你喜欢

解决Safari浏览器下载文件文件名称乱码的问题

Mouse small hand

Face recognition: attack types and anti spoofing techniques

Cloud alibabab notes come out, the whole network detailed explanation only this one hand is slow

分布式共识机制
Template linked list learning

More than 50 object detection datasets from different industries
What? Your computer is too bad? You can handle these moves! (win10 optimization tutorial)

SQL Server 2008R2 18456错误解决方案
![IOS learning note 2 [problems and solutions encountered during the installation and use of cocopods] [update 20160725]](/img/3b/00bc81122d330c9d59909994e61027.jpg)
IOS learning note 2 [problems and solutions encountered during the installation and use of cocopods] [update 20160725]
随机推荐
函数周期表丨筛选丨值丨SELECTEDVALUE - 知乎
The most detailed usage guide for perconaxtradbcluster8.0
【计算机网络】学习笔记,第三篇:数据链路层(谢希仁版)
2020-11-05
Python learning Day1 -- Basic Learning
Littlest JupyterHub| 02 使用nbgitpuller分发共享文件
IOS learning note 2 [problems and solutions encountered during the installation and use of cocopods] [update 20160725]
What? Your computer is too bad? You can handle these moves! (win10 optimization tutorial)
Mate 40 series launch with Huawei sports health service to bring healthy digital life
python_scrapy_房天下
Shiyou's numerical analysis assignment
“智能5G”引领世界,数位智能网优+5G能带来什么?
The difference between vivoy 73s and glory 30 Youth Edition
QT hybrid Python development technology: Python introduction, hybrid process and demo
Rust:命令行参数与环境变量操作
Solve the problem of rabbitmq message loss and repeated consumption
Recommend an economic science video, very valuable!
Is there a big difference between i5 1135g7 and i51035g1? Which is better?
FORTRAN 77 reads some data from the file and uses the heron iteration formula to solve the problem
Blazor 准备好为企业服务了吗?