当前位置:网站首页>CUDA中的存储空间修饰符
CUDA中的存储空间修饰符
2022-07-02 06:12:00 【扫地的小何尚】
Variable Memory Space Specifiers
变量内存空间说明符表示变量在设备上的内存位置。
在设备代码中声明的没有本节中描述的任何 __device__、__shared__ 和 __constant__ 内存空间说明符的自动变量通常驻留在寄存器中。 但是,在某些情况下,编译器可能会选择将其放置在本地内存中,这可能会产生不利的性能后果,如设备内存访问中所述。
1 __device__
__device__ 内存空间说明符声明了一个驻留在设备上的变量。
在接下来的三个部分中定义的其他内存空间说明符中最多有一个可以与 __device__ 一起使用,以进一步表示变量属于哪个内存空间。 如果它们都不存在,则变量:
- 驻留在全局内存空间中,
- 具有创建它的 CUDA 上下文的生命周期,
- 每个设备都有一个不同的对象,
- 可从网格内的所有线程和主机通过运行时库 (
cudaGetSymbolAddress() / cudaGetSymbolSize() / cudaMemcpyToSymbol() / cudaMemcpyFromSymbol()) 访问。
2. __constant__
__constant__ 内存空间说明符,可选择与 __device__ 一起使用,声明一个变量:
- 驻留在常量的内存空间中,
- 具有创建它的 CUDA 上下文的生命周期,
- 每个设备都有一个不同的对象,
- 可从网格内的所有线程和主机通过运行时库 (
cudaGetSymbolAddress() / cudaGetSymbolSize() / cudaMemcpyToSymbol() / cudaMemcpyFromSymbol()) 访问。
3 __shared__
__shared__ 内存空间说明符,可选择与 __device__ 一起使用,声明一个变量:
- 驻留在线程块的共享内存空间中,
- 具有块的生命周期,
- 每个块有一个不同的对象,
- 只能从块内的所有线程访问,
- 没有固定地址。
将共享内存中的变量声明为外部数组时,例如:
extern __shared__ float shared[];
数组的大小在启动时确定(请参阅执行配置)。 以这种方式声明的所有变量都从内存中的相同地址开始,因此必须通过偏移量显式管理数组中变量的布局。 例如,如果想要在动态分配的共享内存中等价于,
short array0[128];
float array1[64];
int array2[256];
可以通过以下方式声明和初始化数组:
extern __shared__ float array[];
__device__ void func() // __device__ or __global__ function
{
short* array0 = (short*)array;
float* array1 = (float*)&array0[128];
int* array2 = (int*)&array1[64];
}
请注意,指针需要与它们指向的类型对齐,因此以下代码不起作用,因为 array1 未对齐到 4 个字节。
extern __shared__ float array[];
__device__ void func() // __device__ or __global__ function
{
short* array0 = (short*)array;
float* array1 = (float*)&array0[127];
}
表 4 列出了内置向量类型的对齐要求。
4. managed
__managed__ 内存空间说明符,可选择与 __device__ 一起使用,声明一个变量:
- 可以从设备和主机代码中引用,例如,可以获取其地址,也可以直接从设备或主机功能读取或写入。
- 具有应用程序的生命周期。
有关更多详细信息,请参阅__managed__内存空间说明符。
5. restrict
nvcc 通过 __restrict__ 关键字支持受限指针。
C99中引入了受限指针,以缓解存在于c类型语言中的混叠问题,这种问题抑制了从代码重新排序到公共子表达式消除等各种优化。
下面是一个受混叠问题影响的例子,使用受限指针可以帮助编译器减少指令的数量:
void foo(const float* a,
const float* b,
float* c)
{
c[0] = a[0] * b[0];
c[1] = a[0] * b[0];
c[2] = a[0] * b[0] * a[1];
c[3] = a[0] * a[1];
c[4] = a[0] * b[0];
c[5] = b[0];
...
}
此处的效果是减少了内存访问次数和减少了计算次数。 这通过由于“缓存”负载和常见子表达式而增加的寄存器压力来平衡。
由于寄存器压力在许多 CUDA 代码中是一个关键问题,因此由于占用率降低,使用受限指针会对 CUDA 代码产生负面性能影响。
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
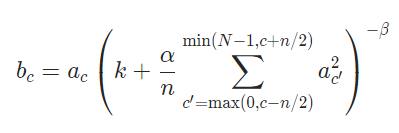
Deep learning classification network -- alexnet

亚马逊aws数据湖工作之坑1
Ros2 --- lifecycle node summary
Eco express micro engine system has supported one click deployment to cloud hosting

The difference between session and cookies

500. Keyboard line
Zhuanzhuanben - LAN construction - Notes
最新CUDA环境配置(Win10 + CUDA 11.6 + VS2019)
LeetCode 78. 子集

线性dp(拆分篇)
随机推荐
利用传统方法(N-gram,HMM等)、神经网络方法(CNN,LSTM等)和预训练方法(Bert等)的中文分词任务实现
LeetCode 27. Removing Elements
递归(迷宫问题、8皇后问题)
深入学习JVM底层(二):HotSpot虚拟机对象
LeetCode 77. 组合
Step by step | help you easily submit Google play data security form
Invalid operation: Load into table ‘sources_ orderdata‘ failed. Check ‘stl_ load_ errors‘ system table
On Web server
Codeforces Round #797 (Div. 3) A—E
LeetCode 78. subset
程序员的自我修养—找工作反思篇
Frequently asked questions about jetpack compose and material you
How to use mitmproxy
TensorRT中的循环
LeetCode 83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
LeetCode 40. Combined sum II
Jetpack Compose 与 Material You 常见问题解答
从设计交付到开发,轻松畅快高效率!
BGP routing optimization rules and notification principles
Web page user step-by-step operation guide plug-in driver js