当前位置:网站首页>Talking about JVM
Talking about JVM
2022-07-04 04:37:00 【ChuChu】
Catalog
Garbage collection mechanism (GC)
Based on reference count (Python And so on )
Based on reachability analysis (Java programme )
JVM Internal division
Program counter
This is a JVM The area with the smallest memory , Save the Next order Where is your address
Instructions are byte codes , JVM You need to load the bytecode , Then put it in memory
Finally, the program takes instructions from memory and puts them into CPU Up operation .
In this process, you need to remember the number of items to be implemented
Program counter each thread has one
Stack
Main storage local variable and Method call information , Memory is not big
Every time you call a function , Will trigger the stack .
Functions entering the stack , Also called stack frame
Each thread of the stack has one
Pile up
yes JVM In the memory The biggest place
We usually new The object is stored in the heap , Include the member variables of the object
Note here , References are not always on the stack
such as :
void func(){
String s = new String();
}there s and new String() Not in a place
s Is a local variable , On the stack . new String() The ontology of the object is on the heap .
Heap one per process , Multiple threads share a heap
Method area
The method area stores " Class object " And static members
.java Will be converted into a .class file
This .class The file will be loaded into memory , By JVM Construct class objects
Class objects contain all the information inside a class ( Variable , Method )
Class loading
Class loading is to put .class The file is loaded into memory , Construct as a class object

Class loading is mainly divided into three steps : loading, linking, initialization
loading
First find and read the corresponding .class file , At the same time, a class object is preliminarily generated
class Each character of the file corresponds to some special meaning , Finally, fill these information into the class object
linking
Generally, it is to establish the connection between many entities , There are also three steps to connect :
verification
