当前位置:网站首页>【GAN】《ENERGY-BASED GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORKS》 ICLR‘17
【GAN】《ENERGY-BASED GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORKS》 ICLR‘17
2022-06-22 06:56:00 【chad_ lee】
《ENERGY-BASED GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORKS》
Let's first introduce EBGAN, Read more about why you did this .
Auto-encoder Discriminator
Energy-based GAN And ordinary GAN The difference is that Discriminator The network architecture is changed from a binary classifier to a auto-encoder, And then use auto-encoder Of reconstruction error As the output of the discriminator . The model diagram is as follows

So the input of the discriminator is the same as that of the common GAN equally , It's still a picture , The output is also a scalar used to provide a gradient for the generator . So this AE How did you get it ?
In the picture Auto-encoder It is pre trained on a large number of real pictures , So when a real picture is entered AE when , The reconstruction error will be relatively small , When the image is generated for input, the reconstruction error will be large . In this way, we can naturally get EBGAN Of loss Function :
L D ( x , z ) = D ( x ) + [ m − D ( G ( z ) ) ] + = ∥ Dec ( Enc ( x ) ) − x ∥ + [ m − ∥ Dec ( Enc ( G ( z ) ) ) − G ( z ) ∥ ] + (1) \begin{aligned} \mathcal{L}_{D}(x, z) &=D(x)+[m-D(G(z))]^{+} \\ &=\|\operatorname{Dec}(\operatorname{Enc}(x))-x\|+[m-\|\operatorname{Dec}(\operatorname{Enc}(G(z)))-G(z)\|]^{+} \end{aligned} \tag{1} LD(x,z)=D(x)+[m−D(G(z))]+=∥Dec(Enc(x))−x∥+[m−∥Dec(Enc(G(z)))−G(z)∥]+(1)
L G ( z ) = ∥ D ( G ( z ) ) ∥ = ∥ Dec ( Enc ( G ( z ) ) ) − G ( z ) ∥ (2) \begin{aligned} \mathcal{L}_{G}(z) &=\|D(G(z))\| \\ &=\|\operatorname{Dec}(\operatorname{Enc}(G(z)))-G(z)\| \end{aligned} \tag{2} LG(z)=∥D(G(z))∥=∥Dec(Enc(G(z)))−G(z)∥(2)
among [ ⋅ ] + = max ( 0 , ⋅ ) [\cdot]^{+}=\max (0, \cdot) [⋅]+=max(0,⋅), D ( ⋅ ) = ∥ Dec ( Enc ( ⋅ ) ) − ⋅ ∥ D(\cdot)=\|\operatorname{Dec}(\operatorname{Enc}(\cdot))-\cdot\| D(⋅)=∥Dec(Enc(⋅))−⋅∥, m m m It's a margin, Then explain . Minimization formula (1) Means minimizing D ( x ) D(x) D(x) And maximize D ( G ( z ) ) D(G(z)) D(G(z)), That is, the discriminator should score real pictures as low as possible , The score of generated pictures should be higher . But not too high , need margin.
margin
It is difficult to fit and approximate a thing in a neural network , But it's easy to destroy a thing , If we try to maximize the cost of reconstruction, it's easy , As long as you output a random noise to all the input pictures, you can get a very large D ( G ( z ) ) D(G(z)) D(G(z)), So we need to constrain an upper bound .
As shown in the figure below

