当前位置:网站首页>Summer 2022 daily question 1 (1)
Summer 2022 daily question 1 (1)
2022-07-07 03:49:00 【Mocha Mocha ~】
List of articles
One 、 School day ( Hash )
4269
The question : First, give the ID card of the alumni , Then give the guest's ID card , Look for the ID card of the alumni in the ID card of the guest , If there are alumni , Then output the oldest , otherwise , Output the oldest guest .
practice : Hash ! Have a good command of !
sample input :
5
372928196906118710
610481197806202213
440684198612150417
13072819571002001X
150702193604190912
6
530125197901260019
150702193604190912
220221196701020034
610481197806202213
440684198612150417
370205198709275042
sample output :
3
150702193604190912
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n;
unordered_set<string>hash;
while(n--)
{
string name;
cin>>name;
hash.insert(name);
}
cin>>m;
string a,b;
int cnt=0;
while(m--)
{
string name;
cin>>name;
if(hash.count(name))
{
cnt++;
if(a.empty()||a.substr(6,8)>name.substr(6,8))a=name;
}
if(b.empty()||b.substr(6,8)>name.substr(6,8))b=name;
}
cout<<cnt<<endl;
if(cnt)cout<<a<<endl;
else cout<<b<<endl;
return 0;
}
y The general evaluation is a very simple question !
Two 、 Sexy prime ( prime number )
4268
The question : Give a number N, If he is sexy prime , Then my output is less than that of him 6 A number of , If not , Then find a smaller sexy prime than him and output .
Linear sieve
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=100000010;
int n;
int primes[N],cnt;
bool st[N];
void get_primes(int n)// Linear sieve
{
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!st[i])primes[cnt++]=i;
for(int j=0;primes[j]<=n/i;j++)
{
st[primes[j]*i]=true;
if(i%primes[j]==0)break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
get_primes(n);
printf("%d\n",cnt);// The output is the maximum prime number screened by the linear sieve
return 0;
}
Last AC Code .
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool is_prime(int x)// Judge whether it is a prime number
{
if(x<2)return false;
for(int i=2;i<=x/i;i++)
if(x%i==0)
return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=n-6;i<=n+6;i+=12)
if(is_prime(i)&&is_prime(n))
{
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
cout<<i<<endl;
return 0;
}
for(int i=n+1;;i++)
if(is_prime(i)&&(is_prime(i+6)||is_prime(i-6)))
{
cout<<"No"<<endl;
cout<<i<<endl;
return 0;
}
return 0;
}
3、 ... and 、 List merge ( Single chain list 、 simulation )
4273
Of course, we convert it into an array .
The question : It's a long list and a short list , We will flip the short list , Then insert the short list into the long list two from front to back .
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=100010;
#define x first
#define y second
int h1,h2,n;
typedef pair<int,int>PII;
int v[N],ne[N];
int main()
{
cin>>h1>>h2>>n;
int add,data,next;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
cin>>add>>data>>next;
v[add]=data;
ne[add]=next;
}
vector<PII> a,b;
for(int i=h1; i!=-1; i=ne[i])
{
a.push_back({
i,v[i]});
}
for(int i=h2; i!=-1; i=ne[i])
{
b.push_back({
i,v[i]});
}
if(a.size()<b.size())swap(a,b);
vector<PII>c;
for(int i=0,j=b.size()-1; i<a.size()||j>=0; i+=2,j--)
{
c.push_back(a[i]);
if(i+1<a.size())c.push_back(a[i+1]);
if(j>=0)c.push_back(b[j]);
}
for(int i=0; i<c.size(); i++)
{
printf("%05d %d ",c[i].x,c[i].y);
if(i+1<c.size())printf("%05d\n",c[i+1].x);
else puts("-1");
}
return 0;
}
Four 、 Postfix expression ( Tree traversal )
4274
The question : Post order traversal ! Recursively call
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=25;
string v[N];
int l[N],r[N],n;
bool st[N];// To determine whether this point has a parent node
void dfs(int rt)
{
cout<<"(";
if(l[rt]!=-1&&r[rt]!=-1)
{
dfs(l[rt]);
dfs(r[rt]);
cout<<v[rt];
}
else if(l[rt]==-1&&r[rt]==-1)
{
cout<<v[rt];
}
else {
cout<<v[rt];
dfs(r[rt]);
}
cout<<")";
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>v[i]>>l[i]>>r[i];
if(l[i]!=-1)st[l[i]]=true;
if(r[i]!=-1)st[r[i]]=true;
}
int root;// To record the root node
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(!st[i])
root=i;
dfs(root);
return 0;
}
5、 ... and 、Dijkstra Sequence ( shortest path )
4275
dijstra: Get the point closest to the origin each time . namely dist[i] Smallest point . So it's dist The sequence is an increasing sequence .
The beginning of this topic is different every time , So you have to recalculate every time .
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1010;
int g[N][N],dist[N];
int n,m;
bool st[N];
int q[N];
bool dijkstra()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
dist[q[0]] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
int t = q[i];
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
if (!st[j] && dist[j] < dist[t])
return false;
st[t] = true;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]);
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
int a,b,c;
memset(g,0x3f,sizeof g);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
cin>>a>>b>>c;
g[a][b]=g[b][a]=c;
}
int k;
cin>>k;
while(k--)
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cin>>q[i];
if(dijkstra())puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
return 0;
}
6、 ... and 、 Longest arithmetic ( Double pointer 、 Difference )
Random door
The question : Give you an array , Ask you to find a sub array in this array , Then this requires that the difference between each adjacent number of this subarray is equal .
