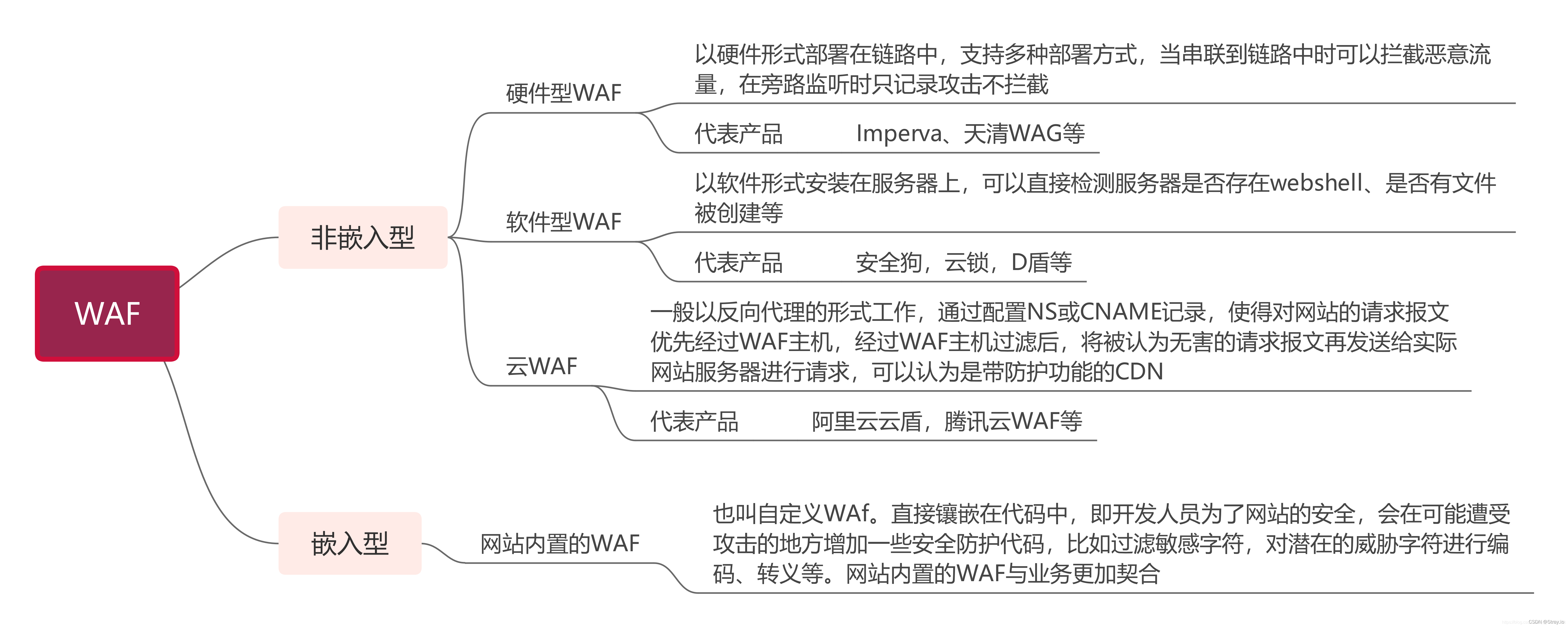
当前位置:网站首页>Educational Codeforces Round 132 (Rated for Div. 2) E. XOR Tree
Educational Codeforces Round 132 (Rated for Div. 2) E. XOR Tree
2022-07-26 04:01:00 【jangyi.】
E. XOR Tree
The question :
Given a tree , Each node has a weight a [ i ] a[i] a[i], If the exclusive or sum of the weights on the simple path between any two nodes in the tree is not 0, Call this tree good . ask : At least modify the weights of several nodes ( Can be modified to any number ) Make the tree a good tree .