Verify whether the read content exactly matches the format specified in the specification
If not, an exception will be thrown
preparation
Responsible for allocating memory to static variables , And set the value to 0
resolution
.class In file , Constants are assigned only numbers
So you need to find the corresponding content according to the number and fill it in the class object
initialization
Start actually initializing class objects , Especially for static members
example
What is the result of the following code execution ?
class A{
public A(){
System.out.println("A Construction method of ");
}
{
System.out.println("A The construction code block of ");
}
static {
System.out.println("A Static code block ");
}
}
class B extends A{
public B(){
System.out.println("B Construction method of ");
}
{
System.out.println("B The construction code block of ");
}
static {
System.out.println("B Static code block ");
}
}
public class Test extends B{
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Test();
new Test();
}
}
Because static members execute when the class is loaded , Before creating an instance, you must Load the class first
But static code blocks are only executed once during the class loading phase
And the construction method and the construction method block , Each instantiation will execute , And Constructor block is before constructor
Finally, the parent class construction is executed before , Subclass after , give the result as follows :

Parent delegate mechanism
This is the class loading process loading Stage is a link to find documents
It's about JVM Class loader in , How to find according to the fully qualified name of a class .class Documentation process
Because there are many file locations , therefore JVM There are many class loaders , A loader is responsible for an area
The default class loading is mainly 3 individual :
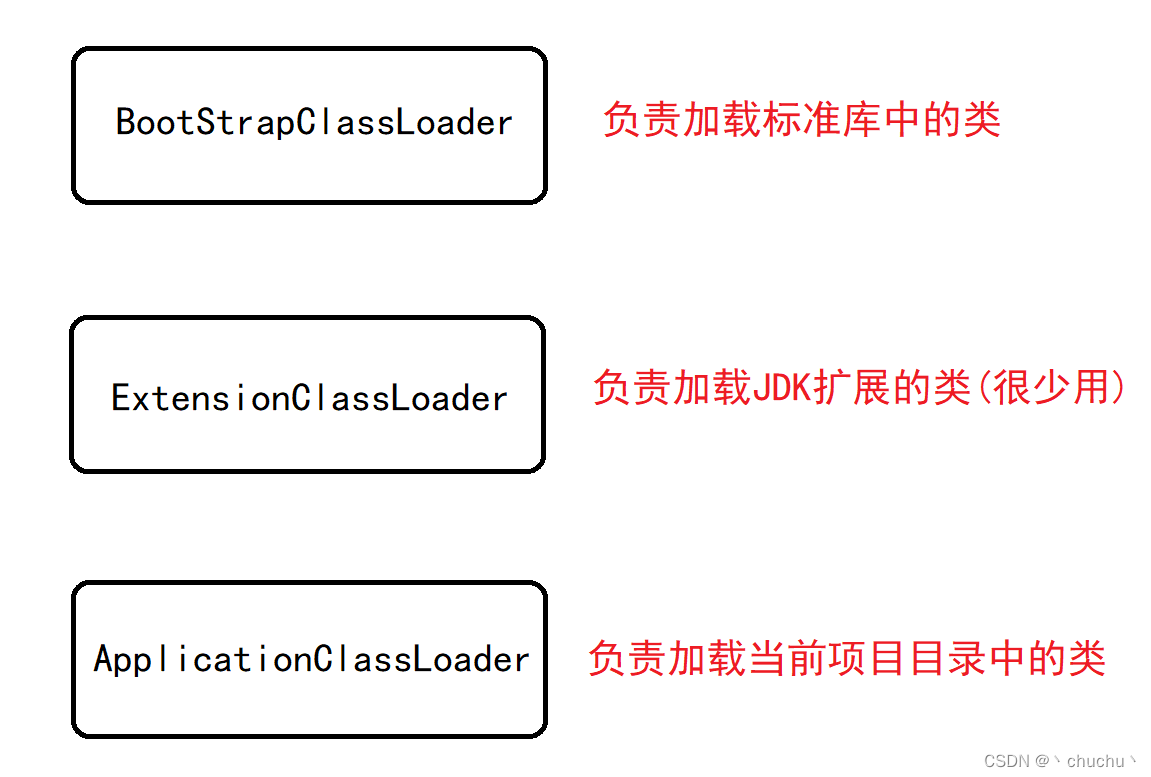
Of course, programmers can define class loaders by themselves , To load classes from other directories
The process
For example, to load java.lang.String
- First of all to enter ApplicationClassLoader Class loader
