当前位置:网站首页>All inherited features
All inherited features
2022-06-11 21:44:00 【Code loving students】
Catalog
2. The basic syntax of inheritance
4. Object model in inheritance
5. The order of construction and deconstruction
6. Processing of functions with the same name
6.1 Member variable with the same name
6.2 Member functions with the same name
7. Static members with the same name
7.1 Static member variable with the same name
7.2 Static member function with the same name
9. Diamond inheritance problem
9.1 What is diamond inheritance ?
9.2 Problems with diamond inheritance
1. What is inheritance ?
Inheritance is one of the three characteristics of object-oriented
Inheritance can be understood as the process that one class obtains member variables and member functions from another class .
For example, class B Inherited from class A, that B have A Member variables and member functions . The inherited class is called the parent or base class , An inherited class is called a subclass or derived class .
2. The basic syntax of inheritance
class Class name : jurisdiction Parent class name
// A child has the characteristics of a father , And children have their own unique characteristics
// Parent class , Also called base class
class BasePage
{
public:
void header()
{
cout << " home page 、 Public class 、 Sign in 、 register ..." << endl;
}
void footer()
{
cout << " Help center 、 Exchange and cooperation 、 Map of the station " << endl;
}
void left()
{
cout << " classification " << endl;
}
void content()
{
cout << "java Subject video " << endl;
}
};
// Subclass , Also becomes a derived class
class Java :public BasePage
{
public:
void content()
{
cout << "java Subject video " << endl;
}
};
class CPP :public BasePage
{
public:
void content()
{
cout << "CPP Subject video " << endl;
}
};
void Test1()
{
Java a;
cout << "Java Website :" << endl;
a.header();
a.footer();
a.left();
a.content();
}
void Test2()
{
CPP a;
cout << "CPP Website :" << endl;
a.header();
a.footer();
a.left();
a.content();
}
int main()
{
Test1();
cout << "--------------------" << endl;
Test2();
return 0;
}
We inherited the member functions and member variables in the parent class , And subclasses also have their unique properties .
3. Inheritance mode
C++ There are three types of inheritance in :1. public Inherit 2. protect Inherit 3. private Inherit
3.1 public Inherit
// Parent class
class A
{
public:
int a;
protected:
int b;
private:
int c;
};
//1. Public inheritance
class Son1 :public A
{
public:
void func()
{
a = 10; // Public permissions of the parent class The subclass is still public
b = 20; // Protection rights of the parent class The subclass is still protected
c = 30; // Private permissions of the parent class Subclass cannot access
}
};
void Test1()
{
Son1 s;
cout << s.a << " " << s.b << endl; // The protection permission cannot be accessed outside the class
cout << s.c << endl;
}
We can find that public inheritance :
| Member functions | Pre inheritance permissions | Post inheritance permissions |
| a | public | public |
| b | protected | protected |
| c | private | private |
In case of public inheritance , The member permissions inherited by the subclass are still the same as those of the parent class , But the subclass cannot access the private member
3.2 protected Inherit
class A
{
public:
int a;
protected:
int b;
private:
int c;
};
//2. Protection succession
class Son2 :protected A
{
public:
void func()
{
a = 10; // Public permissions of the parent class In the subclass is the protection permission
b = 20; // Protection rights of the parent class The subclass is still protected
c = 30; // Private permissions of the parent class Subclass cannot access
}
};
void Test2()
{
Son1 s;
cout << s.a << " " << s.b << endl; // The protection permission cannot be accessed outside the class
cout << s.c << endl;
}
We can find that protected inheritance :
| Member functions | Pre inheritance permissions | Post inheritance permissions |
| a | public | protected |
| b | protected | protected |
| c | private | private |
In the case of protected inheritance , In the parent class is public The number of members will drop to protected, But the subclass cannot access the private member
3.3 private Inherit
class A
{
public:
int a;
protected:
int b;
private:
int c;
};
//3. Private inheritance
class Son3 :private A
{
public:
void func()
{
a = 10; // Public permissions of the parent class The subclass is private
b = 20; // Protection rights of the parent class The subclass is private
//c = 30; // Private permissions of the parent class Subclass cannot access
}
};
void Test3()
{
Son3 s;
cout << s.a << endl; // Private permissions cannot be accessed outside the class
cout << s.b << endl; // Private permissions cannot be accessed outside the class
cout << s.c << endl;
}
We can find that private inheritance :
| Member functions | Pre inheritance permissions | Post inheritance permissions |
| a | public | private |
| b | protected | private |
| c | private | private |
In case of private inheritance , Permission in the parent class is greater than private The number of members will drop to private, But the subclass cannot access the private member
4. Object model in inheritance
We mentioned above that if the parent class has private Decorated member , Access will not be allowed in subclasses , Does it mean that the subclass does not inherit this member ?
// Parent class
class Base
{
public:
int m_a;
protected:
int m_b;
private:
int m_c;
};
// Subclass
class Son1 :public Base
{
public:
/*void func()
{
}*/
private:
int m_d;
};
void test()
{
Son1 s;
cout << "sizeof(s) = " << sizeof(s) << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
} Ee
Ee
We find that the subclass size is 16 Bytes , It indicates that the subclass inherits from the parent class private Decorated member
Be careful :
All non static members in the parent class will inherit from the child class
Private properties are hidden by the compiler , But it is still inherited to subclasses
Through this figure, we can also be more certain :

