当前位置:网站首页>Rust: command line parameter and environment variable operation
Rust: command line parameter and environment variable operation
2020-11-08 08:59:00 【osc_sejgcp0】
Rust in , We often encounter command line parameters and environment variable operations . Let's have a look at .
One 、 Command line arguments
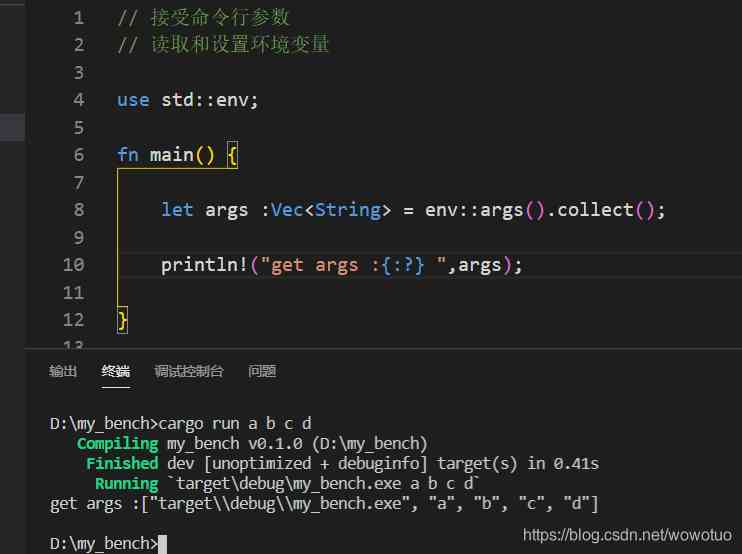
You can see from above ,std::env Realized from cargo run Command line parameters are extracted from the command line a b c Enter the program .
Two 、 Read environment variables
std::env::var function , The function of environment variable in operating system is realized .
env::var()-> std::env::Vars
Vars What is it? , Very complicated , He did Iterator. The following is the source code in the standard library :
#[stable(feature = "env", since = "1.0.0")]
pub struct Vars {
inner: VarsOs,
}
/// An iterator over a snapshot of the environment variables of this process.
///
/// This structure is created by the [`std::env::vars_os`] function. See
/// its documentation for more.
///
/// [`std::env::vars_os`]: vars_os
#[stable(feature = "env", since = "1.0.0")]
pub struct VarsOs {
inner: os_imp::Env,
}
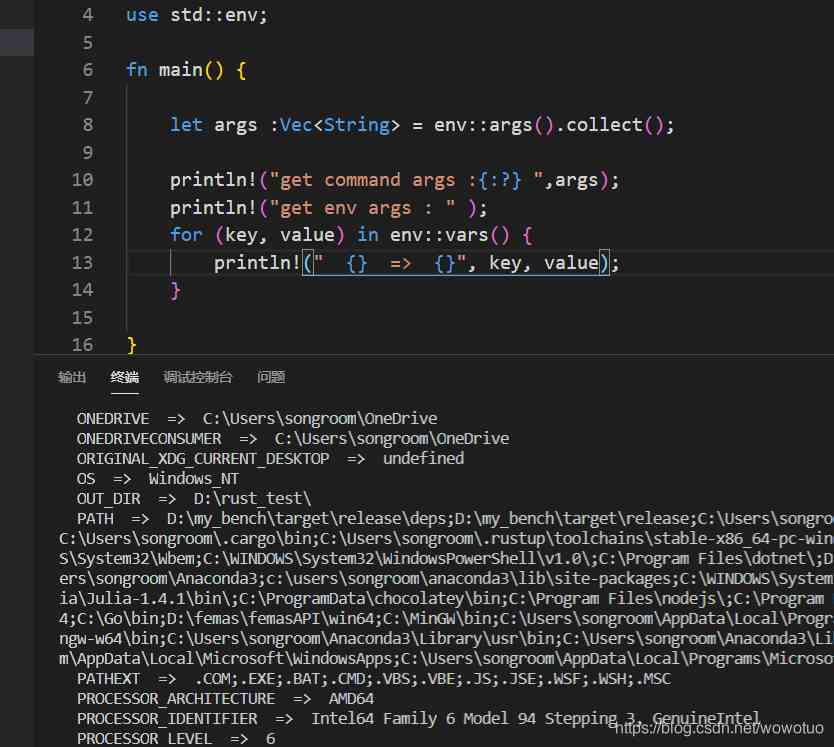 It should be noted that , In the environment variables , Characters don't have to be Unicode The standard , That would be a false report . You can use :
It should be noted that , In the environment variables , Characters don't have to be Unicode The standard , That would be a false report . You can use :
env::vars_os
following : Read specific environment variables
use std::env;
fn main() {
let args: Vec<String> = env::args().collect();
//println!("get command args :{:?} ", args);
//println!("get env args : ");
for (key, value) in env::vars() {
//println!(" {} => {}", key, value);
}
let key = "PATH";
match env::var(key) {
Ok(val) => {
// val is String, splited by ";"
println!("val =>{}",val);
},
Err(e) => println!("couldn't interpret {}: {}", key, e),
}
}
3、 ... and 、 Set the environment variable
Generally include : View all environment variables 、 Set new environment variables and modify old environment variables .
1、 stay cmd Next
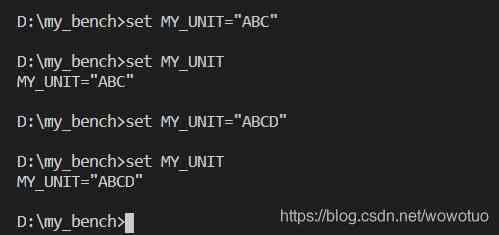
The settings are made above , View individual environment variable operations 、 Modify the operating . It's still relatively simple .
2、powshell
# View all environment variables ls env:
# Search for environment variables ls env:NODE*
# Look at a single environment variable $env:NODE_ENV
# add to / Update environment variables $env:NODE_ENV=development
# Delete environment variables del evn:NODE_ENV
3、linux
modify bashrc file , This method is safer , It can control the permission to use these environment variables to the user level , This is for a specific user , If you need to give a user permission to use these environment variables , You only need to modify the
.bashrc Just file it .vi ~/.bashrc
Add below :
Export PATH="$PATH:/NEW_PATH"
source :
https://www.cnblogs.com/Joans/p/7760378.html
版权声明
本文为[osc_sejgcp0]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- 413【毕设课设】基于51单片机无线zigbee无线智能家居光照温湿度传输监测系统
- Deeplight Technology Bluetooth protocol SRRC certification services
- November 07, 2020: given an array of positive integers, the sum of two numbers equals N and must exist. How to find the two numbers with the smallest multiplication?
- ulab 1.0.0发布
- GET,POST,PUT,DELETE,OPTIONS用法与说明
- Face recognition: attack types and anti spoofing techniques
- python_ scrapy_ Fang Tianxia
- Architect (November 2020)
- 哔哩哔哩常用api
- 高并发,你真的理解透彻了吗?
猜你喜欢

