当前位置:网站首页>[UVM basics] understanding of sequence and sequencer
[UVM basics] understanding of sequence and sequencer
2022-06-26 07:33:00 【ReCclay】
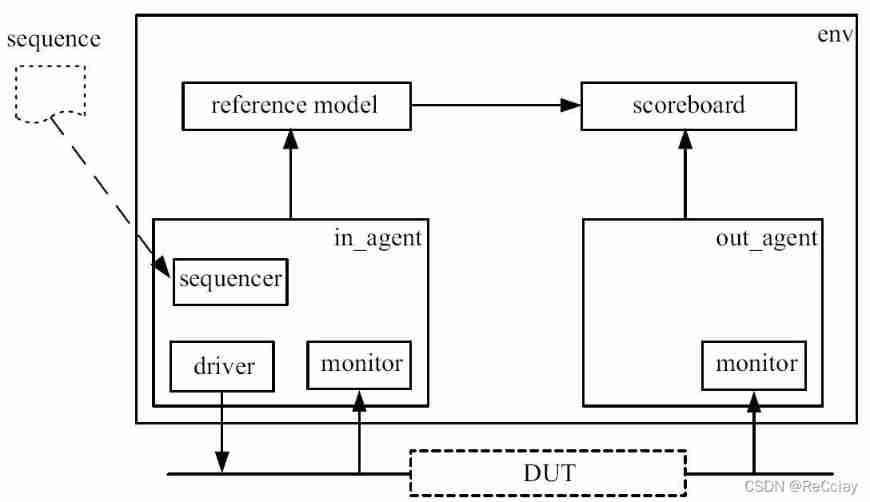
sequence Not part of the validation platform , But it's connected to sequencer There is a close connection between , This can be seen from their names . Only in sequencer With the help of the , sequence Produced transaction To finally give to driver; Again , sequencer Only in sequence The value can only be reflected in the situation , without sequence, sequencer It has little effect .sequence It's like a clip , The bullets inside are transaction, and sequencer It's a gun . The clip only makes sense if it is put in the gun , The gun can only exert its power after it is put into the magazine .
In addition to contact , sequence And sequencer There are also significant differences . essentially , sequencer It's a uvm_component, and sequence It's a uvm_object. And my_transaction equally , sequence It also has its life cycle . Its life cycle is longer than my_transaction A little longer , Inside transaction After all the messages are sent , Its life cycle is over . It's like a clip , There is no meaning when the bullets in it are used up . therefore , One sequence You should use uvm_object_utils Register macros to factory in :
class my_sequence extends uvm_sequence #(my_transaction);
my_transaction m_trans;
function new(string name= "my_sequence");
super.new(name);
endfunction
virtual task body();
repeat (10) begin
`uvm_do(m_trans)
end
#1000;
endtask
`uvm_object_utils(my_sequence)
endclass
every last sequence Should be derived from uvm_sequence, And specify the... To be generated at the time of definition transaction The type of , Here is my_transaction. every last sequence There is one. body Mission , When one sequence After starting , Meeting Automatic execution body The code in . In the example above , A new macro is used :uvm_do. This macro is UVM One of the most commonly used macros in , It is used for :
- ① Create a my_transaction Example m_trans;
- ② Randomize it ;
- ③ Finally give it to sequencer.
If not used uvm_do macro , It can also be used directly start_item And finish_item In a way that produces transaction. But for beginners , Use uvm_do Macro is OK .
One sequence In the sequencer send out transaction front , First of all sequencer Send a request , sequencer Put the request in an arbitration queue . As sequencer, It needs to do two things :
- First of all , Check whether there is a... In the arbitration queue sequence send out transaction Request ;
- second , testing driver Whether to apply for transaction.
1) If there is a send request in the arbitration queue , however driver No application transaction, that sequencer Will always be waiting driver The state of , until driver Apply for a new transaction. here , sequencer agree! sequence Send request for , sequence Get in sequencer After the approval of , Produce a transaction And to sequencer, The latter puts this transaction hand driver.
2) If no request is sent in the arbitration queue , however driver towards sequencer Apply for a new transaction, that sequencer Will be waiting sequence The state of , Until there was sequence Submit send request , sequencer Grant this request immediately , sequence produce transaction And to sequencer, Final driver Get this transaction.
3) If there is a send request in the arbitration queue , meanwhile driver And also to sequencer Apply for a new transaction, Then you will agree to send the request , sequence produce transaction And to sequencer, Final driver Get this transaction.
driver How to talk to sequencer apply transaction Well ? stay uvm_driver There are member variables in seq_item_port, And in the uvm_sequencer There are member variables in seq_item_export, Between the two, a “ passageway ”, Passing through the channel transaction A type is a definition my_sequencer and my_driver When the specified transaction type , Here it is. my_transaction, Yes, of course , There is no need to explicitly specify “ passageway ” The type of , UVM It's done . stay my_agent in , Use connect The function connects the two :
Code list 2-64
file : src/ch2/section2.4/2.4.2/my_agent.sv
function void my_agent::connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.connect_phase(phase);
if (is_active == UVM_ACTIVE) begin
drv.seq_item_port.connect(sqr.seq_item_export); // driver
end
ap = mon.ap;
endfunction
When the two are connected , Can stay driver Pass through get_next_item The task is to sequencer Apply for a new transaction:
Code list 2-65
file : src/ch2/section2.4/2.4.2/my_driver.sv
task my_driver::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
vif.data <= 8'b0;
vif.valid <= 1'b0;
while(!vif.rst_n)
@(posedge vif.clk);
while(1) begin
