当前位置:网站首页>ML11-SKlearn实现支持向量机
ML11-SKlearn实现支持向量机
2022-07-29 05:22:00 【十九岁的花季少女】
SKlearn库 实现 SVM
%matplotlib inline
#为了在notebook中画图展示
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import stats
import seaborn as sns; sns.set()
#随机来点数据,使用sklearn下的方法随机生成数据点
#其中 cluster_std是数据的离散程度
from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_blobs
X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=50, centers=2,
random_state=0, cluster_std=0.60)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, s=50, cmap='autumn')

训练一个基本的SVM
#分类任务
from sklearn.svm import SVC
#线性核函数 相当于不对数据进行变换
model = SVC(kernel='linear')
model.fit(X, y)
绘图函数的模板
#绘图函数
def plot_svc_decision_function(model, ax=None, plot_support=True):
if ax is None:
ax = plt.gca()
xlim = ax.get_xlim()
ylim = ax.get_ylim()
# 用SVM自带的decision_function函数来绘制
x = np.linspace(xlim[0], xlim[1], 30)
y = np.linspace(ylim[0], ylim[1], 30)
Y, X = np.meshgrid(y, x)
xy = np.vstack([X.ravel(), Y.ravel()]).T
P = model.decision_function(xy).reshape(X.shape)
# 绘制决策边界
ax.contour(X, Y, P, colors='k',
levels=[-1, 0, 1], alpha=0.5,
linestyles=['--', '-', '--'])
# 绘制支持向量
if plot_support:
ax.scatter(model.support_vectors_[:, 0],
model.support_vectors_[:, 1],
s=300, linewidth=1, alpha=0.2);
ax.set_xlim(xlim)
ax.set_ylim(ylim)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, s=50, cmap='autumn')
plot_svc_decision_function(model)

这条线就是我们希望得到的决策边界啦
观察发现有3个点做了特殊的标记,它们恰好都是边界上的点
它们就是我们的support vectors(支持向量)
在Scikit-Learn中, 它们存储在这个位置 support_vectors_(一个属性)
观察可以发现,只需要支持向量我们就可以把模型构建出来
接下来我们尝试一下,用不同多的数据点,看看效果会不会发生变化
分别使用60个和120个数据点
def plot_svm(N=10, ax=None):
X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=200, centers=2,
random_state=0, cluster_std=0.60)
X = X[:N]
y = y[:N]
model = SVC(kernel='linear', C=1E10)
model.fit(X, y)
ax = ax or plt.gca()
ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, s=50, cmap='autumn')
ax.set_xlim(-1, 4)
ax.set_ylim(-1, 6)
plot_svc_decision_function(model, ax)
# 分别对不同的数据点进行绘制
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(16, 6))
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.0625, right=0.95, wspace=0.1)
for axi, N in zip(ax, [60, 120]):
plot_svm(N, axi)
axi.set_title('N = {0}'.format(N))

引入核函数的SVM
绘制另一种数据集分布
from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_circles
# 绘制另外一种数据集
X, y = make_circles(100, factor=.1, noise=.1)
#看看这回线性和函数能解决嘛
clf = SVC(kernel='linear').fit(X, y)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, s=50, cmap='autumn')
plot_svc_decision_function(clf, plot_support=False);

#加入了新的维度r
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d
r = np.exp(-(X ** 2).sum(1))
# 可以想象一下在三维中把环形数据集进行上下拉伸
def plot_3D(elev=30, azim=30, X=X, y=y):
ax = plt.subplot(projection='3d')
ax.scatter3D(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], r, c=y, s=50, cmap='autumn')
ax.view_init(elev=elev, azim=azim)
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
ax.set_zlabel('r')
plot_3D(elev=45, azim=45, X=X, y=y)

#加入高斯核函数
clf = SVC(kernel='rbf')
clf.fit(X, y)
#这回厉害了!
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, s=50, cmap='autumn')
plot_svc_decision_function(clf)
plt.scatter(clf.support_vectors_[:, 0], clf.support_vectors_[:, 1],
s=300, lw=1, facecolors='none');