Subclass Son1 Inherited the parent class Base All the members of
5. The order of construction and deconstruction
There are constructs and destructors in every class , So when inheritance , How to construct and destruct ?
// Constructors and destructors in inheritance
class Base
{
public:
Base()
{
cout << "Base Constructor for " << endl;
}
~Base()
{
cout << "Base Destructor of " << endl;
}
};
// There is a parent class before a child class
// Destructor order : Destroy subclasses first , Destroy the parent class again
class Son :public Base
{
public:
Son()
{
cout << "Son Constructor for " << endl;
}
~Son()
{
cout << "Son Destructor of " << endl;
}
};
void test()
{
Son s;
//Base b;
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
We found that the parent class is called first Base Constructor for , Next, call the subclass Son Constructor for , It's easy to understand , Because you can't inherit without a parent class
We only need to keep in mind the order in which destructors are called : Destructors are called in the reverse order of constructors
6. Processing of functions with the same name
6.1 Member variable with the same name
// A member with the same name appears in inheritance
class Base
{
public:
Base()
{
m_a = 10;
}
int m_a;
};
class Son :public Base
{
public:
Son()
{
m_a = 20;
}
int m_a;
};
// Member variable with the same name
void Test()
{
Son s;
cout << "m_a = "<<s.m_a << endl;
}
int main()
{
Test2();
return 0;
} We found that when the default call m_a when , What is called is the member variable in the subclass , How to call a member variable with the same name in the parent class ?
We found that when the default call m_a when , What is called is the member variable in the subclass , How to call a member variable with the same name in the parent class ?
Here we need to call m_a Add scope before : 
In this way, you can call a member variable with the same name in the parent class
6.2 Member functions with the same name
// A member with the same name appears in inheritance
class Base
{
public:
Base()
{
m_a = 10;
}
void func()
{
cout << "Base - func" << endl;
}
int m_a;
};
class Son :public Base
{
public:
Son()
{
m_a = 20;
}
void func()
{
cout << "son - func" << endl;
}
int m_a;
};
// Member functions with the same name
void Test2()
{
Son s;
s.func();
}If we call directly func function :

Will call the function with the same name in the subclass , Instead of calling a function in the parent class , How to call a function with the same name in the parent class ?
Here we still need to add scopes :

If we overload the parent class :
class Base
{
public:
Base()
{
m_a = 10;
}
void func()
{
cout << "Base - func" << endl;
}
void func(int a)
{
cout << "Base - func(int a)" << endl;
}
int m_a;
};This is what we call func(100), Will call... In the parent class func(int a) Function? ?
We found that the call failed , Why is that ?
1. The member function names in the subclass and the parent class are the same , All member functions of the parent class will be hidden
2. If you want to access member functions in the parent class , Scope needs to be added