- ApplicationClassLoader The class loader will check its parent Whether the class loader has been loaded , without , Just call its parent Class loader ExtensionClassLoader
- ExtensionClassLoader Will also check its father Class loader BootStrapClassLoader Whether loaded or not , Call without
- BootStrapClassLoader Is the top class loader , So I scanned the directory I was responsible for
- BootStrapClassLoader eureka java.lang.String, So I am directly responsible for the subsequent loading process . Find the end
Another example is to load your own defined classes :
- First of all, the above 5 Step , however BootStrapClassLoader I didn't find
- So give it to ExtensionClassLoader scanning , I didn't get it
- Give it back ApplicationClassLoader scanning , Found a custom class , Start subsequent loading
Of course , If the last ApplicationClassLoader I didn't find it , Just go back to one ClassNotFoundException abnormal
So the whole process is roughly as follows :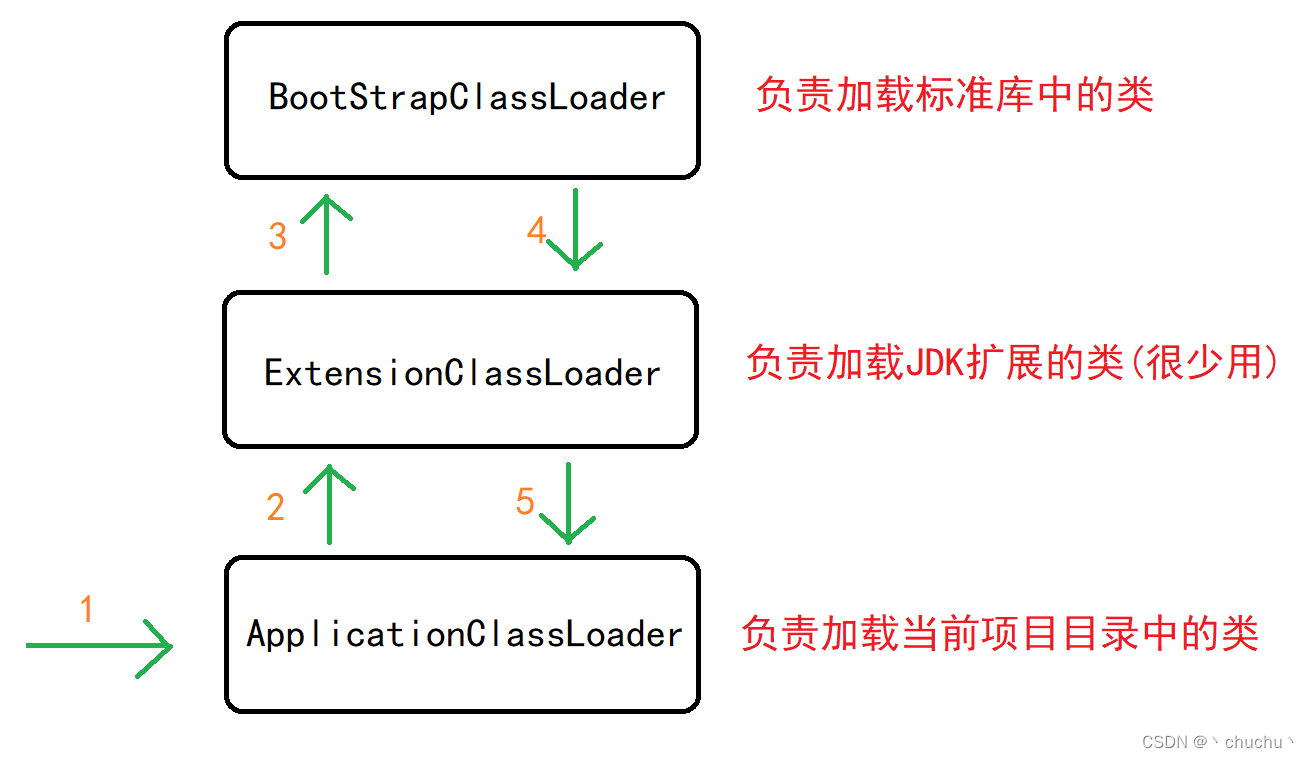
This set of search rules , It's called the parental delegation model .
The reason for this design is that : Once the class written by the programmer and the fully qualified name of the class in the standard library are repeated , Classes that can also be successfully loaded into the standard library .
Garbage collection mechanism (GC)
Creating variables , new Objects or loading classes and other processes will apply for memory
The timing of applying for memory is clear , But the timing of releasing memory is not so clear
because JVM I don't know when you don't use this variable , Unable to release accurately
So how to solve this problem ?
That is the garbage collection mechanism , It can also be called GC.
Garbage collection mechanism , Through complex strategies , Determine whether memory can be recycled , And release automatically
But garbage collection has its disadvantages :
- Consume extra expenses ( It consumes more resources )
- May affect the smooth operation of the program ( May trigger STW problem )
Can't , There is nothing perfect in the world . Garbage collection mechanism still brings great convenience to programmers .
Said along while , What does the garbage collection mechanism recycle ?