调节SVM参数

# 这份数据集中cluster_std稍微大一些,这样才能体现出软间隔的作用
X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=100, centers=2,
random_state=0, cluster_std=0.8)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, s=50, cmap='autumn')

C参数
#加大游戏难度的数据集
X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=100, centers=2,
random_state=0, cluster_std=0.8)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(16, 6))
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.0625, right=0.95, wspace=0.1)
# 选择两个C参数来进行对别实验,分别为10和0.1
for axi, C in zip(ax, [10.0, 0.1]):
model = SVC(kernel='linear', C=C).fit(X, y)
axi.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, s=50, cmap='autumn')
plot_svc_decision_function(model, axi)
axi.scatter(model.support_vectors_[:, 0],
model.support_vectors_[:, 1],
s=300, lw=1, facecolors='none');
axi.set_title('C = {0:.1f}'.format(C), size=14)

噶玛参数,越大映射的维度越高,模型越复杂。
X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=100, centers=2,
random_state=0, cluster_std=1.1)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(16, 6))
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.0625, right=0.95, wspace=0.1)
# 选择不同的gamma值来观察建模效果
for axi, gamma in zip(ax, [10.0, 0.1]):
model = SVC(kernel='rbf', gamma=gamma).fit(X, y)
axi.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, s=50, cmap='autumn')
plot_svc_decision_function(model, axi)
axi.scatter(model.support_vectors_[:, 0],
model.support_vectors_[:, 1],
s=300, lw=1, facecolors='none');
axi.set_title('gamma = {0:.1f}'.format(gamma), size=14)
对于比较大的噶玛值,边界分的很清晰,但是泛化能力比较低;偏小的噶玛值,分错了一些数据点,但是泛化能力强,更加有使用价值。
人脸识别实例
#读取数据集
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_lfw_people
#每个人的人脸至少有60个
faces = fetch_lfw_people(min_faces_per_person=60)
#看一下数据的规模
print(faces.target_names)
print(faces.images.shape)
# 3行5列的布局
fig, ax = plt.subplots(3, 5)
for i, axi in enumerate(ax.flat):
axi.imshow(faces.images[i], cmap='bone')
axi.set(xticks=[], yticks=[],
xlabel=faces.target_names[faces.target[i]])


from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
#降维到150维
pca = PCA(n_components=150, whiten=True, random_state=42)
svc = SVC(kernel='rbf', class_weight='balanced')
#先降维然后再SVM
model = make_pipeline(pca, svc)
划分数据集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
Xtrain, Xtest, ytrain, ytest = train_test_split(faces.data, faces.target,
random_state=40)
使用grid search cross-validation来选择我们的参数,遍历C和噶玛,看看哪个效果好。
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
param_grid = {
'svc__C': [1, 5, 10],
'svc__gamma': [0.0001, 0.0005, 0.001]}
grid = GridSearchCV(model, param_grid)
%time grid.fit(Xtrain, ytrain)
print(grid.best_params_)
选好后用我们的模型来做预测。
model = grid.best_estimator_
yfit = model.predict(Xtest)
yfit.shape
结果展示
fig, ax = plt.subplots(4, 6)
for i, axi in enumerate(ax.flat):
axi.imshow(Xtest[i].reshape(62, 47), cmap='bone')
axi.set(xticks=[], yticks=[])
axi.set_ylabel(faces.target_names[yfit[i]].split()[-1],
color='black' if yfit[i] == ytest[i] else 'red')
fig.suptitle('Predicted Names; Incorrect Labels in Red', size=14);

