当前位置:网站首页>The CAN communication standard frame and extended frame is introduced
The CAN communication standard frame and extended frame is introduced
2022-08-01 11:33:00 【passing bear~】
Introduction
The CAN interface is compliant with specifications 2.0A and 2.0B (active) with bit rates up to 1 Mbit/s.It can receive and transmit standard frames with 11-bit identifiers and extended frames with 29-bit identifiers.
The difference between standard and extended frames is:
1. The arbitration field of Extended frame has 29 bits, and 2^29 messages can appear, and there is a gap on the data link (transparent to the operator), and the frame IDThe range is 0000 0000-1FFF FFFF.(PS: The purpose is to construct a 29-bit CAN ID, which can achieve a larger ID group, and mother no longer has to worry about insufficient IDs!)
Second, the arbitration field of standard frame is continuousThe 11 bits of the frame can appear 2^11 kinds of messages, that is, the frame ID range is 000-7FF;
3. The DLC (data length) in the control frame is exactly the same, but reservedDifferent bits, standard frames IDE, R0, extended frames R1, R0, must be sent at a dominant level (operated by the data link layer), transparent to the programmer;
4. Summary:Everything else is exactly the same, so in fact, the CAN standard frame and the extended frame are only different in the length of the frame ID, so as to expand more CAN nodes and better support the upper layer protocol.
Note: The frame ID here does not indicate the destination address, but the priority of the message accessing the bus (the smaller the frame ID value, the higher the priority, the minimum is 0x00000000).
Standard frame: (0x12)
Extended frame: (0x1314)
CAN standard frame format
CAN standard frame information is 11 bytes (3 + 8), including two parts: information and data parts.The first 3 bytes are the information part.
Byte 1 is frame information.The 7th bit (FF) represents the frame format, in the standard frame, FF=0; the 6th bit (RTR) represents the frame type, RTR=0 represents the data frame, RTR=1 represents the remote frame; DLC represents the data frameThe actual data length of the frame.
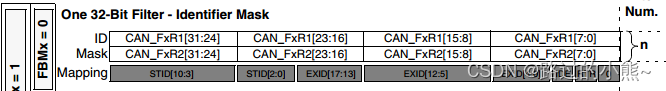
Bytes 2 and 3 are the message identification code, 11 bits are valid.
Bytes 4 to 11 are the actual data of the data frame, and are invalid for remote frames.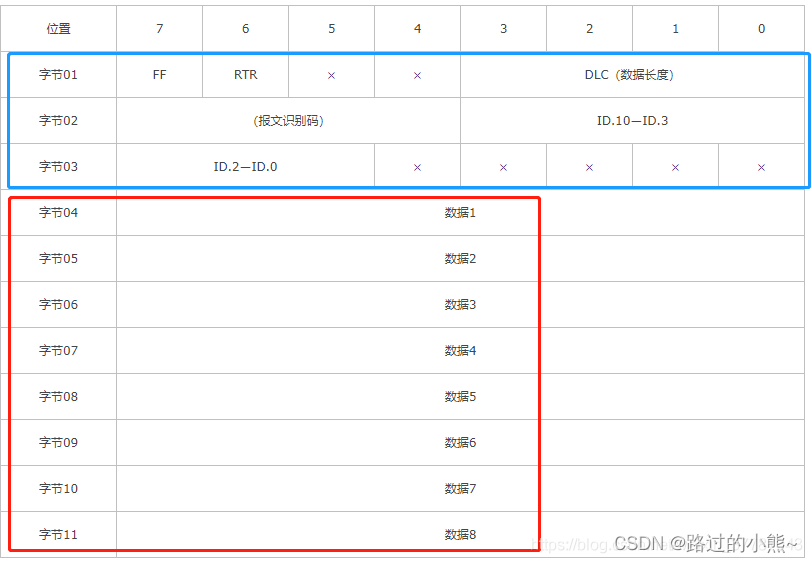
CAN Extended Frame Format
CAN extended frame information is 13 bytes (5 + 8), including two parts, information and data parts.The first 5 bytes are the information part
Byte 1 is frame information.The 7th bit (FF) represents the frame format, in the extended frame, FF=1; the 6th bit (RTR) represents the frame type, RTR=0 represents the data frame, RTR=1 represents the remote frame; DLC represents the data frameThe actual data length of the frame.
Bytes 2 to 5 are the message identification code, and the upper 29 bits are valid.
The actual data of the data frame in bytes 6~13, invalid in remote frame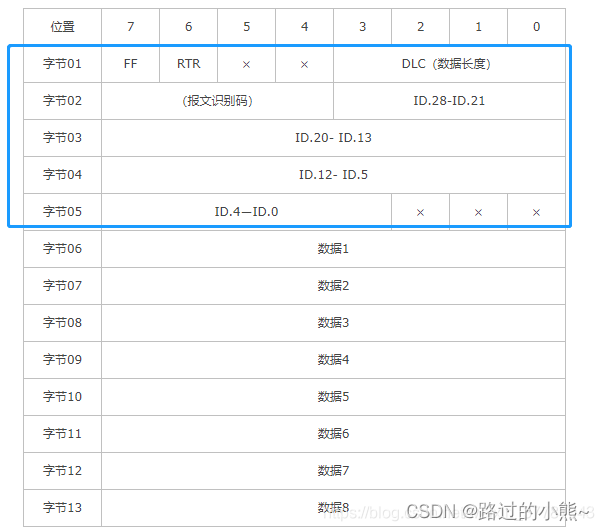
Replenishing knowledge
One of the biggest features of the CAN protocol is that the traditional station address encoding is abolished, and the communication data block is encoded instead.The advantage of this method is that the number of nodes in the network is theoretically unlimited.The above different data blocks, this way of coding according to data blocks, can also enable different nodes to receive the same data at the same time, which is very useful in a distributed control system.The length of the data segment is up to 8 bytes, which can meet the general requirements of control commands, working status and test data in common industrial fields.
At the same time, 8 bytes will not occupy the bus for too long, thus ensuring the real-time communication.CAN protocol adopts CRC check and can provide corresponding error handling function, which ensures the reliability of data communication.CAN's excellent characteristics, high reliability and unique design are especially suitable for the interconnection of industrial process monitoring equipment. Therefore, CAN has been paid more and more attention by the industry and has been recognized as one of the most promising field buses.
Appendix:
The latest download address of the above CANTest software: https://www.zlg.cn/Index/Search/search?selc=all&key=cantest
The CAN box needs to be configured to use
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