I talked about memory partition earlier , Only the heap consumes the most memory , Because there are objects inside
And garbage collection mechanism , The most important thing to recycle is objects
Next, let's talk about how to recycle garbage :
1) Look for trash
Based on reference count (Python And so on )
For each object , A small amount of memory will be introduced , Save how many references this object has to it
void func (){
Test t = new Test();
Test t2 = t;
}Like the code above , When method execution ends , local variable t and t2 It is released along with the stack frame
At this time, these two object references point to 0, Be regarded as garbage , Waiting for recycling
Reference counting is simple and efficient , But there are drawbacks :
- Low space utilization . Each object should be equipped with a counter , Then there is extra space , Especially if the object is relatively small , Space utilization will be lower
- There's a problem with circular references
Circular quotation problem :
class Test { Test t = null; } Test t1 = new Test(); Test t2 = new Test();This is a string of example code , The logic behind it is shown in the figure :
At this time, perform these two operations :
t1.t = t2; t2.t = t1;give the result as follows :
Then carry out the following operations :
t1 = null; t2 = null;The results are as follows :
because
At this time, the two object references are not 0, Can't empty , But no outside world can visit them , So there is a memory leak
Based on reachability analysis (Java programme )
Through additional threads , Periodically scan objects in the entire memory space
In some starting positions , Start an operation similar to depth first traversal , Access all the objects Mark Again
The starting position is also called GCRoots, There are the following 3 class :
- Local variables on the stack
- The object pointed to by the reference in the constant pool
- The object pointed to by the static member in the method area
Objects not marked , That is, unreachable objects , It's garbage
For example, the right subtree of a binary tree is good , Result settings root.right = null
Then many nodes of the right subtree are unreachable , It's all rubbish
But it also has its own shortcomings : The system costs a lot , Traversal may be slow
2) Recycling waste
Recycling garbage means freeing memory , There are three basic strategies :
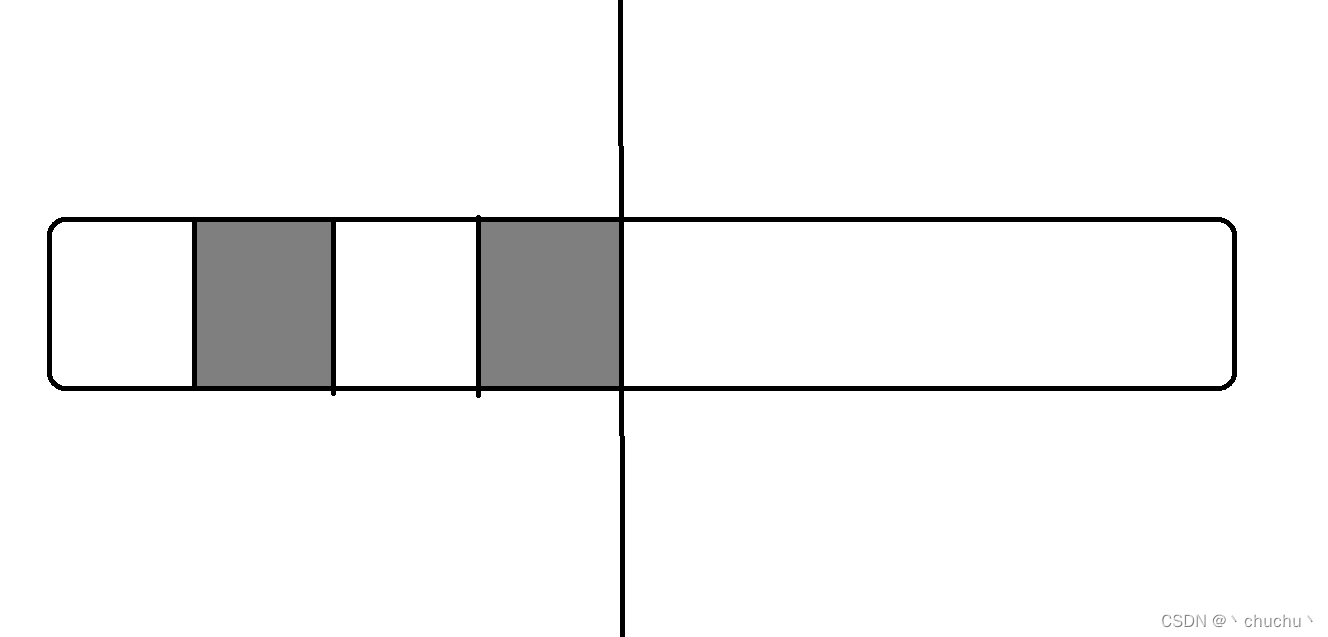
Mark clear
As shown in the figure below , The gray ones are all garbage

If it's released directly , Although the memory is returned to the system , But memory is discrete , Formed a memory fragment
Next time, if you want to apply for a large memory space , The application may fail ,
Because there is no continuous memory space to allocate
Copy algorithm
The replication algorithm is to copy what is not garbage to the other half , And release the whole space
as follows :

In this way, we can get a continuous space .