from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
print(classification_report(ytest, yfit,
target_names=faces.target_names))
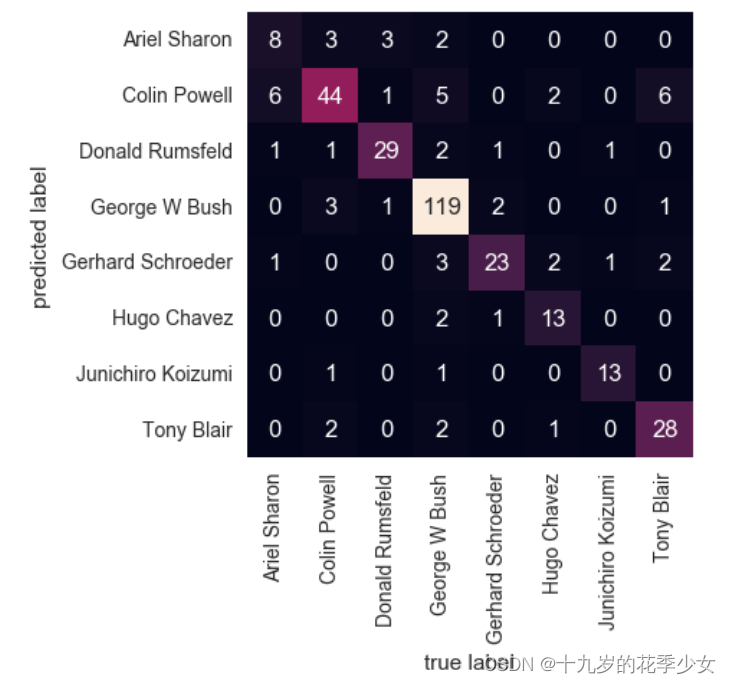
精度值和召回率
混淆矩阵
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
mat = confusion_matrix(ytest, yfit)
sns.heatmap(mat.T, square=True, annot=True, fmt='d', cbar=False,
xticklabels=faces.target_names,
yticklabels=faces.target_names)
plt.xlabel('true label')
plt.ylabel('predicted label');
边栏推荐
- 【语义分割】Mapillary 数据集简介
- 【目标检测】KL-Loss:Bounding Box Regression with Uncertainty for Accurate Object Detection
- Detailed explanation of atomic operation class atomicinteger in learning notes of concurrent programming
- PyTorch中的模型构建
- 【语义分割】SETR_Rethinking Semantic Segmentation from a Sequence-to-Sequence Perspective with Transformer
- 【CV】请问卷积核(滤波器)3*3、5*5、7*7、11*11 都是具体什么数?
- 虚假新闻检测论文阅读(五):A Semi-supervised Learning Method for Fake News Detection in Social Media
- nacos外置数据库的配置与使用
- 【Transformer】ACMix:On the Integration of Self-Attention and Convolution
- Are you sure you know the interaction problem of activity?
猜你喜欢
![[overview] image classification network](/img/2b/7e3ba36a4d7e95cb262eebaadee2f3.png)
[overview] image classification network

迁移学习—Geodesic Flow Kernel for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation

ROS常用指令
![[target detection] generalized focal loss v1](/img/8b/458d51422df8dcda65cb6afaa10b3f.png)
[target detection] generalized focal loss v1

Error in installing pyspider under Windows: Please specify --curl dir=/path/to/build/libcurl solution

研究生新生培训第一周:深度学习和pytorch基础
![[image classification] how to use mmclassification to train your classification model](/img/98/f8536bc4c6a291a028a0c4227653ee.png)
[image classification] how to use mmclassification to train your classification model

Reporting Services- Web Service

【Clustrmaps】访客统计

Yum local source production
随机推荐
PyTorch中的模型构建
【Clustrmaps】访客统计
【Transformer】SegFormer:Simple and Efficient Design for Semantic Segmentation with Transformers
Flink connector Oracle CDC synchronizes data to MySQL in real time (oracle19c)
[image classification] how to use mmclassification to train your classification model
Markdown syntax
电脑视频暂停再继续,声音突然变大
【综述】图像分类网络
fastText学习——文本分类
【DL】关于tensor(张量)的介绍和理解
迁移学习—Geodesic Flow Kernel for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
【Transformer】ACMix:On the Integration of Self-Attention and Convolution
【语义分割】SETR_Rethinking Semantic Segmentation from a Sequence-to-Sequence Perspective with Transformer
迁移学习——Transfer Joint Matching for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Are you sure you know the interaction problem of activity?
【ML】机器学习模型之PMML--概述
Android studio login registration - source code (connect to MySQL database)
ASM piling: after learning ASM tree API, you don't have to be afraid of hook anymore
Activity交互问题,你确定都知道?
Set automatic build in idea - change the code, and refresh the page without restarting the project