7. Static members with the same name
The principle of a static member with the same name is similar to that of a member with the same name
7.1 Static member variable with the same name
#include" Inherit .h"
// Static members with the same name
class Base
{
public:
static int m_a;
};
int Base::m_a = 100;
class Son:public Base
{
public:
static int m_a;
};
int Son::m_a = 10;
void Test()
{
//Son s;
// Object access
cout << s.m_a << endl;
cout << s.Base::m_a << endl;
}
int main()
{
Test2();
return 0;
}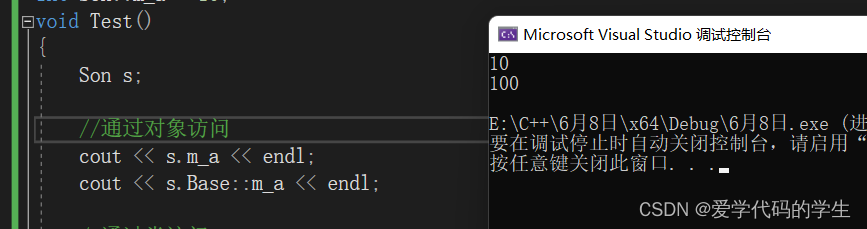
But unlike members of the same name , Static members can be accessed in two ways :1. Object access 2. Such access
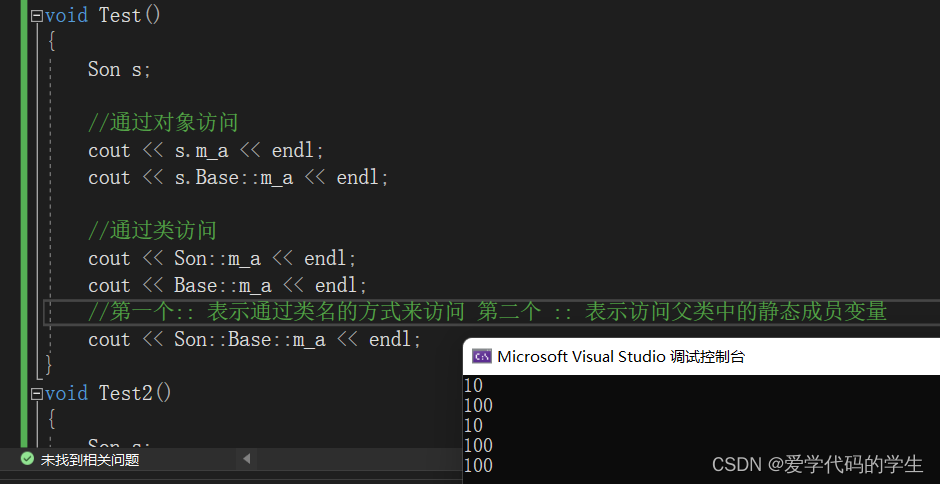
void Test()
{
Son s;
// Object access
cout << s.m_a << endl;
cout << s.Base::m_a << endl;
Access through class
cout << Son::m_a << endl;
cout << Base::m_a << endl;
first :: Means to access by class name the second :: Means to access the static member variables in the parent class
cout << Son::Base::m_a << endl;
}
7.2 Static member function with the same name
// Static members with the same name
class Base
{
public:
static void func()
{
cout << "Base static void fun " << endl;
}
static void func(int a)
{
cout << "Base static void fun(int a) " << endl;
}
static int m_a;
};
int Base::m_a = 100;
class Son:public Base
{
public:
static void func()
{
cout << "Son static void fun " << endl;
}
static int m_a;
};
int Son::m_a = 10;
void Test2()
{
Son s;
// Object access
s.func();
s.Base::func();
// Access through class
Son::func();
Base::func();
// first :: Means to access by class name the second :: Means to access the static member variables in the parent class
Son::Base::func();
Son::Base::func(100);
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}For static functions with the same name , In addition to adding class access , Other operations are the same as those of non static member functions
8. Inheritance syntax
What we talked about before is based on inheriting a parent class , What if we want to inherit multiple superclasses ?
This is called multiple inheritance
Multiple inheritance Syntax :class Class name : Inheritance rights Class name , Inheritance rights ,....
class Base1
{
public:
Base1()
{
m_a = 10;
}
int m_a;
};
class Base2
{
public:
Base2()
{
m_b = 100;
}
int m_b ;
};
class Son :public Base1, public Base2
{
public :
Son()
{
m_c = 20;
m_d = 15;
}
int m_c;
int m_d;
};
void Test()
{
Son s;
cout <<"Base1 Medium m_a = "<< s.m_a << endl;
cout <<"Base2 Medium m_b = "<< s.m_b << endl;
}
But when using multiple inheritance , There may be members with the same name in the parent class , How do we access members with the same name in different classes ?
This is the scope we thought of :