seq_item_port.get_next_item(req); // driver towards sequencer Apply for a new transaction
drive_one_pkt(req);
seq_item_port.item_done();
end
endtask
In the code above , One of the most striking features is the use of while(1) loop , because driver Only responsible for driving transaction, And not responsible for producing , As long as there is transaction Just drive , So it must be in the form of an infinite loop . This is related to monitor、 reference model and scoreboard It's very similar .
adopt get_next_item The task comes to a new req, And drive it , Call after the drive is completed item_done notice sequencer. Why is there a item_done Well ? When driver Use get_next_item Get one transaction when , sequencer I also keep a copy of the just sent transaction. When there is a sequencer Issued transaction, and driver When you don't get situation , sequencer Will keep this transaction Send it out . that sequencer How do you know driver Whether it has been successfully obtained transaction Well ? If the next call get_next_item front , item_done Called , that sequencer I think driver I've got this transaction, Will take this transaction Delete . In other words , This is actually a handshake mechanism used to increase reliability .
stay sequence in , towards sequencer send out transaction It uses uvm_do macro . When will this macro return ? uvm_do The macro produces a transaction And to sequencer, driver Take this transaction after , uvm_do It does not immediately return to the next execution uvm_do macro , But waiting there , until driver return item_done The signal . here , uvm_do The macro is finished , After returning, execute the next uvm_do, And create new transaction.
In the realization of driver after , The next question is : sequence How to talk to sequencer Send out transaction Well ? It has been defined before sequence, Just need to be somewhere component( Such as my_sequencer、 my_env) Of main_phase Start this sequence that will do . In the my_env For example :
Code list 2-66
file : src/ch2/section2.4/2.4.2/my_env.sv
task my_env::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
my_sequence seq;
phase.raise_objection(this);
seq = my_sequence::type_id::create("seq");
seq.start(i_agt.sqr); //
phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask
First create a my_sequence Example seq, Then call start Mission . start The parameter of the task is sequencer The pointer , If this pointer is not specified , be sequence I don't know what will happen transaction To whom sequencer.
What needs attention here is objection, stay UVM in , objection Usually accompanied by sequence, Usually only in sequence Where they appear, they are brought up and revoked objection. As mentioned earlier , sequence It's a clip , When all the bullets in the magazine are used up , You can end the simulation .
It can also be in sequencer Start in sequence:
Code list 2-67
task my_sequencer::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
my_sequence seq;
phase.raise_objection(this);
seq = my_sequence::type_id::create("seq");
seq.start(this);
phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask
stay sequencer Start in and start in my_env In comparison with , The only difference is seq.start The parameter of becomes this.
in addition , In the code list 2-65 Of the 28 The line is used. get_next_item. Actually , except get_next_item outside , You can also use try_next_item. get_next_item yes Blocking Of , It will wait until there is a new one transaction Will return ; try_next_item It is Non blocking Of , It tries to ask sequencer Are there any new ones transaction, If there is , Then you get this transaction, Otherwise, go straight back to .
Use try_next_item Of driver The code for is as follows :
Code list 2-68
task my_driver::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
vif.data <= 8'b0;
vif.valid <= 1'b0;
while(!vif.rst_n)
@(posedge vif.clk);
while(1) begin
seq_item_port.try_next_item(req);
if(req == null)
@(posedge vif.clk);
else begin
drive_one_pkt(req);
seq_item_port.item_done();
end
end
endtask
Compared with get_next_item, try_next_item Your behavior is closer to reality driver act : When there is data , Drive data , Otherwise the bus will remain idle .
边栏推荐
- Error: the specified LINQ expression contains a reference to a query associated with a different context
- Error reported by using two-dimensional array [[]] in thymeleaf: could not parse as expression
- Here is the command to display the disk space usage. Go ahead and pay attention to more wonderful things!
- 5,10,15,20-tetraphenylporphyrin (TPP) and metal complexes fetpp/mntpp/cutpp/zntpp/nitpp/cotpp/pttpp/pdtpp/cdtpp supplied by Qiyue
- 两水先木示身为Unity3D职场人的个人觉悟
- CMDA 3634 image processing
- Jemter stress test - Basic request - [teaching]
- I3wm get window class
- Excel中Unicode如何转换为汉字
- i3wm 获取window class
猜你喜欢