analysis :
Any one of them u − u- u−> v v v The exclusive or sum of paths of is s u m [ u ] ∧ s u m [ v ] ∧ a [ l c a ( u , v ) ] sum[u] \wedge sum[v] \wedge a[lca(u,v)] sum[u]∧sum[v]∧a[lca(u,v)], l c a ( u , v ) lca(u,v) lca(u,v) by u , v u,v u,v The latest public ancestor of . So if there is s u m [ u ] ∧ s u m [ v ] = a [ x ] , x = l c a ( u , v ) sum[u] \wedge sum[v]=a[x],x=lca(u,v) sum[u]∧sum[v]=a[x],x=lca(u,v), It's in x x x At least one node in the subtree of needs to be modified . Because the value that can be modified is arbitrary , So if you want to modify a node , Then the simple path that the node passes through can be ignored ( Directly when this subtree does not exist ).
Then it's easy for us to think , modify x x x This node is the best choice .
For each node x x x, Process its subtree first , If the XOR sum of two nodes in the subtree is equal to a [ x ] a[x] a[x], Then delete x x x node , answer +1. Otherwise, we will combine this subtree , Heuristic merging optimization is adopted in the merging process , It can reduce the complexity to l o g log log.
code:
int n, m, a[N];
int b[N], ans;
set<int> st[N];
vector<int> g[N];
void dfs(int u, int fa) {
b[u] = a[u];
if(fa != -1) b[u] ^= b[fa];
for(int i : g[u]) {
if(i != fa) {
dfs(i, u);
}
}
}
void cals(int u, int fa) {
bool f = 0;
st[u].insert(b[u]);
for(int i : g[u]) {
if(i != fa) {
cals(i, u);
if(st[u].size() < st[i].size()) swap(st[u], st[i]);
for(auto t : st[i]) f |= st[u].count(a[u] ^ t);
for(auto t : st[i]) st[u].insert(t);
}
}
if(f) {
ans++;
st[u].clear();
}
}
void solve() {
re(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) re(a[i]);
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int x, y; re(x), re(y);
x--; y--;
g[x].pb(y); g[y].pb(x);
}
dfs(0, -1);
cals(0, -1);
cout << ans << '\n';
}
边栏推荐
- [in depth study of 4g/5g/6g topic-42]: urllc-13 - in depth interpretation of 3GPP urllc related protocols, specifications and technical principles -7-low delay technology-1-subcarrier spacing expansio
- 微信小程序实现音乐播放器(4)(使用pubsubjs实现页面间通信)
- 6年从零开始的自动化测试之路,开发转测试我不后悔...
- PHP save array to var file_ export、serialize
- Apple removed the last Intel chip from its products
- 《opencv学习笔记》-- 霍夫变换
- Find my technology | the Internet of things asset tracking market has reached US $6.6 billion, and find my helps the market develop
- How does redis implement persistence? Explain the AOF trigger mechanism and its advantages and disadvantages in detail, and take you to quickly master AOF
- STM32 state machine programming example - full automatic washing machine (Part 2)
- 【数字IC/FPGA】热独码检测
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Wechat applet realizes music player (5)
How does redis implement persistence? Explain the AOF trigger mechanism and its advantages and disadvantages in detail, and take you to quickly master AOF
JS upload avatar (you can understand it after reading it, trust me)
[MCU simulation project] external interrupt 0 and 1 control two digit nixie tube to count
微信小程序实现音乐播放器(4)(使用pubsubjs实现页面间通信)
研发了 5 年的时序数据库,到底要解决什么问题?
PHP 对象转换数组
Summary of senior report development experience: understand this and do not make bad reports
PHP save array to var file_ export、serialize
【单片机仿真项目】外部中断0和1控制两位数码管进行计数
按键消抖的Verilog实现
5 years, 1.4W times, NFT og's road to immortality Web3 column
基于Caffe ResNet-50网络实现图片分类(仅推理)的实验复现
leetcode: 102. 二叉树的层序遍历
想要做好软件测试,可以先了解AST、SCA和渗透测试
PHP <=> 太空船运算符(组合比较符)
[MCU simulation project] external interrupt 0 controls 8 LED flashes
通用测试用例写作规范
operator new、operator delete补充讲义
[Reading Notes - > data analysis] Introduction to BDA textbook data analysis