9. Diamond inheritance problem
9.1 What is diamond inheritance ?
Two derived classes inherit from a base class
A subclass inherits two derived classes at the same time
Such inheritance is called diamond inheritance or diamond inheritance
9.2 Problems with diamond inheritance
1. The main problem with diamond inheritance is that subclasses inherit two copies of data , It's a waste of resources
2. The subclass inherits two copies of data , Constitutes a ambiguity
// Animal species
class Animal
{
public:
/*Animal()
{
m_age = 10;
}*/
int m_age;
};
// Sheep
class Sheep: public Animal
{
};
// Camels
class Camel: public Animal
{
};
// Alpacas
class Alpaca: Sheep, public Camel
{
};
int main()
{
Alpaca a;
a.Sheep::m_age = 10;
a.Camel::m_age = 20;
// When diamond inheritance occurs , Two parent classes have the same data , Need to add scope distinction
cout <<"a.Sheep::m_age = "<< a.Sheep::m_age << endl;
cout <<"a.Camel::m_age = "<< a.Camel::m_age << endl;
cout << "sizeof(a) = " << sizeof(a) << endl;
// Diamond inheritance leads to a waste of resources
return 0;
}
When using diamond inheritance , We will find the inherited in subclasses m_age Existence ambiguity , And we just need one m_age, So what do we need to do ?
9.3 Virtual inheritance
// Animal species virtual base class
class Animal
{
public:
/*Animal()
{
m_age = 10;
}*/
int m_age;
};
// Sheep
class Sheep: virtual public Animal
{
};
// By virtual After modification
// Subclasses inherit vbptr virtual base pointer -> vbtable
// Camels
class Camel: virtual public Animal
{
};
// Alpacas
class Alpaca: public Sheep, public Camel
{
};
int main()
{
Alpaca a;
a.Sheep::m_age = 10;
a.Camel::m_age = 20;
cout <<"a.m_age = "<< a.m_age << endl;
cout << "sizeof(a) = " << sizeof(a) << endl;
return 0;
}
And then we found out ,Alpaca Can be called directly m_age 了 , Now let's look at a picture :

When virtual Modified class , It's called virtual base class , At this time, a class named vbptr(virtual base pointer) The pointer to , All the pointers in the class point to Alpaca Inherited from m_age Variable , This ensures that only one variable exists in the entire class , It solves the resource waste caused by the diamond problem
边栏推荐
- 动态内存管理(1)
- 作为一名 ABAP 资深顾问,下一步可以选择哪一门 SAP 技术作为主攻方向?
- JVM | virtual machine stack (local variable table; operand stack; dynamic link; method binding mechanism; method call; method return address)
- 领先企业推进智慧财务的同款效率工具,赶快了解一下?
- [Part 14] source code analysis and application details of completionservice class [key]
- Expérience 10 génération de courbes bezier - amélioration expérimentale - génération de courbes B - spline par point de contrôle
- servlet获取表单数据
- C语言实现八种排序(1)
- RPA丨首席财务官如何找到数字化转型“超级入口”?
- [v2.1] automatic update system based on motion step API (repair bug, increase completion display, support disconnection reconnection and data compensation)
猜你喜欢

如何查看win系统的安装日期

206.反转链表

JVM | runtime data area; Program counter (PC register);
![Analysis on the development history and market development status of China's system integration industry in 2020 [figure]](/img/3c/b53c2a3f59ff6784f128cb98a5a7a2.jpg)
Analysis on the development history and market development status of China's system integration industry in 2020 [figure]

Test plans and test cases

如何利用RPA机器人开启货代行业数字化转型第一步?

How to use RPA robot to start the first step of digital transformation of freight forwarding industry?

Leetcode-129- sum of numbers from root node to leaf node

RPA丨首席财务官如何找到数字化转型“超级入口”?

效率起飞啊!还能这样开发的?
随机推荐
Codeforces Round #740 Div. 2 解题报告
RPA超自动化 | 农耕记携手云扩加速财务智能化运营
Binary search - Learning
剑指Offer 29.顺时针打印矩阵
RPA+低代码助推品牌电商启新创变、重启增长
为什么需要微服务
RPA+低代码为何是加速财务数字化转型之利器?
每日一题 - 罗马数字转整数
The same efficiency tool for leading enterprises to promote smart finance. Let's have a quick look?
C语言实现八种排序(3)
JVM|类加载器;双亲委派机制
建造者模式
JVM|虚拟机栈(局部变量表;操作数栈;动态链接;方法的绑定机制;方法的调用;方法返回地址)
焕新升级 | 创新,从云商店开始
Leetcode-32- longest valid bracket
Customer information management software
Redis basic data type (set)
Chain storage structure of linear table
判断大小端存储两种办法
D. Game With Array