What details does C + + improve on the basis of C

PCR and PTS calculation and inverse operation in TS stream
Do you really understand the high concurrency?
模板链表类学习

狗狗也能操作无人机!你没看错,不过这其实是架自动驾驶无人机 - 知乎

Python learning Day1 -- Basic Learning

Review the cloud computing application scenarios you didn't expect (Part 1)
print( 'Hello,NumPy!' )
Macquarie Bank drives digital transformation with datastex enterprise (DSE)

M 端软件产品设计思虑札记 - 知乎
随机推荐
An error occurred while starting the kernel was successfully resolved
Sum up some useful functions
归纳一些比较好用的函数
i5 1135g7和i5 1035g1参数对比区别大吗? 哪个好
More than 50 object detection datasets from different industries
Bili Bili common API
Do you really understand the high concurrency?
Solve the problem of rabbitmq message loss and repeated consumption
Brief history of computer
golang 匿名结构体成员,具名结构体成员,继承,组合
技术人员该如何接手一个复杂的系统?
The real-time display of CPU and memory utilization rate by Ubuntu
IOS learning note 2 [problems and solutions encountered during the installation and use of cocopods] [update 20160725]
November 07, 2020: given an array of positive integers, the sum of two numbers equals N and must exist. How to find the two numbers with the smallest multiplication?
Julia 是如何风靡起来的?
vivoy73s和荣耀30青春版的区别
5g/4g工业无线路由器
Unparseable date: 'mon Aug 15 11:24:39 CST 2016', time format conversion exception
How does spotify drive data-driven decision making?
nvm