But there are still problems :
- Low memory space utilization
- If there are many objects to keep , There are fewer objects to release , At this point, the replication cost is very high
Tag to sort out
For replication algorithms , Make further improvements , The following animation :

Copy all available memory to one side , Then empty the other side
But the cost of copying still exists
Generational recycling
So the three schemes are not the most perfect , Actually, it will combine various schemes
The idea combined is " Generational recycling "
" Generational recycling " What do you mean ? Here for the object " Age " To classify
An object survived a round GC scanning , It's called " One year old "
The detailed layout in the pile actually looks like this :

The newly created object is placed in Eden, Also called Eden District
If you survive a round , To get into S0, Also known as the survival area ( Most objects can't endure 1 round )
In subsequent rounds GC in , Copy back and forth between the two surviving areas , That is, the replication algorithm
Finally, under repeated screening , Come to the old age
The objects in the elderly generation are recycled by marking
The older an object is , The more likely you are to survive
In generational recycling , There is a special case , Objects that occupy a lot of memory can enter the elderly generation directly , Because it costs a lot to copy
Garbage collector
JVM in , For the above operations , called " Garbage collector "
The first is serial The collector , But this collector is serial
That is, when scanning and releasing garbage , The business thread is going to stop working
And then there was ParNew The collector , This collector introduces multithreading , Adopt concurrent collection
But what is popular now is CMS and G1 The collector
CMS The original intention of the design is to make STW As short as possible
It divides reachability analysis into 3 block : Initial marker , Concurrent Tags , Re label
G1 Divide the whole memory into many areas
Mark these areas differently
Some areas put Cenozoic objects , Some put objects of old age
And then when you scan , Just scan several times , Can effectively reduce STW Time
Thank you for seeing this ヽ( ̄ω ̄( ̄ω ̄〃)ゝ
边栏推荐
- Eig launched Grupo Cerro, a renewable energy platform in Chile
- The five pictures tell you: why is there such a big gap between people in the workplace?
- Keysight n9320b RF spectrum analyzer solves tire pressure monitoring scheme
- [microservice openfeign] @feignclient detailed explanation
- 十字路口通行优先权,十字路口通行规则图解
- How to view installed r packages in R language
- Architecture practice camp - graduation project of module 9 of phase 6
- 虚拟商品帐号交易平台源码_支持个人二维码收款
- Apple CMS imitation watermelon video atmospheric response video template source code
- MySQL 索引和事务
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
1. Mx6u-alpha development board (LED drive experiment in C language version)
多位科技公司创始人向Entrepreneur First提供高达1.58亿美元的C轮融资,协助其投资下一代全球创新者
Asynchronous development process - touch your hand and lead you to realize a promise
Self sharing of a graduate
GUI 应用:socket 网络聊天室
RHCSA 04 - 进程管理
Precautions for accompanying driving these 23 points should be paid attention to!
[Yugong series] go teaching course 002 go language environment installation in July 2022
架构训练毕业设计+总结
资深开发人员告诉你,怎样编写出优秀的代码?
Kivy教程之 格式化文本 (教程含源码)
Redis:哈希hash类型数据操作命令
Deep parsing structured exception handling (SEH) - by Matt Pietrek
What is context?
I.MX6U-ALPHA开发板(C语言版本LED驱动实验)
Pytest基础自学系列(一)
Redis: operation command for collecting set type data
Apple CMS imitation watermelon video atmospheric response video template source code
[wechat applet] good looking carousel map component
十字路口通行优先权,十字路口通行规则图解