职场“大冤种”,不仅身累,心也被掏空……

MySQL

安装homebrew报错汇总

Service interface test guide

Solution to the problem of multi application routing using thinkphp6.0
How to publish function computing (FC) through cloud effect

Redis(4)----浅谈整数集合

Quickly find five channels for high-quality objects, quickly collect and avoid detours
Sanic based services use celery to complete dynamic modification timing tasks
![JMeter stress test web agent local interface test [teaching]](/img/6d/a8b3cd1ca55993fe59c066f95ef093.png)
JMeter stress test web agent local interface test [teaching]
随机推荐
执行npm install -g serve时报错权限权限问题解决方案
多传感器融合感知
职场“大冤种”,不仅身累,心也被掏空……
MySQL
5,10,15,20-tetraphenylporphyrin (TPP) and metal complexes fetpp/mntpp/cutpp/zntpp/nitpp/cotpp/pttpp/pdtpp/cdtpp supplied by Qiyue
When asked during the interview, can redis master-slave copy not answer? These 13 pictures let you understand thoroughly
Alkynyl crosslinked porphyrin based polyimide materials (ppbpi-h-cr, ppbpi Mn cr.ppbpi Fe Cr); Metalloporphyrin based polyimide (ppbpi Mn, ppbpi FE) supplied by Qiyue
Parameter index out of range (0 < 1) (1> number of parameters, which is 0
Jemter stress test - Basic request - [teaching]
Important reference indicators for data center disaster recovery: RTO and RPO
5,10,15,20-tetra (4-bromophenyl) porphyrin (h2tppbr4) /5.2.15,10,15,20-tetra [4-[(3-aminophenyl) ethynyl] phenyl] porphyrin (tapepp) Qiyue porphyrin reagent
MXNet对NIN网络中的网络的实现
The performance of iron and steel enterprises was expected to be good in January this year. Since February, the prices of products of iron and steel enterprises have increased significantly. A mighty
Apache inlong graduated as a top-level project with a million billion level data stream processing capability!
Nine hours, nine people and nine doors (01 backpack deformation) - Niuke
MySQL'replace into'has a self incrementing ID of the pit. There is a problem with the backup opportunity
Liquid crystal texture diagram of purple solid mm-tpp-10c methacrylic acid decanoxy tetraphenyl porphyrin and mm-tpp-12c methacrylic acid dodecanoxy tetraphenyl porphyrin - Qi Yue display
Take you three minutes to get started typescript
QT basics tutorial: qstring
卡尔曼滤波器_Recursive Processing