When there's a margin Constraints , When the curve corresponding to the generated image is raised to a certain extent, there will be no penalty , At this time loss It mainly comes from lowering the curve of the real picture . That's it EGBAN Optimization process of .
Pulling-away Term
Pulling-away Term It is used to ensure the diversity of generation 、 solve mode collapse The problem of . The author first mentioned Salimans et al.,2016 Proposed “minibatch discriminator”, His thoughts are given every time D Enter a batch, and D To test the whole batch Instead of checking each picture separately .Real image batch Each picture in is different , And if it does mode collapse, That is, all pictures are the same , It must be false .
The author proposes here that pulling-away term, abbreviation PT:
f P T ( S ) = 1 N ( N − 1 ) ∑ i ∑ j ≠ i ( S i ⊤ S j ∥ S i ∥ ∥ S j ∥ ) 2 (3) f_{P T}(S)=\frac{1}{N(N-1)} \sum_{i} \sum_{j \neq i}\left(\frac{S_{i}^{\top} S_{j}}{\left\|S_{i}\right\|\left\|S_{j}\right\|}\right)^{2}\tag{3} fPT(S)=N(N−1)1i∑j=i∑(∥Si∥∥Sj∥Si⊤Sj)2(3)
The idea is generative fake image batch Each picture in the goes through D Of Encoder After encoding, a vector is generated , Two vectors calculate cosine Distance and sum to average . Making this term as small as possible means that the two vectors are closer to orthogonality , The generated image batch The greater the internal diversity . Note this is only for G Training when generating fake pictures .PT It also has weight , In the experiment, the author takes 0.1.
Energy-based
Now we know EBGAN 了 , there energy It means auto-encoder Output .Energy Function Namely AE,AE The output of is energy.Energy Function Will tend to give real pictures (high quality) Lower energy , Generate pictures (low quality) Higher energy . use MSE To represent energy is also more vivid , Entropy is the unit of energy , The minimum entropy is the minimum energy .AE Train on lots of real pictures , Has been able to simulate the distribution of real pictures , The generated picture goes through AE The entropy of the output is naturally larger .
use energy Not two 01 Values can also avoid GAN The problem of gradient disappearance , It can give different gradient values to different quality generated pictures .
Another angle
Borrow the article of sujianlin 《 From the perspective of energy GAN Model 》 Graph :
At first the energy function is just a straight line .

Then the real sample x 1 , x 2 , … x n x_{1}, x_{2}, \ldots x_{n} x1,x2,…xn In turn U ( x ) U(x) U(x) On , Extrude a bumpy function , Secure it , U ( x ) U(x) U(x) It forms an energy function .(EBGAN Inside Auto-encoder)
Next, we get a batch of generated samples , x 1 ^ , x 2 ^ , … x n ^ \widehat{x_{1}}, \widehat{x_{2}}, \ldots \widehat{x_{n}} x1,x2,…xn, Put them anywhere in U ( x ) U(x) U(x) On . And fix it U ( x ) U(x) U(x), Release x 1 ^ , x 2 ^ , … x n ^ \widehat{x_{1}}, \widehat{x_{2}}, \ldots \widehat{x_{n}} x1,x2,…xn, therefore x 1 ^ , x 2 ^ , … x n ^ \widehat{x_{1}}, \widehat{x_{2}}, \ldots \widehat{x_{n}} x1,x2,…xn Will follow “ energy ” The slope slowly rolled down to the bottom of the pit ( Fixed discriminator , Training generator ), And the bottom of the pit represents the real sample , therefore x 1 ^ , x 2 ^ , … x n ^ \widehat{x_{1}}, \widehat{x_{2}}, \ldots \widehat{x_{n}} x1,x2,…xn They all look like real samples .
And when training the generator , Because there are many “ pit ”, There are many options for optimization :

For example, the generated sample in the above figure x 1 ^ \hat{x_1} x1^ Slide slowly , Not necessarily x 1 x_1 x1 The pit of , But just get to the middle one “ Secondary truth ” The pit of , So it needs to be improved 、 correct , Try to cross the barrier and slide to the lowest point .
Consider adding momentum to the optimization , As shown in the figure below :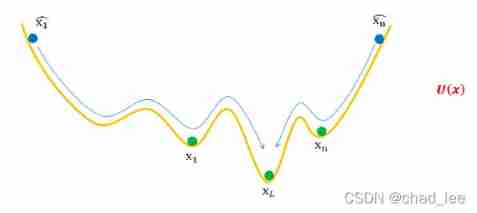
But this will lead to new problems : False samples leaped across the nearest pit , To reach a very far but low pit , Gather near some real samples , And then there comes Mode Collapse problem :