Double pointers can put us O(n2) The enumeration of is optimized to O(n)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=200010;
int a[N];
int n,t;
int main()
{
cin>>t;
for(int cse=0;cse<t;cse++)
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)cin>>a[i];
int res=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int j=i+2;
while(j<n&&a[j]-a[j-1]==a[j-1]-a[j-2])j++;
res=max(res,j-i);
i=j-2;
}
printf("Case #%d: %d\n",cse+1,res);
}
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- Search of linear table
- Gpt-3 is a peer review online when it has been submitted for its own research
- It's too convenient. You can complete the code release and approval by nailing it!
- The true face of function pointer in single chip microcomputer and the operation of callback function
- pip只下载不安装
- Baidu map JS development, open a blank, bmapgl is not defined, err_ FILE_ NOT_ FOUND
- The latest 2022 review of "small sample deep learning image recognition"
- [dpdk] dpdk sample source code analysis III: dpdk-l3fwd_ 001
- 接口数据安全保证的10种方式
- Adaptive non European advertising retrieval system amcad
猜你喜欢
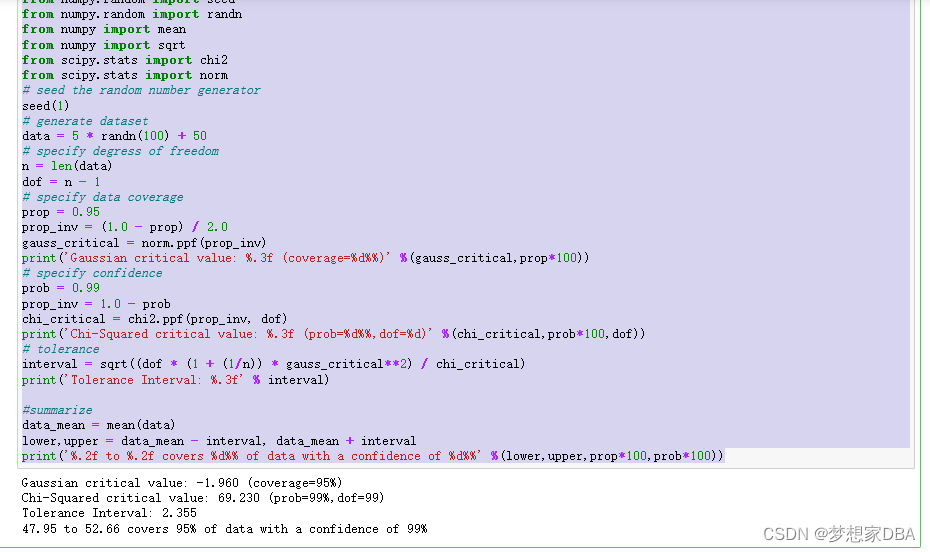
About Tolerance Intervals
2022.6.28
Appx code signing Guide
Codeworks 5 questions per day (1700 average) - day 7

CVPR 2022 best paper candidate | pip: six inertial sensors realize whole body dynamic capture and force estimation
Preprocessing - interpolation
![[development software] tilipa Developer Software](/img/b8/de2a1ea6474bb3f9b44e7ea01c441b.png)
[development software] tilipa Developer Software
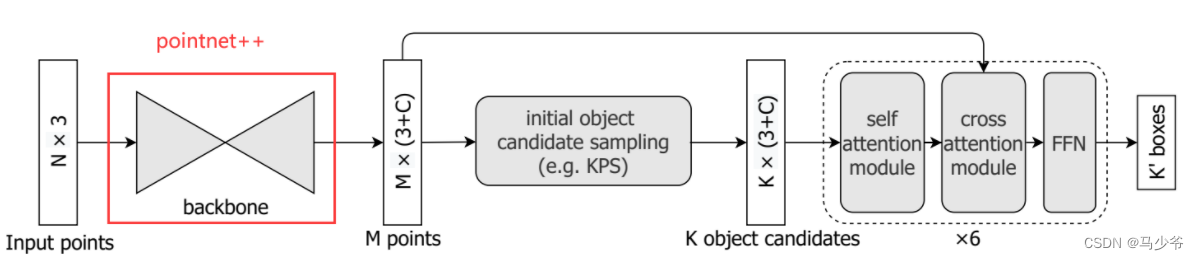
How to replace the backbone of the model
![[security attack and Defense] how much do you know about serialization and deserialization?](/img/1c/e5ae74e65bacf688d7f61cc1b71d3e.png)
[security attack and Defense] how much do you know about serialization and deserialization?

亚像素级角点检测Opencv-cornerSubPix
随机推荐
Construction of Hisilicon universal platform: color space conversion YUV2RGB
概率论公式
My brave way to line -- elaborate on what happens when the browser enters the URL
函数重入、函数重载、函数重写自己理解
Probability formula
qt-线程等01概念
25. (ArcGIS API for JS) ArcGIS API for JS line modification line editing (sketchviewmodel)
Open3d mesh filtering
Install torch 0.4.1
MySQL的索引
[security attack and Defense] how much do you know about serialization and deserialization?
密码学系列之:在线证书状态协议OCSP详解
ubuntu20安装redisjson记录
RestClould ETL 社区版六月精选问答
华为小米互“抄作业”
VHDL实现任意大小矩阵加法运算
The latest 2022 review of "small sample deep learning image recognition"
[leetcode] 700 and 701 (search and insert of binary search tree)
R data analysis: how to predict Cox model and reproduce high score articles
21.(arcgis api for js篇)arcgis api for js矩形采集(SketchViewModel)