石头科技打造硬核品牌力 持续出海拓展全球市场
2022 Go生态圈 rpc 框架 Benchmark

Promise to learn several key questions (3) the Promise - state change, execution sequence and mechanism, multitasking series, abnormal penetration, interrupt the chain of Promise

新一代超安全蜂窝电池, 思皓爱跑上市13.99万元起售

Pytest电商项目实战(下)
How to use DevExpress controls to draw flowcharts?After reading this article, you will understand!
Mini Program Graduation Works WeChat Food Recipes Mini Program Graduation Design Finished Products (2) Mini Program Functions

Dapr 与 NestJs ,实战编写一个 Pub & Sub 装饰器
STM32 CAN filter configuration details

Promise learning (1) What is Promise?how to use?How to solve callback hell?
随机推荐
R语言拟合ARIMA模型:使用forecast包中的auto.arima函数自动搜索最佳参数组合、模型阶数(p,d,q)、设置seasonal参数指定在模型中是否包含季节信息
Promise learning (4) The ultimate solution for asynchronous programming async + await: write asynchronous code in a synchronous way
Envoy source code flow chart
在线GC日志分析工具——GCeasy
数字化转型实践:世界级2B数字化营销的方法框架
Transfer learning to freeze the network:
冰冰学习笔记:gcc、gdb等工具的使用
一文说明白ECDSA spec256k1 spec256r1 EdDSA ed25519千丝万缕的关系
Mini Program Graduation Works WeChat Food Recipes Mini Program Graduation Design Finished Products (4) Opening Report
【Unity3D插件】AVPro Video插件分享《视频播放插件》
千万级乘客排队系统重构&压测方案——总结篇
【likeshop】回收租凭系统100%开源无加密 商城+回收+租赁
Promise学习(一)Promise是什么?怎么用?回调地狱怎么解决?
如何利用DevExpress控件绘制流程图?看完这篇文章就懂了!
C language implementation!20000 in 4 seconds
【公开课预告】:超分辨率技术在视频画质增强领域的研究与应用
重庆市大力实施智能建造,推动建筑业数字化转型,助力“建造强市”
【CLion】CLion 总是提示 “This file does not belong to any project target xxx” 的解决方法
分类预测 | MATLAB实现1-DCNN一维卷积神经网络分类预测
【钛晨报】国家统计局:7月制造业PMI为49%;玖富旗下理财产品涉嫌欺诈,涉及390亿元;国内航线机票燃油附加费8月5日0时起下调