( This may explain W-GAN Compare with GAN improvement :“ Don't use momentum based optimization algorithms ( Include momentum and Adam), recommend RMSProp,SGD It's OK ”)
This is also in the EBGAN Add Pulling-away Term Why .
advantage
EBGAN The discriminator can hardly require negative example training , Only a large number of real samples are needed to train the discriminator , Big advantage .
Energy models and anomalies API Sequence detection
I think this EBGAN And the previous exception API The core idea of sequence detection is very similar to , It can also be an energy model :
stay EBGAN in , The energy function is Auto-Encoder, Fitting training on a large number of real samples in advance , So we can give the real sample a lower entropy 、 False samples have higher entropy ; stay GAN During training, the entropy of real samples is continuously reduced 、 Properly increase the entropy of false samples .
In anomaly detection , The energy function is “API Prediction module ”, In advance in a large number of normal API Prediction training on the sequence , So as to give normal API The lower entropy of the sequence 、 malice API The higher entropy of the sequence ; Keep decreasing the normal level during model training API Entropy on a sequence 、 Appropriately increase malicious API Entropy on a sequence (Unlearning).
Include DeepLog、《Lifelong Anomaly Detection Through Unlearning》 Seems to fit into the energy model , It's just Energy Function Different forms .
边栏推荐
- June training (day 22) - orderly gathering
- 成功解决raise KeyError(f“None of [{key}] are in the [{axis_name}]“)KeyError: “None of [Index([‘age.in.y
- Data security practice guide - data collection security practice - data classification and classification
- [CPU design practice] fundamentals of digital logic circuit design (I)
- JDBC query result set, which is converted into a table
- Training penetration range 02 | 3-star VH LLL target | vulnhub range node1
- OpenGL - Textures
- Py's scorecardpy: a detailed introduction to the introduction, installation and use of scorecardpy
- SQL injection vulnerability (x) secondary injection
- [fundamentals of machine learning 04] matrix factorization
猜你喜欢

Flink core features and principles
![[out of distribution detection] learning confidence for out of distribution detection in neural networks arXiv '18](/img/07/d5479dde181c355d95c73e2f58c0da.jpg)
[out of distribution detection] learning confidence for out of distribution detection in neural networks arXiv '18

Event preview edgex developer summit @ Nanjing station is coming!

The tidb community offline exchange meeting was seen by the partners from Tianjin and Shijiazhuang~

Don't throw away the electric kettle. It's easy to fix!

SQL injection vulnerability (x) secondary injection

Xh_ CMS penetration test documentation

Rebuild binary tree

深度解析Optimism被盗2000万个OP事件(含代码)

一个算子在深度学习框架中的旅程
随机推荐
Golang calls sdl2, plays PCM audio, and reports an error signal arrived during external code execution.
[out of distribution detection] energy based out of distribution detection nips' 20
Pytest data parameterization & data driven
golang調用sdl2,播放pcm音頻,報錯signal arrived during external code execution。
Vector of relevant knowledge of STL Standard Template Library
Sharing the strongest summer vacation plan of ape tutoring: the summer vacation plan is the same as learning and playing
Neuron+eKuiper 实现工业物联网数据采集、清理与反控
Error encountered while importing keras typeerror: descriptors cannot not be created directly If this call came from a _
Cactus Song - online operation (5)
Difference between grail layout and twin wing layout
【M32】单片机 svn 设置忽略文件
JDBC query result set, which is converted into a table
Shengxin literature learning (Part1) -- precision: a approach to transfer predictors of drug response from pre-clinical ...
[openairinterface5g] RRC NR resolution (I)
Golang appelle sdl2, lit l'audio PCM et signale une erreur lors de l'exécution externe du Code.
The journey of an operator in the framework of deep learning
流程引擎解决复杂的业务问题
Wildfire stm32f407zgt6 learning notes beginner level chapter basic knowledge points
Theory and application of naturallanguageprocessing
C skill tree evaluation - customer first, making excellent products